15.10.
Testing of Starter System
Malfunctioning of the starting system may result due to defective battery, circuit resistances, improper switches, defective starting motor, starter drive problems or engine resistance. The battery must be checked first for state-of-charge of at least 75% to perform satisfactorily in the test. A voltage drop test of all of the starter cables, switches, and grounds should follow the battery test.
Starter Current Draw Test.
A starter draw test is the first test conducted on the starter after the battery and circuit tests perform satisfactorily. The battery voltage is checked while the starter cranks the engine by connecting a voltmeter across the battery terminals. A carbon pile rheostat with an ammeter is placed across the battery as shown in Fig. 15.33 and adjusted so that the rheostat draws enough current to cause the voltmeter to read the same voltage, which it did when the starter was cranking the engine.
Starter draws from 160 to 200 A current on medium sized engine. It draws high amperage when the starter cranks slowly, but if it draws too high a current while the battery and circuit are sound, the fault is with the starter so that further checks are needed.
Starter Free Speed Test.
Two tests are performed on the starter that
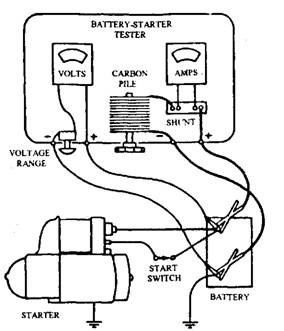
Fig. 15.33. Set-up for starter current draw test.
has been removed from the engine. In the first test, armature free speed and amperage draw are measured at a specified voltage. A tachometer is used as shown in Fig. 15.34 to measure armature speed. Voltage is supplied by a battery through a carbon-pile rheostat, which controls the voltage. Low readings of speed and amperage at the specified voltage indicate starter problems.

Fig. 15.34. Starter free speed test.
The second test is a stall test, run with the armature locked so it can not turn, using the same connections as for the free speed test. The voltage is adjusted to the specified value and the amperage value is compared to the starter specifications. Low amperage readings indicate a resistance in the starter and high readings indicate a short circuit. A faulty starter should be disassembled to check each component for correct operation, called bench checking the starter.
