9.5.
Fuel Filters
Despite all the care taken in refining, during storing and delivering of gasoline some impurities get into the automotive fuel system. Fuel filters remove dirt, rust, water and other harmful materials from the gasoline before it reaches the carburettor. The useful life of all filters is limited. During use the filters become clogged and hence restrict fuel flow if they are not cleaned or replaced according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Several different types of fuel filters are in use, and some systems contain two or even more filters. Filters are being located in several places within the fuel system.
Fuel Tank Filters and Strainers
A sleeve-type filter of woven Saran is normally fitted to the end of the fuel pick-up tube inside the fuel tank (Fig. 9.21). This filter prevents sediment, settled at the bottom of the tank, from entering the

Fig. 9.21. Filter attached to pick-up tube.
fuel line. It also protects against water contamination by plugging itself up. If enough water somehow enters the fuel tank, it accumulates on the outside of the filter forming a jelly-like mass. If this situation occurs the filter is required to be replaced, and except for this, no other maintenance of the filter is necessary.
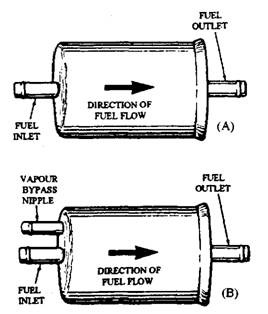
Fig. 9.22. In-line fuel filter.
A. Without vapour bypass system. B. With vapour bypass system.
In-line Filters.
In-line filter (Fig. 9.22 A and B) is installed in the line between the fuel pump and carburettor. This protects the carburettor from contamination but does not protect the fuel pump. The in-line filter is usually a throw away plastic or metal container with a pleated paper element sealed inside. Care should be taken while installing in-line filters so that gasoline flows through them in the direction marked by the arrow on the body. Some in-line filters have a built-in vapour by-pass system. These filters have a third nipple (Fig. 9.22B) that connects a fuel return line back to the fuel tank.
Some automobiles incorporate a sediment bowl (Fig. 9.23) between the fuel pump and carburettor. The bowl contains a pleated paper, ceramic, fibre, or metal filter element (strainer), which works like an in-line filter in cleaning the petrol. Water and other particles are collected in the bowl and are removed through periodical cleaning of the filter. When the filter becomes plugged the engine does not produce its usual power or speed. Paper and fibre filter elements are replaced when they are dirty.
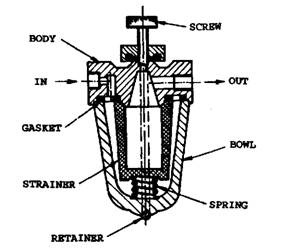
Fig. 9.23. Sediment bowl in sectional view.
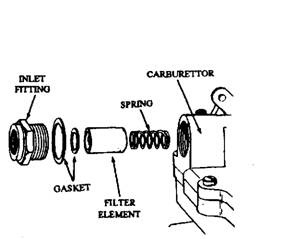
Fig. 9.24. Carburettor inlet filter.
Carburettor Inlet Filters.
Some automatic manufacturers install a filter at the carburettor inlet (Fig. 9.24). The filter is screwed into the carburettor fuel inlet and is clamped to the inlet hose at the other end.
Pump Outlet Filters.
Some cars incorporate fuel filters at the outlet side of the fuel pump (Fig. 9.25). In Fig. 9.25 A, the filter is installed in the fuel pump outlet tower whereas in Fig. 9.25 B it is located at the bottom of the pump.

Fig. 9.25. Pump outlet filters. A. Installed in outlet tower. B. Installed at the bottom.
