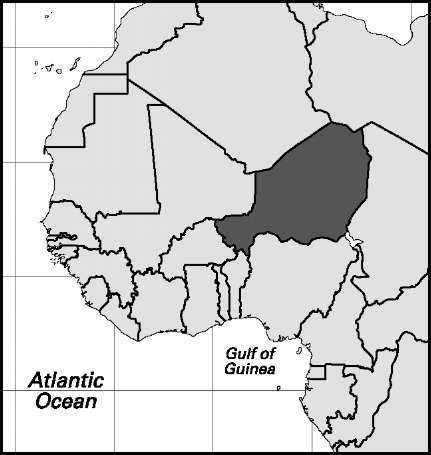
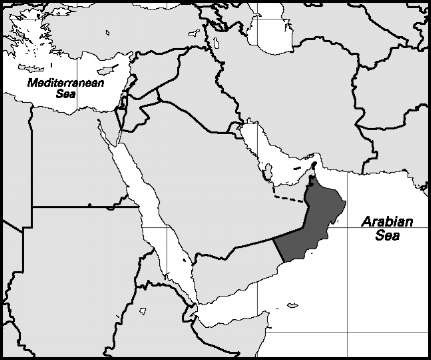
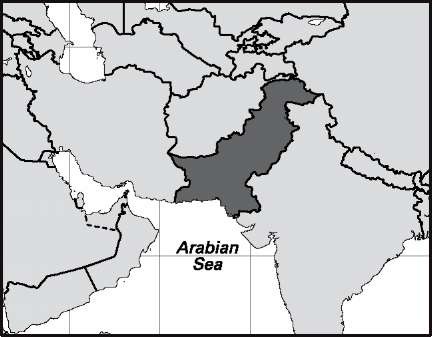
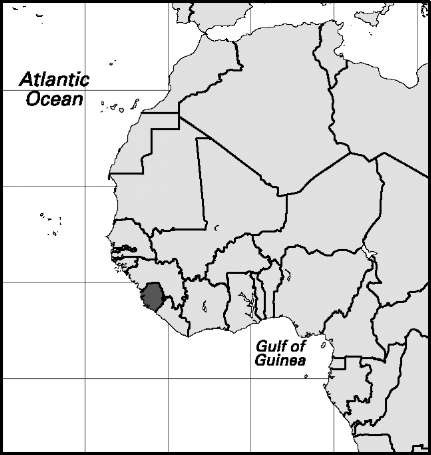
Niger
Official name: Republique du Niger (Republic of Niger). Form of government: multiparty republic with one legislative house (National Assembly [113]). Head of state and government: President Mamadou Tandja (from 1999), assisted by Prime Minister Seyni Oumarou (from 2007). Capital: Niamey. Official language: French. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 CFA franc (CFAF) = 100 centimes; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = CFAF 414.60.
Demography
Area: 459,286 sq mi, 1,189,546 sq km. Population (2007): 14,226,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 31.0, persons per sq km 12.0. Urban (2006): 16.6%. Sex distribution (2005): male 50.69%; female 49.31%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 47.9%; 15-29, 24.1%; 30-44, 14.7%; 45-59, 8.5%; 60-74, 3.6%; 75-84, 0.9%; 85 and over, 0.3%. Eth-nolinguistic composition (2001): Hausa 55.4%; Zarma-Songhai-Dendi 21.0%; Tuareg 9.3%; Fulani (Peul) 8.5%; Kanuri 4.7%; other 1.1%. Religious affiliation (2005): Muslim 90%, of which Sunni 85%, Shi’i 5%; traditional beliefs 9%; other 1%. Major cities (2001): Niamey 707,951 (urban agglomeration [2005] 850,000); Zinder 170,575; Maradi 148,017; Agadez 78,289; Tahoua 73,002. Location: western Africa, bordering Algeria, Libya, Chad, Nigeria, Benin, Burkina Faso, and Mali.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 50.7 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 20.9 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 29.8 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 7.46. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 43.8 years; female 43.7 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue:CFAF 365,000,000,000 (taxes 55.8%, of which import duties 26.2%; external aid and grants 32.3%; nontax revenue 11.9%). Expenditures: CFAF 359,600,000,000 (capital expenditures 50.8%; current expenditures 46.3%, of which wages and salaries 18.9%, debt service 3.0%; other 2.9%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2006): US$1,800,-000,000. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 34; remittances (2006) 60; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 14; official development assistance (2005) 515. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 32; remittances (2006) 25; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 1.0. Gross national income (2006): US$3,361,000,000 (US$245 per capita). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): millet 3,200,000, sorghum 800,000, cowpeas 690,584; livestock (number of live animals) 7,700,000 goats, 4,900,000 sheep, 2,430,000 cattle, 439,000 camels; roundwood (2005) 9,217,477 cu m, of which fuelwood 96%; fisheries production (2005)50,058. Mining and quarrying (2006): uranium 3,431; salt (2004) 2,000; gold 2,615 kg. Manufacturing (value added in CFAF ’000,000; 2002): textiles 1,876; food and food products 1,695; soaps and other chemical products 1,302. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 403,000,000 (461,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2006) 176,000 ([2005] 173,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (233,000). Population economically active (2006): total 6,139,000; activity rate of total population 42.6% (participation rates: ages 16 and over 83.5%; female 41.9%; registered unemployed [2001] 1.6%). Households. Average household size (2004) 6.2; expenditure (2005; Niamey only): food, beverages, and tobacco products 53.7%, housing and rent 10.3%, transportation 9.9%, clothing and footwear 5.3%. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in tem-porarycrops 11.4%, in permanentcrops0.01%, in pasture 18.9%; overall forest area (2005) 1.0%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): CFAF 361,037,000,000 (live animals, food products, and beverages 33.4%; mineral fuels 14.8%; mechanical apparatus and machinery 12.8%; transportation equipment 7.5%). Major import sources: France 16.8%; Cote d’Ivoire 9.3%; Nigeria 5.9%; China 5.4%; Togo 5.2%. Exports (2005; f.o.b.): CFAF 163,508,000,000 (uranium 48.0%; gold 22.6%; onions 6.8%; cattle 6.3%; other live animals 5.5%). Major export destinations: France 34.4%; Nigeria 14.4%; Japan 13.2%; Ghana 4.2%; Spain 3.2%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2005): total length 18,423 km (paved 21%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 21,360. Air transport (2005; Niamey airport only): passenger arrivals 50,002, passenger departures 59,824; cargo unloaded 3,085 metric tons, cargo loaded 140 metric tons. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2006): 5,000 (0.3); televisions (2004): 150,000 (13); telephone landlines (2005): 24,000 (1.9); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 324,000 (25); personal computers (2005): 10,000 (0.8); total Internet users (2006): 40,000 (3.1); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 200 (0.02).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2006). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling/unknown 86.2%; incomplete primary education 6.9%; complete primary 1.0%; incomplete secondary 3.7%; complete secondary 0.4%; higher 0.9%. Literacy (2006): total population ages 15 and over literate 28.7%; males literate 42.9%; females literate 15.1%. Health (2005): physicians 452 (1 per 27,599 persons); hospital beds 1,865 (1 per 6,689 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 118.2. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,060 (vegetable products 95%, animal products 5%); 114% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 5,300 (army 98.1%, air force 1.9%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2004): 1.2%; per capita expenditure US$3.
Background
In the territory of Niger, there is evidence of Neolithic culture, and several kingdoms existed there before the colonialists arrived. First explored by Europeans in the late 18th century, it became a French colony in 1922. It became an overseas territory of France in 1946 and gained independence in 1960. The first multiparty elections were held in 1993.
Recent Developments
The government’s control over northern Niger in 2007 was threatened as Tuaregs belonging to the Movement of Nigerians for Justice (MNJ) launched a series of deadly raids throughoutthe region. A uranium mine was hit in April, and in June the MNJ struck a Saharan garrison post, killing 15 and taking 72 hostages. The MNJ also claimed to have killed 17 soldiers in August when it attacked a convoy near Gougaram.
Nigeria
Official name: Federal Republic of Nigeria. Form of government: federal republic with two legislative bodies (Senate [109]; House of Representatives [360]). Head of state and government: President Umaru Yar’Adua (from 2007). Capital: Abuja. Official language: English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Nigerian naira (N) = 100 kobo; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = N117.80.
Demography
Area: 356,669 sq mi, 923,768 sq km. Population (2007): 144,077,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 404.0, persons per sq km 156.0. Urban (2005): 48.2%. Sex distribution (2006): male 51.22%; female 48.78%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 44.4%; 15-29, 27.7%; 30-44, 15.0%; 45-59, 8.3%; 60-74, 3.8%; 75-84, 0.7%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Ethnic composition (2000): Yoruba 17.5%; Hausa 17.2%; Igbo (Ibo) 13.3%; Fulani 10.7%; Ibibio 4.1%; Kanuri 3.6%; Egba 2.9%; Tiv 2.6%; Igbira 1.1%; Nupe 1.0%; Edo 1.0%; Ijo 0.8%; detribalized 0.9%; other 23.3%. Religious affiliation (2003): Muslim 50.5%; Christian 48.2%, of which Protestant 15.0%, Roman Catholic 13.7%, other (mostly independent Christian) 19.5%; other 1.3%. Major urban agglomerations (2005): Lagos (2006) 9,013,534; Kano 2,993,000; Ibadan 2,437,000; Kaduna 1,375,000; Benin City 1,055,000. Location: western Africa, bordering Niger, Chad, Cameroon, the Gulf of Guinea, and Benin.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 41.3 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 17.2 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 24.1 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 5.58. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 46.7 years; female 47.3 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:N5,621,000,000,000 (oil and gas revenue 84.7%, of which crude oil export proceeds 34.5%, oil profits tax 23.3%, crude oil sales to domestic refineries 13.7%; non-oil revenue 15.3%). Expenditures: N4,234,000,000,000 (state and local governments46.3%; current expenditure 44.4%; capital expenditure 8.1%; other 1.2%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$20,342,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): cassava 41,565,000, yams 34,000,000, sorghum 9,178,000, millet 7,168,000, corn (maize) 5,957,000; livestock (number of live animals) 28,000,000 goats, 15,875,000 cattle; round-wood 70,692,260 cu m, of which fuelwood 87%; fisheries production 579,500 (from aquaculture 10%). Mining and quarrying(2005): granite 2,000,000; marble 149,000. Manufacturing (value added in N’000,000; 2005): refined petroleum 29,037; cement 8,502; other unspecified (particularly food, beverages, and textiles) 375,167. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 20,636,000,000 ([2004] 20,224,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) 3,000 (3,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006) 814,000,000 ([2004] 38,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 4,363,000,000 (9,985,000,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 22,388,000,000 (9,668,000,000). Households. Average household size (2003): 4.9; expenditures (2003): food 63.8%, housing/energy 18.1%, transportation 4.2%. Gross national income (at current market prices; 2006): US$116,374,000,000 (US$800 per capita). Population economically active (2003): total 45,165,000; activity rate of total population 35.9% (participation rates:ages 15-64,65.9%; female 35.1%; officially unemployed [December2005] 11.9%).Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 18; remittances (2006) 3,329; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 2,204; official development assistance (2005) 5,989 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 1,109; remittances (2006) 18; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 179. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 33.5%, in permanent crops 3.2%, in pasture 43.0%; overall forest area (2005) 12.2%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2003; c.i.f.): US$14,892,000,000 (machin-eryand apparatus 25.6%; mineral fuels 16.0%; food 14.0%; chemical products 10.3%; ships and boats 6.4%). Major import sources (2003): US 15.6%; UK 9.5%; Germany 7.3%; China 7.2%; Italy 4.3%; unspecified 15.0%. Exports (2006; f.o.b.): US$45,116,000,000 (crude petroleum 95.9%). Major export destinations (2005): US 52%; Spain 8%; Brazil 6%; France 3%; Cote d’Ivoire 3%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2005): length 3,505 km; pas-senger-km 75,170,000. Roads (2005): total length 34,403 km (paved 64%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 2,176,000. Air transport (2006; Virgin Nigeria Airways only): passenger-km 969,900,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2000): 2,770,000 (23); televisions (2003): 8,393,000 (64); telephone land-lines (2006): 1,688,000 (12); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 32,322,000 (229); personal computers (2005): 1,200,000 (8.7); total Internet users (2006): 8,000,000 (57); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 500.
Education and health
Unknown 50.4%; primary education 20.4%; secondary 20.1%; higher 9.1%. Literacy (2006): total population ages 15 and over literate 76.3%; males literate 84.2%; females literate 68.4%. Health (2005): physicians 42,563 (1 per 3,234 persons); hospital beds 85,523 (1 per 1,609 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 112.5. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,731 (vegetable products 96%, animal products 4%); 149% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 85,000 (army 78.8%, navy 9.4%, air force 11.8%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 0.7%; per capita expenditure US$5.
Background
Inhabited for thousands of years, Nigeria was the center of the Nok culture from 500 bc to ad 200 and of several precolonial empires, including the state of Kanem-Bornu and the Songhai, Hausa, and Fulani kingdoms. Visited in the 15th century by Europeans, it became a center for the slave trade. The area began to come under British control in 1861; by 1903 British rule was total. Nigeria gained independence in 1960 and became a republic in 1963. Ethnic strife soon led to military coups, and military groups ruled the country from 1966 to 1979 and from 1983 to 1999. A civil war between the central government and the former Eastern Region—which seceded and called itself Biafra—began in 1967 and ended in 1970 with Biafra’s surrender after widespread starvation and civilian deaths. In 1991 the capital was moved from Lagos to Abuja. The government’s execution of environmental activist Ken Saro-Wiwa in 1995 led to international sanctions, and civilian rule was finally reestablished in 1999. By far the most populous nation in Africa, Nigeria suffers from rapid population increase, political instability, foreign debt, slow economic growth, a high rate of violent crime, and rampant government corruption.
Recent Developments
In May 2007 a milestone was reached in Nigeria’s history when outgoing Pres. Olusegun Obasanjo handed over power to Umaru Musa Yar’Adua, marking the first time that a civilian head of state had been succeeded by another civilian. Yar’Adua had won the country’s presidential election in a landslide with 24.6 million votes. In the Niger Delta, the source of 90% of Nigeria’s wealth, the security situation deteriorated. Armed militia, backed by local inhabitants, edged dangerously closer to turning into an insurgency. In February the Movement for the Emancipation of the Niger Delta, a coalition of militant groups, released a proclamation threatening war. Kidnappings of foreign oil workers accelerated, with a new dimension of random abductions in the center of Port Harcourt. After the elections militants in various places, claiming that victorious politicians had reneged on promised payments for their services as party thugs, seized 11 Ondo state officials and a number of relatives of politicians, including children and the elderly mothers of two governors. Meanwhile, their truce with the government fell apart in August when fighting broke out among rival gangs in Port Harcourt, and many were killed or wounded. To restore order the government mobilized the Joint Task Force into the region to round up the militants and destroy their strongholds; this was followed in October by a federal army operation on the Port Harcourt waterfront. Residents, however, were skeptical of a military solution and urged the development of effective economic reforms and poverty alleviation. The attacks and kidnappings continued in 2008.
Norway
Official name: Kongeriket Norge (Kingdom of Norway). Form of government: constitutional monarchy with one legislative house (Parliament [169]). Chief of state: Norwegian King Harald V(from 1991). Head of government: Prime Minister Jens Stoltenberg (from 2005). Capital: Oslo. Official language: Norwegian. Official religion: Evangelical Lutheran. Monetary unit: 1 Norwegian krone (NOK) = 100 0re; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = NOK 5.06.
Demography
Area: 148,726 sq mi, 385,199 sq km. Population (2007): 4,702,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 37.1, persons per sq km 14.3. Urban (2005): 77.4%. Sex distribution (2004): male 49.59%; female 50.41%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 19.4%; 15-29, 18.7%; 30-44, 22.0%; 45-59, 19.7%; 60-74, 12.6%; 75-84, 5.4%; 85 and over, 2.2%. Ethnic composition (2000): Norwegian 93.8%; Vietnamese 2.4%; Swedish 0.5%; Punjabi 0.4%; Urdu 0.3%; US white 0.3%; Lapp 0.3%; other 2.0%. Religious affiliation (2003): Evangelical Lutheran 85.7%; other Christian 4.5%; Muslim 1.8%; other/nonreligious 8.0%. Major cities (2006; populations of municipalities): Oslo 548,617 (urban agglomeration 839,423); Bergen 236,590; Trondheim 154,530; Stavanger 115,087; B^rum 105,574. Location: northern Europe, bordering the Barents Sea, Russia, Finland, Sweden, the North Sea, and the Norwegian Sea.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 12.6 (world avg. 20.3); (2005) within marriage 48.2%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 8.9 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 3.7 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.84. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 78.1 years; female 82.7 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: NOK 1,066,860,000,000 (tax on income 41.1%; social security 16.2%; VAT 14.8%). Expenditures: NOK 763,318,000,000 (social security and welfare 40.5%; health 17.2%; education 14.0%; general public service 9.7%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): barley 619,000, wheat 410,000, oats 359,000; livestock (number of live animals) 2,417,000 sheep, 920,300 cattle; roundwood 9,667,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 12%; fisheries production 3,049,570 (from aquaculture 21%); aquatic plants production 148,322. Mining and quarrying (2004): ilmenite concentrate 860,000, iron ore (metal content) 408,000, cobalt (refined metal) 4,670. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2001): food products 2,353; ships and oil platforms 1,543; nonelectrical machinery 1,257. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 138,073,000,000 (126,029,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) 2,900,000 (1,360,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2005) 1,019,000,000 ([2004] 108,270,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 19,001,000 (10,022,000); natural gas (cu m; 2005) 87,563,000,000 ([2004] 5,107,000,000). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 3,278; remittances (2005) 429; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 2,427. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 9,753; remittances (2005) 953; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 12,085. Population economically active (2006): total 2,446,000; activity rate of total population 52.5% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 80.8%; female 47.1%; unemployed 3.4%). Gross national income (2006): US$335,314,000,000 (US$71,822 per capita). Public debt (2003): US$79,880,000,000. Households. Average household size (2001) 2.3; average annual net income per household (2004) NOK 359,300 (US$53,302); sources of income (2004): wages and salaries 63.3%, transfers 22.1%, self-employment 6.0%; expenditure (2003-05): housing 20.7%, transportation 18.1%, recreation and culture 12.3%, food 10.5%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): NOK 357,750,300,000 (machinery and transport equipment 43.2%, of which road vehicles 9.7%, ships 1.6%; metals and metal products 10.4%; food products 6.0%; petroleum products 4.3%). Major import sources (2004): Sweden 15.7%; Germany 13.6%; Denmark 7.3%; UK 6.5%; US 4.9%. Exports (2005; f.o.b.): NOK 668,949,200,000 (crude petroleum 43.3%; natural gas 15.4%; metals and metal products 8.1%; machinery and transport equipment 7.4%; fish 4.7%). Major export destinations (2004): UK 22.6%; Germany 13.2%; The Netherlands 10.2%; France 8.8%; US 7.7%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2005): route length 4,087 km; passenger-km 2,723,000,000; metric ton-km cargo (2001) 2,449,000,000. Roads (2005): total length 92,864 km (paved [2002] 78%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 2,028,909; trucks and buses 431,257. Air transport (2004; SAS [Norwegian part], Braa-thens, Norwegian, and Wider0e only): passenger-km 13,229,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 177,522,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 2,405,000 (524); televisions (2003): 7,110,000 (1,557); telephone landlines (2006): 2,055,000 (443); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 5,041,000 (1,086); personal computers (2004): 2,630,000 (578); total Internet users (2005): 3,400,000 (736); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 991,000 (215).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2000). Percentage of population ages 16 and over having: primary and lower secondary education 21.5%; higher secondary 55.0%; higher 21.3%; unknown 2.2%. Literacy (2000): virtually 100%. Health (2006): physicians 15,443 (1 per 302 persons); hospital beds 16,303 (1 per 286 persons); infant mortality rate 3.2. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,447 (vegetable products 69%, animal products 31%).
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 25,800 (army 57.0%, navy 20.6%, air force 19.4%, other 3.0%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.7%; per capita expenditure US$1,058.
Background
Several principalities were united into the kingdom of Norway in the 11th century. From 1380 it had the same king as Denmark until it was ceded to Sweden in 1814. The union with Sweden was dissolved in 1905, and Norway’s economy grew rapidly. The country remained neutral during World War I, although its shipping industry played a vital role in the conflict. It declared its neutrality in World War II but was invaded and occupied by German troops. Norway is a member of NATO butturned down membership in the EU in 1994. Its economy grew consistently during the 1990s.
Recent Developments
Norway’s economy continued to be strong in 2007. Only 2.5% of the workforce was unemployed, and GDP grew by 3.5%. Exports of oil, natural gas, fish, and industrial products—combined with the importation of cheap industrial products from China and other low-cost countries—gave Norway a trade surplus of some NOK 377 billion (about US$70 billion). The Norwegian Government Pension Fund reached NOK 1.94 trillion (about US$357 billion). The government promised to make Norway carbon neutral by 2050, partly by buying carbon quotas from less-developed countries and partly through domestic efforts, including investment in new offshore technology that could pump carbon gas back into former reservoirs of oil and gas.
Oman
Official name: Saltanat ‘Uman (Sultanate of Oman). Form of government: monarchy with two advisory bodies (State Council [70]; Consultative Council [84]). Head of state and government: Sultan (from 1970) and Prime Minister (from 1972) Qabus ibn Sa’id. Capital: Muscat. Official language: Arabic. Official religion: Islam. Monetary unit: 1 rial Omani (RO) = 1,000 baizas; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = RO 0.39.
Demography
Area: 119,500 sq mi, 309,500 sq km. Population (2007): 2,595,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 21.7, persons per sq km 8.4. Urban (2005): 71.5%. Sex distribution (2004): male 56.34%; female 43.66%. Age breakdown (2003): under 15, 33.9%; 15-29, 32.2%; 30-44, 20.8%; 45-59, 8.9%; 60-74, 3.2%; 75-84, 0.7%; 85 and over, 0.3%. Ethnic composition (2000): Omani Arab 48.1%; Indo-Pakistani 31.7%, of which Balochi 15.0%, Bengali 4.4%, Tamil 2.5%; other Arab 7.2%; Persian 2.8%; Zanzibari (blacks originally from Zanzibar) 2.5%; other 7.7%. Religious affiliation (2005): Muslim 89%, of which Ibadiyah 75%, Sunni 8%, Shi’i 6%; Hindu 5%; Christian 5%; other 1%. Major cities (2005; populations of districts): As-Sib 242,363; Matrah 173,483; Salalah 171,074; Bawshar 168,025; Suhar 110,917; Muscat 26,668 (urban agglomeration 695,435). Location: the Middle East, bordering the Gulf of Oman, the Arabian Sea, Yemen, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE; the Ru’us al-Jibal enclave occupies the northern tip of the Musandam Peninsula and borders the UAE, the Persian Gulf, and the Strait of Hormuz.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 24.8 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 2.5 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 22.3 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 5.84. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 73.2 years; female 75.4 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue: RO 5,027,200,000 (oil revenue 64.2%; natural gas revenue 12.2%; tax revenue 7.2%; other 16.4%). Expenditures: RO 4,936,100,000 (current expenditure 71.5%, of which defense 31.4%, education 11.3%, social security and welfare 6.8%; capital expenditure 24.3%; other 4.2%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$842,000,000. Gross national income (2006): US$28,710,000,000 (US$11,275 per capita). Households. Average household size (2003) 6.8; expenditure (2000): food and nonalcoholic beverages 29.9%, transportation and communications 22.2%, housing 15.3%. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing(2006): dates 258,700, tomatoes 40,440, bananas 25,960; livestock (number of live animals) 1,598,250 goats, 358,050 sheep, 307,580 cattle, 119,650 camels; fisheries production (2005) 150,744. Mining and quarrying (2005): marble 140,000; gypsum 60,000; chromite (gross weight) 19,000. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2004): petroleum products 1,168; cement, bricks, and ceramics 232; food products 152. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 12,648,000,000 (12,023,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006) 269,000,000 ([2004] 27,300,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2005) 4,306,000 ([2004] 3,300,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 18,096,000,000 (8,019,000,000). Population economically active (2003): total 736,624; activity rate of total population 31.5% (participation rates: female 15.4%; unemployed [2004] 15%). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 481; remittances (2006) 39; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 304. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 643; remittances (2006) 2,257; FDI (2003-05 avg.) 149. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 0.1%, in permanent crops 0.1%, in pasture 3.2%; overall forest area (2005) 0.01%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f. for commodities and trading partners): RO 3,394,000,000 (motor vehicles and parts 26.6%; electrical machinery and equipment 21.6%; base and fabricated metals 11.3%; food and live animals 7.9%; chemical products 6.4%). Major import sources: UAE 26.5%; Japan 15.7%; Germany 6.9%; US 6.2%; India 4.5%. Exports (2005): RO 7,186,900,000 (domestic exports 91.9%, of which crude and refined petroleum 71.8%, natural gas 12.4%, food and live animals 1.8%; reexports 8.1%, of which motor vehicles and parts 6.1%). Major export destinations: China 22.7%; Thailand 11.9%; Japan 11.6%; South Korea 11.1%; UAE 7.1%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2004): total length 40,116 km (paved 37%). Vehicles (2003): passenger cars 324,085; trucks and buses 116,438. Air transport (2006; Oman Air only): passenger-km 1,749,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 11,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 108,000 (45); televisions (2003): 1,557,000 (633); telephone land-lines (2006): 278,000 (107); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 1,818,000 (696); personal computers (2005): 130,000 (51); total Internet users (2006): 319,000 (122); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 152,000 (60).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2003). Percentage of population ages 10 and over having: no formal schooling (illiterate) 15.9%; no formal schooling (literate) 22.3%; primary 35.3%; secondary 17.0%; higher technical 3.3%; higher undergraduate 5.2%; higher graduate 0.7%; other 0.3%. Literacy (2003): percentage of total population ages 15 and over literate 75.8%; males literate 83.0%; females literate 67.2%. Health (2005): physicians 4,093 (1 per 602 persons); hospital beds 5,178 (1 per 476 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 10.3.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 41,700 (army 60.0%, navy 10.1%, air force 9.8%, royal household/foreign troops 20.1%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 11.9%; per capita expenditure US$1,516.
Background
Oman has been inhabited for at least 10,000 years. Arabs began migrating there in the 9th century bc. Tribal warfare was endemic until the conversion to Islam in the 7th century ad. Itwas ruled by Ibadi imams until 1154, when a royal dynasty was established. The Portuguese controlled the coastal areas from about 1507 to 1650, when they were expelled. The Al Bu Sa’id dynasty, founded in the mid-18th century, still rules Oman. Oil was discovered in 1964. In 1970 the sultan was deposed by his son, who began a policy of modernization, and under him the country joined the Arab League and the UN. In the Persian Gulf War, Oman cooperated with the allied forces against Iraq. In the 1990s it continued to expand its foreign relations.
Recent Developments
Record-high oil prices continued to fuel Oman’s robust economic growth in 2007. Highlights included the addition of a third train of liquefied natural gas exports, the use of new technology to enhance recovery of oil from existing fields, and the accelerated development of Oman’s newest port and aluminum facility at Sohar, located outside the Hormuz Strait. In addition the expansion of transportation and tourism services further diversified the economy and increased employment opportunities for the country’s burgeoning population.
Pakistan
Official name: Islam-i Jamhuriya-e Pakistan (Islamic Republic of Pakistan). Form of government: military-backed constitutional regime with two legislative houses (Senate [100]; National Assembly [342]). Chief of state and government: President Asif Ali Zardari (from 2008), assisted by Prime Minister Yousaf Raza Gilani (from 2008). Capital: Islamabad. Official language: Urdu. Official religion: Islam. Monetary unit: 1 Pakistan rupee (PKR) = 100 paisa; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = PKR 68.40.
Demography
Demographic information, except ethnic and religious data, excludes Afghan refugees and the 2007 populations of Azad Kashmir (3,527,000) and the Northern Areas (1,096,000); area and density data exclude 33,136-sq-mi (85,823-sq-km) area of Pakistani-administered Jammu and Kashmir (comprising both Azad Kashmir and the Northern Areas). Area: 307,374 sq mi, 796,096 sq km. Population (2007): 159,060,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 517.5, persons per sq km 199.8. Urban (2006): 34.5%. Sex distribution (2005): male 51.44%; female 48.56%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 37.2%; 15-29, 29.9%; 30-44, 16.8%; 45-59, 10.2%; 60-74, 4.7%; 75-84, 1.0%; 85 and over, 0.2%. Ethnic composition (2000): Punjabi 52.6%; Pashtun 13.2%; Sindhi 11.7%; Urdu-speaking muha-jirs 7.5%; Balochi 4.3%; other 10.7%. Religious affiliation (2000): Muslim 96.1%; Christian 2.5%; Hindu 1.2%; others (including Ahmadiyah) 0.2%. Major urban agglomerations (2005): Karachi 11,608,000; Lahore 6,289,000; Faisalabad 2,494,000; Rawalpindi 1,770,000; Multan 1,452,000. Location: southern Asia, bordering China, India, the Arabian Sea, Iran, and Afghanistan.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 26.1 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 8.2 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 3.28. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 63.9 years; female 63.8 years.
National economy
Budget (2005-06). Revenue:PKR 1,022,704,000,000 (tax revenue 70.0%, of which sales tax 28.0%, income/corporate profits 21.1%, customs 13.3%; nontax revenue 25.9%; other 4.1%). Expenditures: PKR 1,072,225,000 (general public service 61.4%, of which debt servicing 28.4%; defense 22.4%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): sugarcane 47,244,000, wheat 21,612,000, rice 8,321,000; livestock (number of live animals) 56,700,000 goats, 26,300,000 buffalo, 24,900,000 sheep; roundwood 29,270,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 91%; fisheries production 515,095 (from aquaculture 16%). Mining and quarrying (2005): limestone 14,857,000; gypsum 552,496. Manufacturing (value of production in PKR ’000,000,000; 2000-01): textiles 321; food products 189; refined petroleum and coke 94. Energy production (consumptions-electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 85,699,000,000 (85,699,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) 4,587,000 (7,894,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2005) 24,000,000 ([2004] 85,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 10,031,000 (14,748,000); natural gas (cu m; 2005) 38,089,000,000 ([2004] 32,162,000,000). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 28.0%, in permanent crops 0.8%, in pasture 6.5%; overall forest area (2005) 2.5%. Population economically active (2006): total 50,055,000; activity rate of total population 32.2% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 54.2%; female 20.1%; officially unemployed 6.2%). Gross national income (2006): US$149,784,000,000 (US$930 per capita). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$29,490,-000,000. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 181; remittances (2006-07 avg.) 5,491; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 1,008; official development assistance (2005) 1,917 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 1,275; remittances (2006) 3.0. Households (2001-02). Average household size (2005) 6.8; income PKR 86,102 (US$1,416); sources of income: self-employment 41.3%, wages and salaries 33.5%, transfer payments 11.6%; expenditure: food 48.3%, housing 13.2%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006-07): US$26,652,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 19.1%; chemicals and chemical products 15.0%; refined petroleum 14.9%; crude petroleum 12.7%; food 9.1%). Major import sources: Saudi Arabia 12.2%; UAE 11.7%; China 8.7%; Kuwait 6.7%; Japan 5.5%. Exports (2006-07): US$16,924,-000,000 (textiles 59.2%, of which woven cotton fabric 13.7%, knitwear 12.4%, bedding 8.2%, ready-made garments 6.5%; cotton yarn 6.4%; rice 6.7%; petroleum products 5.2%). Major export destinations: US 22.7%; UAE 7.5%; UK 5.9%; Hong Kong 4.4%; Germany 4.0%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2004-05): length 11,515 km; passenger-km 24,238,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 5,013,540,000. Roads (2006-07): total length 259,197 km (paved 67%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 1,559,824; trucks and buses 507,945. Air transport (2006; Pakistan International Airlines only): passenger-km 15,110,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 426,991,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2003): 6,246,000 (42); televisions (2003): 12,223,000 (82); telephone landlines (2006): 5,240,000 (33); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 34,507,000 (220); personal computers (2005): 803,000 (5.2); total Internet users (2006): 12,000,000 (76); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 57,000 (0.4).
Education and health
Health (2005): physicians 122,798 (1 per 1,263 persons); hospital beds 101,490 (1 per 1,517 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 76.7. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,422 (vegetable products 81%, animal products 19%); 137% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 619,000 (army 88.8%, navy 3.9%, air force 7.3%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 3.5%; per capita expenditure US$29.
Did you knows
Harappa lies on the left bank of a now dry course of the Ravi River, west-southwest of the town of Sahiwal, in the Punjab of eastern Pakistan. The village stands on an extensive series ot mounds in which excavations since 1921 have disclosed the remains of a large city of the Indus civilization, second in size to Mohenjo-daro, which lies about 400 miles (644 km) to the southwest.
Background
Pakistan has been inhabited since about 3500 bc. From the 3rd century bc to the 2nd century ad, it was part of the Mauryan and Kushan kingdoms. The first Muslim conquests were in the 8th century ad. The British East India Company subdued the reigning Mughal dynasty in 1757. During the period of British colonial rule, what is now Pakistan was part of India. When the British withdrew in 1947, the new state of Pakistan came into existence by act of the British Parliament. Kashmir remained a disputed territory between Pakistan and India, resulting in military clashes and full-scale war in 1965. Civil war between East Pakistan (now Bangladesh) and West Pakistan resulted in independence for Bangladesh in 1971. Many Afghan refugees migrated to Pakistan during the Soviet-Afghan War in the 1980s. Pakistan elected Benazir Bhutto, the first woman to head a modern Islamic state, in 1988. She was ousted in 1990 on charges of corruption and incompetence. During the 1990s border flare-ups with India continued, and Pakistan conducted nuclear tests.
Recent Developments
The assassination of former prime minister Benazir Bhutto on 27 Dec 2007, only days after the lifting of a state of emergency imposed by Pres. Pervez Musharraf in early November, plunged Pakistan into its deepest domestic crisis since the 1971 civil war. It is uncertain whethershe was shot or struck her head, but a suicide bomber also blew himself up near her vehicle, killing more than 20. Her tragic passing framed the events of 2007. Musharraf, who had been reelected to another five-year term as Pakistan’s president in a controversial election in October, placed the country on red alert and ordered all military and police to quell the riots that paralyzed many sectors of society. Bhutto’s death and its aftermath placed the national and provincial elections scheduled for 2008 in question, but the elections were carried out in February 2008 and resulted in victory for the Pakistan People’s Party (PPP), which had campaign platforms of defeating extremism and bringing modernity and democracy to the country. The cochairman of the PPP was Asif Ali Zardari, widower of Benazir Bhutto. The Pakistan Muslim League-N, led by former prime minister Nawaz Sharif, polled second. Yousaf Raza Gilani, a longtime ally of Bhutto, was sworn in as prime minister in March 2008. One of his first acts was to free the former chief justice, who had been placed under house arrest by Musharraf in 2007 for having challenged his October reelection. In August 2008 Musharraf resigned the presidency.
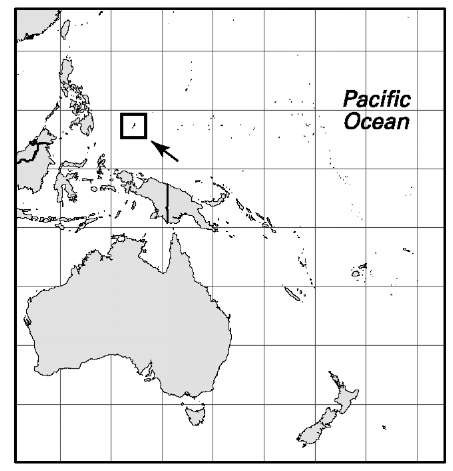
Palau
Official name: Belu’u er a Belau (Palauan); Republic of Palau (English). Form of government: nonparty republic with two legislative houses (Senate [9]; House of Delegates [16]). Head of state and government: President Tommy Remengesau, Jr. (from 2001). Capital: Melekeok. Official languages: Palauan; English; Sonsorolese-Tobian. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 US dollar (US$) = 100 cents.
Demography
Area: 188 sq mi, 488 sq km. Population (2007): 20,200. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 107.4, persons per sq km 41.4. Urban (2005): 70.0%. Sex distribution (2006): male 53.72%; female 46.28%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 23.4%; 15-29, 21.6%; 30-44, 28.4%; 45-59, 18.3%; 60-74, 5.9%; 75 and over, 2.4%. Ethnic composition (2005; population ages 18 and over only): Palauan 65.2%; Asian 30.3%, of which Filipino 21.6%, Vietnamese 2.3%; other Micronesian 3.1%; white 1.1%; other 0.3%. Religious affiliation (2005; population ages 18 and over only): Roman Catholic 51.0%; Protestant 26.7%; Modekngei (marginal Christian sect) 8.9%; other Christian 1.8%; other 11.6%. Major cities (2005): Koror 10,743; Meyuns 1,153; Kloulklubed 680. Location: island group in the North Pacific Ocean, east of the Philippines.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 12.9 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 7.2 (world avg. 8.6). Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 68.0 years; female 72.0 years.
National economy
Budget (2005-06). Revenue:US$83,671,000 (grants from the US 53.7%; tax revenue 34.9%; nontax revenue 7.9%; trust fund revenue 3.5%). Expenditures: US$87,586,000 (current expenditure 74.1%; capital expenditure 25.9%). Public debt (gross external debt; 2002-03): US$19,429,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (value of sales in US$; 2001): eggs (2003) 638,750, cabbages 116,948, cucumbers 44,009; livestock (number of live animals; 2001) 702 pigs, 21,189 poultry; fisheries production (2005) 937 (from aquaculture 1%). Manufacturing: includes handicrafts. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 171,000,000 ([2006] 114,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (78,000). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2004) 97; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 4.8; official development assistance (2005) 29 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2004) 2.0. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 9%, in permanent crops 4%, in pasture 7%; overall forest area (2005) 88%. Population economically active (2005): total 10,203; activity rate of total population 51.3% (participation rates: over age 15, 69.1%; female 39.1%; unemployed 4.2%). Gross national income (2006): US$162,000,000 (US$8,011 per capita). Households. Average household size (2005) 3.9; annual average income per household (2005) US$20,422; expenditure (1997): food 42.2%, beverages and tobacco 14.8%, entertainment 13.1%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2001): US$95,700,000 (machinery and transport equipment 24.2%; food and live animals 15.2%; mineral fuels and lubricants 10.4%; beverages and tobacco products 8.3%; chemicals and chemical products 7.4%). Major import sources (2003): South Korea 56.4%; Japan 18.7%; Germany 11.3%; Indonesia 3.6%; Australia 3.0%. Exports (2001): US$9,000,000 (mostly high-grade tuna and garments). Major export destinations (2003): Japan 86.7%; Vietnam 5.9%; Zambia 4.6%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2004): total length 61 km (paved 59%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars and trucks 7,247. Air transport (2003): passenger arrivals 80,017, passenger departures 78,608. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Telephone landlines (2006): 8,000 (399); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 8,300 (414); total Internet users (2003): 3,150(160).
Education and health
Primary 3.9%; incomplete secondary 14.9%; complete secondary 42.2%; postsecondary/voca-tional 14.1%; higher 14.0%. Literacy (2005): virtually 100%. Health (2004): physicians 21 (1 per 942 persons); hospital beds 135 (1 per 147 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 7.7.
Military
The US is responsible for the external security of Palau, as specified in the Compact of Free Association of 1 Oct 1994.
Background
Palau’s inhabitants began arriving 3,000 years ago in successive waves from the Indonesian and Philippine archipelagos and from Polynesia. The islands had been under nominal Spanish ownership for more than three centuries when they were sold to Germany in 1899. They were seized by Japan in 1914 and taken by Allied forces in 1944 during World War II. Palau became part of the UN Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands in 1947 and became a sovereign state in 1994; the US provides economic assistance and maintains a military presence in the islands.
Recent Developments
Palau vowed to join the United States and Russia in the fight against nuclear terrorism in 2007. In February Palau approved the statutory documents of the Global Initiative to Combat Nuclear Terrorism, which US Pres. George W. Bush and Russian Pres. Vladimir Putin had created.
Panama
Official name: Republica de Panama (Republic of Panama). Form of government: multiparty republic with one legislative house (Legislative Assembly [78]). Head of state and government: President Martfn Tor-rijos (from 2004). Capital: Panama City. Official language: Spanish. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 balboa (B) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = B 1.00.
Demography
Area: 28,973 sq mi, 75,040 sq km. Population (2007): 3,343,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 115.4, persons per sq km 44.5. Urban (2005): 70.8%. Sex distribution (2005): male 50.54%; female 49.46%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 30.5%; 15-29, 26.3%; 30-44, 21.4%; 45-59, 12.8%; 60-74, 6.6%; 75 and over, 2.4%. Ethnic composition (2000): mestizo 58.1%; black and mulatto 14.0%; white 8.6%; Amerindian 6.7%; Asian 5.5%; other 7.1%. Religious affiliation (2000): Roman Catholic 70.6%; Protestant/independent Christian 14.0%; Muslim 4.4%; Baha’i 1.2%; Buddhist 0.8%; traditional beliefs 0.7%; nonreligious 2.5%; other 5.8%. Major cities (2000): Panama City 415,964 (urban agglomeration [2005] 1,216,000); San Miguelito 293,745; David (population of cabecera) 77,734; Arraijan (population of cabecera) 63,753; La Chorrera 55,871. Location: Central America, bordering the Caribbean Sea, Colombia, the North Pacific Ocean, and Costa Rica.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 20.0 (world avg. 20.3); (2006) within marriage 17.3%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 4.4 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 2.40. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 72.7 years; female 77.9 years.
National economy
Budget (2004). Revenue: B 2,042,000,000 (tax revenue 59.2%, of which income taxes 23.9%, taxes on domestic transactions 20.9%; other current revenue 39.9%, of which revenue from Panama Canal 9.0%). Expenditures: B 2,810,000,000 (current expenditure 83.8%, of which wages and salaries 27.2%, transfers 26.3%, debt service 21.1%; development expenditure 16.2%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$7,514,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): sugarcane 1,766,000, bananas 439,200, rice 280,000; livestock (number of live animals) 1,564,000 cattle, 286,000 pigs, 180,000 horses; roundwood (2005) 1,298,218 cu m, of which fuel-wood 93%; fisheries production (2005) 222,756 (from aquaculture 4%). Mining and quarrying (2005): limestone 270,000. Manufacturing (value added in B ’000,000; 2004): food products 410; beverages 167; cement, bricks, and ceramics 70. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 5,475,000,000 (4,495,000,000); crude petroleum, none (negligible); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (1,710,000). Households. Average household size (2004) 4.1; average annual income per household (1990) B 5,450 (US$5,450); expenditure (2001): food 22%, energy 18%, health care 14%. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 7.4%, in permanent crops 2.0%, in pasture 20.6%; overall forest area (2005) 57.7%. Population economically active (2006): total 1,332,059; activity rate of total population 39.8% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 66.9%; female 37.1%; unemployed 9.1%). Gross national income (2006): US$15,536,-000,000 (US$4,726 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 780; remittances (2006) 149; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 605. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 271; remittances (2006) 121; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 1,777.
Foreign trade
Imports (2003; c.i.f.): B 3,122,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 18.7%; mineral fuels 13.0%; chemical products 12.4%; transport equipment 11.1%). Major import sources (2006): US 26.8%; direct imports from Colon Free Zone 11.9%; Curasao 10.1%; Costa Rica 5.1%; Japan 4.7%. Exports (2003; f.o.b.): B 799,000,000 (marine products 42.3%, of which tuna 16.4%, shrimp and lobster 9.6%, salmon 7.0%; bananas 13.2%; melons 5.9%). Major export destinations (2006): US 38.5%; Spain 8.2%; The Netherlands 6.7%; Sweden 5.6%; Costa Rica 4.5%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2002): route length (2005) 355 km; passenger-km (data for Panama Canal Railway and National Railway of Chiriquf) 35,693,000,000; metric ton-km cargo (data for Panama Canal Railway) 20,665,000,000. Roads (2005): total length 11,984 km (paved 72%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 269,704; trucks and buses 78,699. Panama Canal traffic (2005-06): oceangoing transits 12,764; cargo 205,058,000 metric tons. Airtransport (2006; COPA only): passenger-km 6,560,000,000; metric ton-km cargo (2005) 37,226,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 164,000 (52); televisions (2004): 620,000 (195); telephone landlines (2006): 433,000 (132); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 1,694,000 (525); personal computers (2005): 147,000 (47); total Internet users (2006): 220,000 (67); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 18,000 (5.6).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2000). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling/unknown 13.8%; primary 36.4%; secondary 33.9%; undergraduate 14.4%; graduate 1.5%. Literacy (2005): total population ages 15 and over literate 93.0%; males literate 93.6%; females literate 92.4%. Health (2004): physicians 4,321 (1 per 715 persons); hospital beds 7,564 (1 per 408 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 14.8. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,627 (vegetable products 82%, animal products 18%); 144% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): none. Paramilitary expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.1%; per capita expenditure US$50.
Background
Panama was inhabited by Native Americans when the Spanish arrived in 1501. The firstsuccessful Spanish settlement was founded by Vasco Nunez de Balboa in 1510. Panama was part of the viceroyalty of New Granada until it declared its independence from Spain in 1821 to join the Gran Colombia union. In 1903 it revolted against Colombia and was recognized by the US, to which it ceded the Canal Zone. The completed Panama Canal was opened in 1914; its jurisdiction reverted from the US to Panama in 1999. An invasion by US troops in 1989 overthrew the de facto ruler, Gen. Manuel Noriega.
Recent Developments
In June 2007 Panama’s free-trade agreement with the US was signed by government representatives, and the National Assembly quickly ratified the treaty. On 3 September Pres. Martin Torrijos presided over the official opening of the US$5.25 billion expansion of the Panama Canal. The project involved constructing a third set of locks and new access channels and widening and deepening existing channels. The expansion was expected to increase the canal’s capacity significantly, allowing cargo ships that currently are too large to pass through the canal, and extend its role in global maritime trade.
Papua New Guinea
Official name: Independent State of Papua New Guinea. Form of government: constitutional monarchy with one legislative house (National Parliament [109]). Chief of state: British Queen Elizabeth II (from 1952), represented by Governor-General Sir Paulias Matane (from 2004). Head of government: Prime Minister Sir Michael Somare (from 2002). Capital: Port Moresby. Official language: English; English, Motu, and Tok Pisin (English Creole) are national languages. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Papua New Guinea kina (K) = 100 toea; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = K 2.60.
Demography
Area: 178,704 sq mi, 462,840 sq km. Population (2007): 6,331,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 35.4, persons per sq km 13.7. Urban (2005): 13.4%. Sex distribution (2005): male 50.79%; female 49.21%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 40.6%; 15-29, 27.3%; 30-44, 18.9%; 45-59, 9.3%; 60-74, 3.3%; 75-84, 0.5%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Ethnic composition (1983): New Guinea Papuan 84.0%; New Guinea Melanesian 15.0%; other 1.0%. Religious affiliation (2005): Protestant/independent Christian 44%; Roman Catholic 22%; traditional beliefs 34%. Major cities (2004): Port Moresby 337,900; Lae 109,800; Madang 36,000; Wewak 28,600; Arawa 20,800. Location: group of islands, including the eastern half of the island of New Guinea, in the South Pacific Ocean near the Equator, bordering Indonesia and to the north of Australia.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 31.8 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 9.8 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 22.0 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 4.05. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 54.3 years; female 60.2 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: K 5,243,000,000 (tax revenue 71.4%, of which taxes on minerals and petroleum 20.5%, indirecttaxes 18.6%, income tax 16.0%; grants 23.3%; nontax revenue 5.3%). Expenditures:K 4,104,000,000 (current expenditure 69.0%;developmentex-penditure 31.0%). Public debt (external, outstanding; March 2007): US$1,170,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): oil palm fruit 1,300,000, bananas 919,800, coconuts 795,100; livestock (number of live animals) 1,750,000 pigs; roundwood 7,241,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 76%; fisheries production 250,280. Mining and quarrying (2005): copper (metal content; 2006) 194,355; gold 68,483 kg; silver 51,125 kg. Manufacturing (value of exports in US$’000; 2005): forest products 153,000; palm oil 126,100; coconut oil 30,200; copra 5,600; refined petroleum, n.a. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 1,399,000,000 (1,399,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) none (1,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) 18,300,000 (476,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 46,000 (712,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 85,300,000 (85,300,000). Population economically active (2000): total 2,413,357; activity rate of total population 46.5% (participation rates: ages 15-64,73.2%; female 47.9%). Gross national income (2006): US$5,523,000,000 (US$890 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 3.6; remittances (2006) 13; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 48; official development assistance (2005) 233 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 56; remittances (2006) 135; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 11. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 0.5%, in permanent crops 1.4%, in pasture 0.4%; overall forest area (2005) 65.0%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2003; f.o.b. in trading partners and c.i.f. in commodities): K 4,628,000,000 (nonelectrical machinery 18.5%; food products 14.8%; refined petroleum 12.9%; transport equipment 8.8%; chemical products 8.4%). Major import sources (2006): Australia 34.2%; US 21.0%; Singapore 19.2%; Japan 5.0%; New Zealand 2.8%. Exports (2006): K 12,731,000,000 (copper 34.0%; gold 24.3%; crude petroleum 23.5%; logs 3.9%; palm oil 2.4%). Major export destinations (2006): Australia 40.7%; Japan 14.3%; Philippines 9.7%; Germany 4.5%; South Korea 4.4%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (1999): total length 19,600 km (paved 4%). Vehicles (2002): passenger cars 24,900; trucks and buses 87,800. Air transport (2006; Air Ni-ugini only): passenger-km 748,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 22,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 51,000 (8.6); televisions (2003): 130,000 (22); telephone landlines (2005): 64,000 (11); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 75,000 (13); personal computers (2005): 391,000 (64); total Internet users (2006): 110,000 (18).
Education and health
Educational attainment (1990). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling 82.6%; some primary education 8.2%; completed primary 5.0%; some secondary 4.2%. Literacy (2003): total population ages 15 and over literate 57.3%; males literate 63.4%; females literate 50.9%. Health (2005): physicians 750 (1 per 7,849 persons); hospital beds (2000) 14,516 (1 per 371 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 63.0.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 3,100 (army 80.6%, maritime element [coastal patrol] 12.9%, air force 6.5%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 0.6%; per capita expenditure US$5.
Background
Papua New Guinea has been inhabited since prehistoric times. The Portuguese sighted the coast of New Guinea in 1512, and in 1545 the Spanish claimed the island. The first colony was founded in 1793 by the British. In 1828 the Dutch claimed the western half as part of the Dutch East Indies. In 1884 Britain annexed the southeastern part and Germany took over the northeastern sector. The British part became the Territory of Papua in 1906 and passed to Australia, which also governed the German sector after World War I. After World War II, Australia governed both sectors as the Territory of Papua and New Guinea. Dutch New Guinea was annexed to Indonesia in 1969. Papua New Guinea achieved independence in 1975 and joined the British Commonwealth. It moved to resolve its war with Bougainville independence fighters in 1997. The decadelong war on the island of Bougainville ended when final terms for peace were negotiated on 1 Jun 2001.
Recent Developments
Papua New Guinea Prime Minister Michael Somare, reelected in August 2007 to a second term, was forced to defend himself in 2008 from opposition accusations of financial impropriety. At issue was the government’s attempts to block investigation intoSomare’s personal taxes. As well, he was linked to a scandal involving a proposal for the country to recognize Taiwan, allegedly for a paymentof almost US$30 million.
Paraguay
Official name: Republicadel Paraguay (Spanish); Teta Paraguaype (Guarani) (Republic of Paraguay). Form of government: multiparty republic with two legislative houses (Chamber of Senators [45]; Chamber of Deputies [80]). Head of state and government: President Fernando Lugo (from 2008). Capital: Asuncion. Official languages: Spanish; Guaranf. Official religion: none (Roman Catholicism enjoys special recognition in the 1992 constitution). Monetary unit: 1 guaranf (plural guaranies; @) = 100 centimos; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = @ 3,950.00.
Demography
Area: 157,048 sq mi, 406,752 sq km. Population (2007): 6,127,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 39.0, persons per sq km 15.1. Urban (2006): 58.1%. Sex distribution (2006): male 49.57%; female 50.43%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 35.9%; 15-29, 28.6%; 30-44, 17.4%; 45-59, 11.2%; 60-74, 5.2%; 75 and over, 1.7%. Ethnic composition (2000): mixed (white/Amerindian) 85.6%; white 9.3%, of which German 4.4%, Latin American 3.4%; Amerindian 1.8%; other 3.3%. Religious affiliation (2002): Roman Catholic 89.6%; Protestant (including all Evangelicals) 6.2%; other Christian 1.1%; nonreligious/atheist 1.1%; traditional beliefs 0.6%; other/unknown 1.4%. Major urban areas (2002): Asuncion (2006) 519,661 (urban agglomeration [2005] 1,858,000); Ciudad del Este 222,274; San Lorenzo 204,356; Luque 170,986; Capiata 154,274. Location: central South America, bordering Brazil, Argentina, and Bolivia.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 25.8 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 5.7 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 20.1 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 3.30. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 69.2 years; female 73.4 years.
National economy
Budget (2006-07): Revenue: @10,174,723,-000,000 (tax revenue 65.2%, of which VAT 28.5%, income tax 10.9%, taxes on international trade 8.5%; nontax revenue 34.8%). Expenditures: @9,682,282,-000,000 (current expenditure 77.3%, of which wages and salaries 42.9%; capital expenditure 22.7%). Public debt (external, outstanding; August 2007): US$2,151,725,000. Population economically active (2006): total 2,735,646; activity rate 46.0% (participation rates: ages 15-64 [2002], 61.4%; female 38.5%; unemployed 11.1%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006-07): soybeans 6,250,000, cassava 4,800,000, sugarcane 4,100,000, mate (2004-05) 74,000; livestock (number of live animals; 2006) 9,982,932 cattle, 1,600,000 pigs, 17,000,000 chickens; roundwood (2005) 10,090,794 cu m, of which fuelwood 60%; fisheries production (2005) 23,100 (from aquaculture 9%). Mining and quarrying (2005): kaolin 66,600. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2001): food products 325; beverages 114; chemical products 77. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 51,921,000,000 (Paraguay is the world’s second largest net exporter of electricity) (6,925,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) none (491,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 64,000 (1,254,000). Gross national income (2006): US$9,281,000,000 (US$1,543 per capita). Households. Average household size (2005) 4.3. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 76; remittances (2006) 268; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 74; official development assistance (2005) 81 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 79; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 5.0. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 7.2%, in permanent crops 0.2%, in pasture 54.6%; overall forest area (2005) 46.5%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006): US$5,254,271,000 (machinery and apparatus 35.9%; mineral fuels 13.2%; transport equipment 11.5%; chemical products 6.3%; food, beverages, and tobacco products 6.1%). Major import sources: China 27.0%; Brazil 20.0%; Argentina 13.6%; Japan 8.3%; US 6.4%. Exports (2006): US$1,906,367,000 (soybeans 23.0%; meat 22.3%; cereals 11.4%; flour 7.5%; vegetable oils 6.2%). Major export destinations: Uruguay 22.0%; Brazil 17.2%; Russia 11.9%; Argentina 8.8%; Chile 6.9%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2006): operational route length 36 km. Roads (1999): total length 29,500 km (paved 51%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 360,070; trucks 81,207. Air transport (2005; Transportes Aereos del Mercosur only): passenger-km 501,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 145,000 (25); televisions (2004): 1,300,000 (224); telephone landlines (2006): 331,000 (55); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 3,233,000 (537); personal computers (2005): 460,000 (78); total Internet users (2006): 260,000 (43); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 16,000 (2.7).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2003). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: no formal schooling 4.1%; incomplete primary education 30.2%; complete primary 30.8%; secondary 26.9%; higher 8.0%. Literacy (2005): percentage of total population ages 15 and over literate 94.9%; males literate 95.9%; females literate 93.9%. Health (2005): physicians 5,517 (1 per 873 persons); hospital beds 5,843 (1 per 1,010 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 33.8. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,563 (vegetable products 78%, animal products 22%); 139% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 10,100 (army 75.2%, navy 13.9%, air force 10.9%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 0.7%; per capita expenditure US$9.
Background
Seminomadic tribes speaking Guaranf were in Paraguay long before it was settled by Spain in the 16th and 17th centuries. Paraguay was part of the Viceroyalty of the Rio de la Plata until it became independent in 1811. It suffered from dictatorial governments in the 19th century and from the 1865 war with Brazil, Argentina, and Uruguay. The Chaco War with Bolivia over disputed territory was settled primarily in Paraguay’s favor by the peace treaty of 1938. Military governments, including that of Alfredo Stroessner, predominated in the mid-20th century until the election of a civilian president, Juan Carlos Wasmosy, in 1993. Paraguay suffered a financial crisis in the late 1990s, and democratic government was in jeopardy.
Recent Developments
Political maneuvering in advance of the April 2008 presidential elections dominated Paraguay’s attention during 2007, even as the country was hit by a series of corruption scandals. In December 2006 Fernando Lugo, the popular Roman Catholic bishop of San Pedro, resigned to run for the presidency, since Paraguay’s constitution prohibited members of the clergy from holding office. Pres. Nicanor Duarte Fru-tos, after unsuccessfully seeking a constitutional amendment permitting him to run for a second term, began grooming his education minister, Blanca Ove-lar, as his successor. Although Duarte took office on an anticorruption platform, allegations of corruption, bribery, and embezzlement by various government figures dogged his administration—including a case involving Education Ministry officials (serving under Ovelar) accused of having embezzled nearly US$6 million from a school meals program. In July 2007 the six leading opposition parties announced that they had forged an alliance behind Lugo, and in April 2008 he was elected, defeating Ovelar, whose Colorado Party had retained power in Paraguay since 1947.
Peru
Official name: Republica del Peru (Spanish) (Republic of Peru). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with one legislative house (Congress [120]). Head of state and government: President Alan Garcia (from 2006), assisted by Prime Minister Jorge del Castillo (from 2006). Capital: Lima. Official languages: Spanish; Quechua; Aymara. Official religion: Roman Catholicism. Monetary unit: 1 nuevo sol (S/.) = 100 centimos; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = S/. 2.96.
Demography
Area: 496,218 sq mi, 1,285,198 sq km. Population (2007): 27,903,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 56.2, persons per sq km 21.7. Urban (2005): 72.6%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.94%; female 50.06%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 31.1%; 15-29, 28.0%; 30-44, 20.0%; 45-59, 12.1%; 60-74, 6.3%; 75-84, 1.9%; 85 and over, 0.6%. Ethnic composition (2000): Quechua 47.0%; mestizo 31.9%; white 12.0%; Aymara 5.4%; Japanese 0.5%; other 3.2%. Religious affiliation (2005): Roman Catholic 85%; Protestant 7%; independent Christian 4%; other 4%. Major cities (2005): metropolitan Lima 7,753,439; Arequipa 783,000; Trujillo 644,547; Chi-clayo 495,415; Piura 361,832. Location: western South America, bordering Ecuador, Colombia, Brazil, Bolivia, Chile, and the South Pacific Ocean.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 20.9 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 6.3 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 2.56. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 67.8 years; female 71.4 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: S/. 41,432,000,000 (tax revenue 85.8%, of which VaT 44.6%, corporate taxes 14.8%; nontax revenue 14.2%). Expenditures: S/. 43,534,000,000 (current expenditure 77.1%, of which transfers 30.1%; debt service 11.7%; capital expenditure 11.2%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): sugarcane 7,600,000, alfalfa 5,606,000, potatoes 3,290,000 (in 2006 Peru ranked second in the world in coca production [114,100 metric tons produced]); livestock (number of live animals) 14,822,226 sheep, 5,241,298 cattle, (2005) 4,500,000 llamas and alpacas; roundwood (2005) 9,142,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 81%; fisheries production (2005) 9,416,130. Mining and quarrying (2005; metal content): iron ore 4,638,027; zinc 1,028,418; copper 790,198. Manufacturing (value in S/. ’000,000; 2005): food products 11,854; textiles and clothing 5,310; chemical products 4,212. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 23,822,000,000 (21,100,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) 16,000 (963,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2005) 40,600,000 ([2004] 60,011,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 8,286,000 (7,233,000); natural gas (cu m; 2005) 4,956,000,000 (561,000,000). Households. Average household size (2005) 4.3; income per household (1988) US$2,173; sources of income (1991): self-employment 67.1%, wages 23.3%, transfers 7.6%; expenditure (1990): food 29.4%, recreation and education 13.2%, household durables 10.1%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 1,241; remittances (2006) 1,825; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 1,763. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 680; remittances (2006) 133. Population economically active (2002): total 12,892,000; activity rate of total population 48.2% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 72.6%; female 42.0%; urban unemployed [2005] 9.6%). Gross national income (2006): US$86,579,000,000 (US$3,138 per capita). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$22,222,000,000. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 2.9%, in permanent crops 0.5%, in pasture 13.2%; overall forest area (2005) 53.7%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): US$12,076,000,000 (consumer goods 19.2%; mineral fuels 19.2%; capital goods 17.5%; food products 6.2%). Major import sources (2006): US 16.5%; China 10.3%; Brazil 10.3%; Ecuador 7.2%; Colombia 6.1%. Exports (2005): US$17,336,000,000 (copper 19.4%; gold 18.3%; crude and refined petroleum 8.8%; textiles and clothing 7.4%; fishmeal 6.6%; molybdenum 6.6%). Major export destinations (2006): US 24.0%; China 9.6%; Switzerland 7.1%; Canada 6.8%; Chile 6.0%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2002): length (2005) 3,462 km; passenger-km 98,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 1,008,000,000. Roads (2004): total length 78,829 km (paved 14%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 824,613; trucks and buses 462,803. Air transport (2006): passenger-km 4,440,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 100,092,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 946,000 (35); televisions (2002): 4,592,000 (172); telephone landlines (2006): 2,332,000 (82); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 8,500,000 (300); personal computers (2005): 2,800,000 (103); total Internet users (2006): 6,100,000 (215); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 485,000 (17).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2005). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: no formal schooling 11.8%; incomplete primary education 24.3%; complete primary 11.5%; incomplete secondary 15.3%; complete secondary 19.0%; higher 18.1%. Literacy (2005): total population ages 15 and over literate 91.6%; males literate 95.6%; females literate 87.7%. Health (2004): physicians 41,266 (1 per 651 persons); hospital beds (2005) 42,159 (1 per 647 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 31.9. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,583 (vegetable products 88%, animal products 12%); 141% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 80,000 (army 50.0%, navy 31.3%, air force 18.7%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.4%; per capita expenditure US$39.
Background
Peru was the center of the Inca empire, which was established about 1230 with its capital at Cuzco. In 1533 it was conquered by Francisco Pizarro, and it was dominated by Spain for almost 300 years as the Viceroyalty of Peru. It declared its independence in 1821, and freedom was achieved in 1824. Peru was defeated in the War of the Pacific with Chile (1879-83). A bound-arydispute with Ecuador erupted intowarin 1941and gave Peru control over a larger part of the Amazon basin; further disputes ensued until the border was demarcated again in 1998. The government was overthrown bya militaryjunta in 1968, and civilian rule was restored in 1980. The government of Alberto Fujimori dissolved the legislature in 1992 and promulgated a new constitution the followingyear. It later successfully combated the Sendero Luminoso (Shining Path) and TupacAmaru rebel movements. Fujimori wonasecond term in 1995 and a controversial third term in 2000, but he left office and the country late that year amid allegations of corruption.
Recent Developments
Probably the most notable event in Peru in 2007 was the magnitude-8.0 earthquake that on 15 August struck the southern coast near the city of Ica. The final death toll was about 540, with some 200,000 in need of shelter. Macroeconomic indicators were strong throughout the year; economic growth surpassed 7.0% and there were substantial government revenues, significant trade surpluses, and large foreign reserves. Inflation stayed low (at about 2.5%). However, extreme disparities remained between Peru’s wealthy and its poor. One of Peru’s economic mainstays—mining— showed signs of trouble. Numerous mining communities protested against low wages and such environmental ills as water pollution and mercury spills. The city of La Oroya, a mining town with a refinery in the central Andean highlands, was reportedly one of the 10 worst polluted places in the world; more than 90% of children in the area had high levels of lead in their blood. Pres. Alan Garcia supported a free-trade agreement with the US, and the Peru Trade Promotion Agreement was approved in November by the US House of Representatives and in December by the US Senate.
Philippines
Official name: Republika ng Pilipinas (Filipino); Republic of the Philippines (English). Form of government: unitary republic with two legislative houses (Senate [24]; House of Representatives [240]). Chief of state and head of government: President Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo (from 2001). Capital: Quezon City/Manila. Official languages: Filipino; English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Philippine peso (P) = 100 centavos; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = P 45.08.
Demography
Area: 122,121 sq mi, 316,294 sq km. Population (2007): 87,960,000. Density (2006): persons per sq mi 759.4, persons per sq km 293.2. Urban (2003): 61.0%. Sex distribution (2005): male 50.35%; female 49.65%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 35.1%; 15-29, 28.8%; 30-44, 19.0%; 45-59, 11.0%; 60-74, 5.0%; 75-84, 1.0%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Ethnic composition (2000): Tagalog 20.9%; Visayan (Cebu) 19.0%; Ilocano 11.1%; Hiligaynon (Visaya) 9.4%; Waray-Waray (Binisaya) 4.7%; Central Bikol (Naga) 4.6%; Filipino mestizo 3.5%; Pampango 3.1%; other 23.7%. Religious affiliation (2005): Roman Catholic 64.9%; independent Christian 17.7%; Muslim 5.1%; Protestant 5.0%; traditional beliefs 2.2%; other 5.1%. Major cities (2000): Quezon City 2,173,831; Manila 1,581,082 (Metro Manila [2003] 10,352,249); Caloocan 1,177,604; Davao 1,147,116; Cebu 718,821. Location: southeastern Asia, archipelago between the Philippine Sea and the South China Sea, east of Vietnam.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 24.1 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 5.6 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 3.41. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 67.0 years; female 72.9 years.
National economy
Budget (2004). Revenue: P 757,945,000,000 (income taxes 42.1%; international duties 17.5%; sales tax 14.4%; nontax revenues 10.6%). Expenditures: P 899,990,000,000 (debt service 33.5%; economic affairs 17.7%; education 15.1%; transportation and communications 6.1%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): sugarcane 24,350,000, rice 15,330,000, coconuts 14,960,000; livestock (number of live animals) 13,046,680 pigs, 3,735,816 goats, 3,357,956 buffalo; roundwood (2005) 15,819,034 cu m, of which fu-elwood 82%; fisheries production (2005) 2,803,603 (from aquaculture 20%); aquatic plants production 1,338,859 (from aquaculture 100%). Miningand quarrying (2005): chromite 36,070; nickel (metal content) 22,560; copper (metal content) 16,320. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2003): petroleum products 1,980; electronic products 1,696; food products 1,338. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 55,957,000,000 (55,957,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2004) 2,482,000 (9,456,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) I,000,000 (816,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 9,345,000 (14,427,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 2,479,000,000 (2,479,000,000). Households (2000). Average household size (2004) 5.0; income per family (2003) P 148,616 (US$2,742); sources of income: wages 52.1%, self-employment 25.1%, remittances 11.1%; expenditure: food, beverages, and tobacco45.4%, housing 14.2%, transportation 6.8%. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 19.1%, in permanentcrops 16.8%, in pasture 5.0%; overall forest area (2005) 24.0%. Gross national income (2006): US$127,832,000,000 (US$1,482 per capita). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$35,233,000,000. Population economically active (2007): total 36,434,000; activity rate of total population 41% (participation rates: ages 15 and over 63.6%; female [2006] 39.4%; unemployed [July 2007] 7.8%). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 2,130; remittances (2006) 14,923; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 810. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 1,279; remittances (2006) 15.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006): US$51,774,000,000 (electronic products 47.2%; mineral fuels 15.4%; machinery and transport equipment 7.7%). Major import sources (2004): Japan 20.6%; US 16.0%; Singapore 8.4%; China 7.4%; Taiwan 7.3%. Exports (2006): US$47,410,000,000 (electronic products 62.6%; clothing 5.6%; copper cathodes 2.6%). Major export destinations (2004): US 17.4%; Japan 15.8%; China II.4%; Hong Kong 8.3%; Singapore 7.7%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2004): route length 897 km; passenger-km 83,400,000; metric ton-km cargo (2000) 660,000,000. Roads (2003): total length 200,037 km (paved 10%). Vehicles (2006): passenger cars 767,000; trucks and buses 240,000. Airtransport (2006; Philippines Airlines only): passenger-km 13,513,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 257,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2003): 5,902,000 (73); televisions (2003): 14,770,000 (182); telephone landlines (2006): 3,633,000 (43); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 42,869,000 (508); personal computers (2005): 4,521,000 (54); total Internet users (2005): 4,615,000 (55).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2000). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling/unknown 6.1%; primary education 38.5%; incomplete secondary 12.5%; complete secondary 17.2%; technical 5.9%; incomplete undergraduate 11.8%; complete undergraduate 7.3%; graduate 0.7%. Literacy (2003): total population ages 15 and over literate 92.6%. Health: physicians (2005) 98,210 (1 per 857 persons); hospital beds (2004) 82,775 (1 per 999 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2004) 24.2. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,474 (vegetable products 84%, animal products 16%); 137% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 106,000 (army 62.3%, navy 22.6%, air force 15.1%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 0.9%; per capita expenditure US$10.
Background
In ancient times, the inhabitants of the Philippines were a diverse agglomeration of peoples who arrived in various waves of immigrants from the Asian mainland. Ferdinand Magellan arrived in 1521. The islands were colonized by the Spanish, who retained control until the islands were ceded to the US in 1898 following the Spanish-American War. The Commonwealth of the Philippines was established in 1935 to prepare the country for political and economic independence, which was delayed by World War II and the Japanese invasion. The islands were liberated by US forces during 1944-45, and the Republic of the Philippines was proclaimed in 1946, with a government patterned on that of the US. In 1965 Ferdinand Marcos was elected president. He declared martial law in 1972, and it lasted until 1981. After 20 years of dictatorial rule, he was driven from power in 1986. Corazon Aquino became president and instituted a period of democratic rule that continued with the 1992 election of Fidel Ramos. Through the 1990s the government tried to come to terms with independence fighters in the southern islands.
Recent Developments
Opponents of Philippine Pres. Gloria Macapagal Arroyo asked voters to treat the national elections held in May 2007 as a referendum on her administration. In the elections, which were marred by violence that claimed at least 126 lives, Arroyo’s supporters won more than 200 of the 219 seats that were contested in the House of Representatives to maintain their control there for another three years, though her opponents claimed 7 of the 12 Senate seats contested, enough to give them control of the 24-seat upper chamber. This contributed to a highly partisan situation that slowed or obstructed legislation recommended by Arroyo. In the southern Philippines in 2007, the heaviest fighting in three years disrupted a government cease-fire with the terrorist groups Abu Sayyaf and the Moro Islamic Liberation Front, extremists seeking a separate Muslim state. In December the two groups reached a tentative accord, but talks between the separatists and the government stalled and fighting continued in 2008. The Philippine economy grew 10.3% in 2007, and the unemployment rate fell to 7.4%. The economy benefited from remittances estimated at more than US$13 billion a year from some eight million Filipinos working abroad.
Poland
Official name: Rzeczpospolita Polska (Republic of Poland). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with two legislative houses (Senate [100]; Sejm [460]). Chief of state: President Lech Kaczynski (from 2005). Head of government: Prime Minister Donald Tusk (from 2007). Capital: Warsaw. Official language: Polish. Official religion: none (Roman Catholicism has special recognition per 1997 concordat with Vatican City). Monetary unit: 1 zloty (Zl) = 100 groszy; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = Zl 2.12.
Demography
Area: 120,726 sq mi, 312,679 sq km. Population (2007): 38,110,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 315.7, persons per sq km 121.9. Urban (2006): 61.3%. Sex distribution (2006): male 48.33%; female 51.67%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 15.8%; 15-29, 24.1%; 30-44, 20.2%; 45-59, 22.3%; 60-74, 11.8%; 75-84, 4.8%; 85 and over, 1.0%. Ethnic composition (2000): Polish 90.0%; Ukrainian 4.0%; German 4.0%; Belarusian 0.5%; Kashubian 0.4%; other 1.1%. Religious affiliation (2005): Roman Catholic 89.6%; other Catholic 0.3%; Polish Orthodox 1.3%; Protestant 0.4%; Jehovah’s Witness 0.3%; other (mostly nonreligious) 8.1%.
Major cities (2006): Warsaw 1,702,139; Lodz 760,251; Krakow 756,267; Wroclaw 634,630; Poz-nan 564,951. Location: central Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea, Russia (exclave of Kaliningrad), Lithuania, Belarus, Ukraine, Slovakia, Czech Republic, and Germany.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 9.8 (world avg. 20.3); (2005) within marriage 81.5%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 9.7 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 0.1 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 1.27. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 70.9 years; female 79.6 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue: Zl 197,640,000,000 (VAT 42.7%; excise tax 21.3%; income tax 14.2%). Expenditures: Zl 222,703,000,000 (social security and welfare 22.6%; transfers 15.5%; public debt 12.5%; wages and salaries 10.4%). Gross national income (2006): US$324,482,000,000 (US$8,508 per capita). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): sugar beets 11,474,820, potatoes 8,981,976, wheat 7,059,671; livestock (number of live animals) 18,813,000 pigs, 5,281,000 cattle; roundwood (2005) 31,944,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 11%; fisheries production (2005) 192,854 (from aquaculture 19%). Mining and quarrying (2005): sulfur 1,262,000; copper ore (metal content of concentrate) 614,800; silver (recoverable metal content) 1,344. Manufacturing (value of sales in Zl ’000,000; 2006): food products 137,089; transport equipment 84,568; fabricated metals 49,106. Energy production (consumption): electricity (’000,000 kW-hr; 2006-07) 156,065 ([2005] 131,186); hard coal (’000 metric tons; 2006-07) 93,135 ([2004] 83,915); lignite (’000 metric tons; 2006) 60,844 ([2005] 61,589); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006) 5,900,000 ([2005] 134,900,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2005) 23,153,000 (16,000,000); natural gas (cu m; 2006) 5,650,000,000 ([2005] 16,304,000,000). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2006): US$43,360,000,000. Population economically active (2006): total 16,938,000; activity rate of total population 44.4% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 64.3%; female 45.2%; unemployed [September 2006-August 2007] 14.0%). Households (2006). Average household size 3.1; average disposable annual income Zl 9,629 (US$3,103); sources of income: wages 49.4%, transfers 34.9%, self-employment 8.8%; expenditure: food, beverages, and tobacco 29.8%, housing and energy 19.7%, transportation and communications 13.9%, recreation 7.1%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 6,274; remittances (2006) 4,364; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 7,006. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 4,341; remittances (2006) 785; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 539. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 41.1%, in permanent crops 1.0%, in pasture 10.7%; overall forest area (2005) 30.0%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; c.i.f.): Zl 394,030,015,000 (electrical equipment 14.8%; chemical products 12.6%; transportation equipment 12.4%; base and fabricated metals 12.0%; machinery and apparatus 10.7%; mineral fuels 10.2%). Major import sources: Germany 24.0%; Russia 9.7%; Italy 6.8%; China 6.1%; France 5.5%. Exports (2006; f.ob.): Zl 343,778,977,000 (transportation equipment 20.9%; base and fabricated metals 13.7%; electrical equipment 12.1%; machinery and apparatus 8.6%; food products 8.3%; chemical products 6.4%). Major export destinations: Germany 27.2%; Italy 6.5%; France 6.2%; UK 5.7%; Czech Republic 5.5%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2006): length (2006) 20,176 km; passenger-km 18,552,100,000; metric ton-km cargo 53,622,500,000. Roads (2006; public roads only): total length 382,615 km (paved 67%). Vehicles (2006): passenger cars 13,384,299; trucks and buses 2,477,167. Air transport (2006): passenger-km 11,640,600,000; metric ton-km cargo 109,700,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 4,333,000 (113); televisions (2007): 7,820,000 (205); telephone landlines (2007): 11,284,000 (296); cellular telephone subscribers (2007): 36,758,000 (964); personal computers (2004): 7,362,000 (191); total Internet users (2006): 11,000,000 (288); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 2,640,000 (69).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2005). Percentage of population ages 13 and over having: no formal schooling/incomplete primary education 2.5%; complete primary 21.8%; lower secondary/vocational 28.5%; upper secondary and postsecondary 33.0%; university 14.2%. Literacy (2003): virtually 100%. Health (2005): physicians 76,046 (1 per 458 persons); hospital beds 236,980 (1 per 162 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 6.0. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,503 (vegetable products 74%, animal products 26%); 174% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 141,500 (army 62.9%, navy 10.1%, air force 21.2%, centrally controlled staff 5.8%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.9%; per capita expenditure US$154.
Background
Established as a kingdom in 922 under Mieszko I, Poland was united with Lithuania in 1386 under the Jagiellon Dynasty (1386-1572) to become the dominant power in east-central Europe. In 1466 it wrested western and eastern Prussia from the Teutonic Order, and its lands eventually stretched to the Black Sea. Wars with Sweden and Russia in the late 17th century led to the loss of considerable territory. In 1697 the electors of Saxony became kings of Poland, virtually ending Polish independence. In the late 18th century Poland was divided among Prussia, Russia, and Austria and ceased to exist. After 1815 the former Polish lands came under Russian domination, and from 1863 Poland was a Russian province. After World War I an independent Poland was established by the Allies. The invasion of Poland in 1939 by the USSR and Germany precipitated World War II, during which the Nazis sought to purge its culture and its large Jewish population. Reoccupied by Soviet forces in 1945, it was controlled by a Soviet-dominated government from 1947. In the 1980s the Solidarity labor movement achieved major political reforms, and free elections were held in 1989. An economic austerity program instituted in 1990 sped the transition to a market economy. In 2004 Poland joined the EU.
Recent Developments
Donald Tusk, the chairman of the pro-European Civic Platform, took office as prime minister in November 2007, vowing that Poland would be a more cooperative member of the EU and try to repair ties with Germany and defuse tensions with Russia. He wanted Polish troops to be pulled out of Iraq in 2008, the Polish militarycontribution in Afghanistan to be strengthened, and 350 troops to be sent in an EU mission to Chad. Tough negotiations led in August 2008 to an agreement to deploy US antimissile interceptors in Poland, a controversial move that angered Russia. Poland’s economic growth in 2007 was vibrant. GDP grew 9.7%, the unemployment rate dropped from 15.2% in 2006 to 12.4%, inflation was held in check at 3.5%, and the budget deficit was low at 3.0%.
Portugal
Official name: Republica Portuguesa (Portuguese Republic). Form of government: republic with one legislative house (Assembly of the Republic [230]). Chief of state: President Anfbal Cavaco Silva (from 2006). Head of government: Prime Minister Jose Socrates (from 2005). Capital: Lisbon. Official language: Portuguese. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 euro (€) = 100cents; valuation(1 Jul 2008) US$1 = €0.63.
Demography
Urban 57.6%. Sex distribution (2005): male 48.40%; female 51.60%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 15.7%; 15-29, 20.4%; 30-44, 22.6%; 45-59, 19.2%; 60-74, 14.8%; 75-84, 5.9%; 85 and over, I.4%. Ethnic composition (2000): Portuguese 91.9%; mixed-race people from Angola, Mozambique, and Cape Verde 1.6%; Brazilian 1.4%; Marrano 1.2%; other European 1.2%; Han Chinese 0.9%; other 1.8%. Religious affiliation (2000): Christian 92.4%, of which Roman Catholic 87.4%, independent Christian 2.7%, Protestant 1.3%, other Christian 1.0%; nonreli-gious/atheist 6.5%; Buddhist 0.6%; other 0.5%. Major cities (2001): Lisbon 564,657 (urban agglomeration [2005] 2,761,000); Porto 263,131 (urban agglomeration [2005] 1,309,000); Braga 164,192; Coimbra 148,443; Funchal 103,961. Location: southwestern Europe, borderingSpainand the North Atlantic Ocean.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 10.4 (world avg. 20.3); (2004) within marriage 70.9%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 10.2 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 0.2 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2004): 1.42. Life expectancy at birth (2004-05): male 74.9 years; female 81.4 years.
National economy
Budget (2004). Revenue: €59,636,000,000 (social contributions 30.9%; indirect taxes 28.4%; direct taxes 21.0%). Expenditures: €63,511,000,000 (current expenditure 90.0%; development expenditure 10.0%). Public debt (2006): US$25,000,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): grapes 973,400, tomatoes 922,000, potatoes 577,000, cork (2004) 120,000; livestock (number of live animals) 3,583,000 sheep, 2,344,000 pigs, 1,441,000cattle; roundwood (2005) II,106,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 5%; fisheries production (2005) 218,242 (from aquaculture 3%). Mining and quarrying (2005): marble 800,000; kaolin 160,000; copper (metal content) 89,541. Manufacturing (value added in US$000,000; 2003): food products 2,148; cement, tiles, and ceramics 1,611; fabricated metals 1,536. Energy production (con-sumption):electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 45,105,000,000 (51,586,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) none (5,514,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) none (93,100,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 11,369,000 (12,377,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) none (3,938,000,000). Population economically active (2006): total 5,587,300; activity rate of total population 52.5% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 73.9%; female 46.6%; unemployed 7.7%). Gross national income (at current market prices; 2006): US$188,263,000,000 (US$17,800 per capita). Households. Average household size (2004) 3.0; average annual household income (2001): €15,512 (US$13,881); sources of income (1995): wages and salaries 44.4%, self-employment 23.4%, transfers 22.2%; expenditure (2003): food and nonalcoholic beverages 18.7%, transportation 16.3%, housing and energy 10.7%, restaurants and hotels 10.0%, clothing and footwear 7.1%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 7,893; remittances (2006) 3,329; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 4,421. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 3,073; remittances (2006) 1,386; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 4,649. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 17.6%, in permanent crops 8.4%, in pasture 15.6%; overall forest area (2005) 41.3%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004): €40,293,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 20.0%; road vehicles 12.4%; chemical products 11.4%; food products 10.0%; crude petroleum 6.8%). Major import sources: Spain 29.3%; Germany 14.3%; France 9.3%; Italy 6.1%; UK 4.6%. Exports (2004): €26,220,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 18.5%; road vehicles and parts 13.9%; apparel and accessories 9.7%; chemical products 6.7%; fabrics and made-up articles 5.3%; footwear 4.6%). Major export destinations: Spain 24.9%; France 14.0%; Germany 13.5%; UK 9.6%; US 6.1%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2004): length 2,836 km; pas-senger-km 3,217,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 2,588,000,000. Roads (2004): total length 78,470 km (paved [1999] 86%). Vehicles (2003): passenger cars 4,918,310; trucks and buses 372,179. Air transport (2006; TAP, Portugalia, and SATA domestic and international airlines only): passenger-km 18,688,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 293,549,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 680,000 (65); televisions (2003): 4,312,000 (413); telephone landlines (2006): 4,231,000 (401); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 12,226,000 (1,160); personal computers (2005): 1,406,000 (133); total Internet users (2006): 3,213,000 (305); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 1,460,000 (137).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2002). Percentage of population ages 25-64 having: no formal schooling through complete primary 67%; complete lower secondary 13%; complete upper secondary 11%; higher 9%. Literacy (2002): total population ages 15 and over literate 92.5%; males literate 95.2%; females literate 90.3%. Health: physicians (2004) 35,312 (1 per 297 persons); hospital beds (2005) 37,330(1 per 283 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 3.3. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,635 (vegetable products 72%, animal products 28%).
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 43,960 (army 60.7%, navy 22.8%, air force 16.5%); US troops (2006) 940. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 2.3%; per capita expenditure US$398.
Background
Celtic peoples settled the Iberian peninsula in the 1st millennium bc. They were conquered about 140 bc by the Romans, who ruled until the 5th century ad, when the area was invaded by Germanic tribes. A Muslim invasion in 711 left only the northern part of Portugal in Christian hands. In 1139 it became the kingdom of Portugal and expanded as it reconquered the Muslim-held sectors. The boundaries of modern continental Portugal were completed in 1270 under King Afonso III. In the 15th and 16th centuries the monarchy encouraged exploration that took Portuguese navigators to Africa, India, Indonesia, China, the Middle East, and South America, where colonies were established. Antonio de Oliveira Salazar ruled Portugal as a dictator in the mid-20th century; he died in office in 1970, and his successor was ousted in a coup in 1974. A new constitution was adopted in 1976 (revised 1982), and civilian rule resumed. Portugal was a charter member of NATO and is a member of the European Union.
Recent Developments
Portugal saw modest economic growth in 2007, and efforts continued to rein in spending and reduce the swollen budget deficit. GDP grew by 4.9% for the year, held back a bit by rising interest rates and market turmoil in the US and in some other EU countries. Inflation was relatively cool at 2.5%, though unemployment had crept up to a multiyear high of 8.0%. Portugal also focused on alternative- and renewable-energy projects, with the aim to put Portugal at the forefront of the EU in reducing carbon-dioxide emissions. In March the world’s largest photovoltaic generating site, with a capacity of some 11 MW, opened near Serpa in the sunny Alentejo region, and plans were afoot to build more solar facilities, expand the country’s wind farms, and launch a prototype wave-power facility off the Atlantic coast. In May 2008 Portugal’s parliament voted to approve a radical, controversial set of changes to the Portuguese language to reflect the spellings of the hundreds of millions of Portuguese speakers in Brazil, Angola, and elsewhere.
Puerto Rico
Official name: Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico (Spanish); Commonwealth of Puerto Rico (English). Political status: self-governing commonwealth in association with the US, with two legislative houses (Senate [27]; House of Representatives [51]). Chief of state: US President George W. Bush (from 2001).
Head of government: Governor Anfbal Acevedo Vila (from 2005). Capital: San Juan. Official languages: Spanish; English. Monetary unit: 1 US dollar (US$) = 100 cents.
Demography
Area: 3,515 sq mi, 9,104 sq km. Population (2007): 3,967,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 1,129, persons per sq km 435.7. Urban (2003): 96.7%. Sex distribution (2005): male 48.04%; female 51.96%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 22.0%; 15-29, 22.8%; 30-44, 20.1%; 45-59, 17.8%; 60-74, 11.9%; 75-84, 4.0%; 85 and over, 1.4%. Ethnic composition (2000): local white 72.1%; black 15.0%; mulatto 10.0%; US white 2.2%; other 0.7%. Religious affiliation (2000): Roman Catholic 74%; Protestant 13%; independent Christian 6%; Jehovah’s Witness 2%; nonreligious/atheist 2%; Spiritist 1%; other 2%. Major metropolitan areas (2006): San Juan 2,590,824; Aguadilla 333,408; Ponce 263,799; San German 144,595; Yauco 123,441. Location: island in the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 12.8 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 7.7 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.91. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 74.5 years; female 82.5 years.
National economy
Budget. Revenue (2005): US$12,444,000,000 (tax revenue 60.8%, of which income taxes 44.2%, excise taxes 14.7%; federal grants 26.7%; nontax revenue 12.5%). Expenditures (2002): US$10,556,400,000 (2001; welfare 22.3%; education 22.3%; public safety 15.7%; debt service 9.8%; health 9.2%). Public debt (December 2005): US$42,449,000,000. Production (in metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): plantains 76,350, bananas 52,200, oranges 18,770; livestock (number of live animals) 376,925 cattle, 48,679 pigs; fisheries production (2005) 2,968 (from aquaculture 14%). Mining (2004): crushed stone 8,660. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2001): chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and allied products 17,365; nonelectrical machinery 3,320; professional and scientific equipment 1,874. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2006) 24,900,000,000 (20,600,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2002) none (176,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2005) none (70,809,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2002) 3,001,000 (6,610,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) none (680,000,000). Gross national income (2006): US$58,418,000,000 (US$14,720 per capita). Population economically active (2006): total 1,420,000; activity rate of total population 35.9% (participation rates: ages 16 and over 47.8%; female [2002] 42.6%; unemployed [August 2007] 11.9%). Households (2002). Average family size 3.6; average annual income per family (2005) US$41,258; sources of income: wages and salaries 49.7%, transfers 30.6%, rent 7.7%, self-employment 6.1%; expenditure (2005): food and beverages 17.1%, health care 16.7%, housing 15.3%, transportation 13.4%, household furnishings 11.5%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2006) 3,369. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 1,143. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 7.8%, in permanent crops 4.7%, in pasture 12.6%; overall forest area (2005) 46.0%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004-05): US$38,905,200,000 (chemicals 43.9%; electronics 9.4%; petroleum and coal products 7.5%; transport equipment 7.2%). Major import sources (2006): US 50.4%; Ireland 18.6%; Japan 4.3%. Exports (2004-05): US$56,543,200,000 (pharmaceutical and chemical products 65.7%; electronic and electrical products 12.5%). Major export destinations (2006): US 82.6%; The Netherlands 3.9%; Belgium 2.4%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2004): length 96 km (privately owned railway for sugarcane transport only). Roads (2005): total length 25,735 km (paved 95%). Vehicles: passenger cars (2001) 2,064,100; trucks and buses (1999) 306,600. Air transport (2001): passenger arrivals and departures 9,396,306; cargo loaded and unloaded (Luis Munoz Marin International Airport only) 215,603 metric tons. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 541,000 (139); televisions (2000): 1,290,000 (338); telephone landlines (2005): 1,038,000 (262); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 3,354,000 (848); personal computers (2005): 33,000 (8.3); total Internet users (2005): 916,000 (232).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2000). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling to lower secondary education 25.4%; some upper secondary to some higher 56.3%; undergraduate or graduate degree 18.3%. Literacy (2002): total population ages 15 and over literate 94.1%. Health: physicians (2001) 7,623 (1 per 504 persons); hospital beds (2002) 12,351 (1 per 312 persons); infant mortality rate (2006) 9.1.
Military
Total active duty US personnel (2006): 198.
Puerto Rico is a commonwealth in free association with the United States; its residents are US citizens. According to the constitution of 1952. executive power resides in the governor, who is elected directly for a term of four years.
Background
Puerto Rico was inhabited by Arawak Indians when it was settled by the Spanish in the early 16th century. It remained largely undeveloped economically until the late 18th century. After 1830 it gradually developed a plantation economy based on the export crops of sugarcane, coffee, and tobacco. The independence movement began in the late 19th century, and Spain ceded the island to the US in 1898, after the Spanish-American War. In 1917 Puerto Ricans were granted US citizenship, and in 1952 the island became a commonwealth with autonomy in internal affairs. The question of Puerto Rican statehood has been a political issue, with commonwealth status approved by voters in 1967, 1993, and 1998.
Recent Developments
Puerto Rican Gov. Anibal Acevedo Vila was indicted in March 2008 on 19 counts stemming from financial dealings in three political campaigns. He denied the charges of illegal fundraising and election fraud.
Qatar
Official name: Dawlat Qatar (State of Qatar). Form of government: constitutional emirate; Islamic law is the basis of legislation in the state. Head of state and government: Emir Sheikh Hamad ibn Khalifah al-Thani (from 1995), assisted by Prime Minister Sheikh Hamad ibn Jassim ibn Jabr al-Thani (from 2007). Capital: Doha. Official language: Arabic. Official religion: Islam. Monetary unit: 1 riyal (QR) = 100 dirhams; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = QR 3.64.
Demography
Area: 4,184 sq mi, 10,836 sq km. Population (2007): 841,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 201.0, persons per sq km 77.6. Urban (2005): 95.4%. Sex distribution (2005): male 67.15%; female 32.85%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 21.8%; 15-29, 25.5%; 30-44, 33.7%; 45-59, 16.3%; 60-74, 2.4%; 75 and over, 0.3%. Ethnic composition (2000): Arab 52.5%, of which Palestinian 13.4%, Qatari 13.3%, Lebanese 10.4%, Syrian 9.4%; Persian 16.5%; Indo-Pakistani 15.2%; black African 9.5%; other 6.3%. Religious affiliation (2000): Muslim 83%, of which Sunni 73%, Shi’i 10%; Christian 10%, of which Roman Catholic 6%; Hindu 3%; Buddhist 2%; nonreligious 2%. Major cities (2004): Al-Dawhah (Doha) 339,847; Al-Rayyan 258,193; Al-Wakrah 26,993; Umm Salal Muhammad 25,413; Al-Khawr 18,036. Location: the Middle East, bordering the Persian Gulf and Saudi Arabia.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 18.0 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 2.1 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 2.80. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 74.4 years; female 75.8 years.
National economy
Budget (2005-06). Revenue: QR 64,984,000,000 (oil and natural gas revenue 67.1%; investment income 21.9%; other 11.0%). Expenditures:QR 50,833,000,000 (current expenditure 64.4%; capital expenditure 35.6%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): dates 19,844, tomatoes 5,328, cantaloupes and other melons 4,909; livestock (number of live animals) 152,700 goats, 111,500 sheep, 13,800 camels; fisheries production 13,946. Mining and quarrying (2005): limestone 1,000,000; gypsum, sand and gravel, and clay are also produced. Manufacturing (value added in qR ’000,000; 2005): refined petroleum products 4,502; chemical products 2,168; base metals 1,959. Energy production (consumption):electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 14,396,000,000 ([2004] 13,233,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006) 272,600,000 ([2004] 33,585,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 11,286,000 (6,131,000); natural gas (cu m; 2005) 43,500,000,000 ([2004] 16,872,000,000). Households. Average household size (2004) 7.4; expenditure (2001): housing 17.8%, food and beverages 16.3%, transportation 15.8%, household furnishings 8.6%, clothing and footwear 7.1%. Population economically active (2004): total 444,133; activity rate of total population 59.7% (participation rates: ages 15 and over, 77.1%; female 15.1%; unemployed 1.5%). Gross national income (2006): US$54,259,000,000 (US$66,060 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 760; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 843. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 1,759; remittances (2006-07) 5,000; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 108. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 1.6%, in permanent crops 0.3%, in pasture 4.5%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): QR 36,621,000,000 (nonelectrical machinery and apparatus 22.3%; road vehicles 14.0%; electrical machinery and apparatus 11.2%; iron and steel 11.0%; chemical products 6.7%). Major import sources (2006): Japan 12.0%; US 9.9%; Germany 9.3%; Italy 9.3%; UAE 6.0%. Exports (2005): QR 92,234,000,000 (crude petroleum and refined petroleum 55.9%; natural gas 34.4%; manufactured fertilizers 2.7%; plastics 2.4%). Major export destinations (2006): Japan 42.0%; South Korea 14.1%; Singapore 9.5%; India 4.9%; UAE 3.9%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (1999): total length 1,230 km (paved 90%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 265,609; trucks and buses 114,115. Air transport (2006; Qatar Airways only): passenger-km 24,032,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 888,498,000.
Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 143,000 (180); televisions (2004): 315,000 (412); telephone landlines (2006): 228,000 (272); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 920,000 (1,096); personal computers (2005): 145,000 (182); total Internet users (2006): 290,000 (346); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 47,000 (56).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2004). Percentage of population ages 10 and over having: no formal education/unknown 34.9%, of which illiterate 10.2%; primary 13.0%; preparatory (lower secondary) 16.2%; secondary 20.0%; postsecondary 15.9%. Literacy (2004): total population ages 15 and over literate 89.0%; males literate 89.1%; females literate 88.6%. Health (2005): physicians (public sector only) 1,657 (1 per 480 persons); hospital beds (public sector only) 1,567 (1 per 508 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 9.0.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 12,400 (army 68.6%, navy 14.5%, air force 16.9%); US troops (2006) 430. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 6.2%; per capita expenditure US$2,751.
Background
Qatar was partly controlled by Bahrain in the 18th and 19th centuries and was part of the Ottoman Empire until World War I. In 1916 it became a British protectorate. Oil was discovered in 1939, and the country rapidly modernized. Qatar declared independence in 1971, when the British protectorate ended. In 1991 it served as a base for air strikes against Iraq in the Persian Gulf War.
Recent Developments
Economic highlights in Qatar in 2007 included the ongoing success of state-owned Qatar Airways, which garnered international awards for superior service, and Qatar National Bank, which again received the highest possible credit rating from the world’s leading rating institutions. Qatar’s continued meteoric expansion as one of the world’s most important producers and exporters of liquefied natural gas and gas-to-liq-uids fuels, combined with record-high oil revenues, underscored the country’s expanded role as a major center of international modernization and project financing, and, increasingly, industrialization and economic integration in the Persian Gulf.
Reunion
Official name: Departement de la Reunion (Department of Reunion). Political status: overseas department of France with two legislative houses (General Council [49]; Regional Council [45]). Chief of state: French President Nicolas Sarkozy(from 2007). Head of government: Prefect Pierre-Henry Maccioni (from 2006). Capital: Saint-Denis. Official language: French. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 euro (€) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = €0.63 (the euro replaced the French franc [F] 1 Jan 2002, at the rate of €1 = 6.56 F).
Demography
Area: 968 sq mi, 2,507 sq km. Population (2007): 799,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 825.4, persons per sq km 318.7. Urban (2005): 92.4%. Sex distribution (2003): male 49.12%; female 50.88%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 27.3%; 15-29, 23.7%; 30-44, 24.1%; 45-59, 15.1%; 60-74, 7.3%; 75-84, 2.0%; 85 and over, 0.5%. Ethnic composition (2000): mixed race (black-white-South Asian) 42.6%; local white 25.6%; South Asian 23.0%, of which Tamil 20.0%; Chinese 3.4%; East African 3.4%; Malagasy 1.4%; other 0.6%. Religious affiliation (2000): Christian 87.8%, of which Roman Catholic 81.8%, Pentecostal 4.2%; Hindu 4.5%; Muslim 4.2%; nonreligious 1.7%; other 1.8%. Major cities (2004; population of commune): Saint-Denis 133,600 (urban agglomeration [2003] 178,000); Saint-Paul 92,500; Saint-Pierre 74,000 (urban agglomeration 140,600); Le Tampon 66,600; Saint-Louis (1999) 43,519. Location: island in the western Indian Ocean, east of Madagascar and near Mauritius.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 19.0 (world avg. 20.3); within marriage 33.0%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 5.6 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 2.42. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 72.3 years; female 80.1 years.
National economy
Budget (2003). Revenue: €750,000,000 (receipts from the French central government and local administrative bodies 50.0%; indirect taxes 20.0%; direct taxes 9.2%; loans 7.3%). Expenditures: €729,000,-000 (current expenditures 68.6%; development expenditures 31.4%). Gross domestic product (2005): US$14,910,000,000 (US$19,130 per capita). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): sugarcane 2,000,000, corn (maize) 11,700, pineapples 10,550, geranium essence (2005) 1.9; livestock (number of live animals) 77,118 pigs, 36,210 cattle, 36,141 goats; roundwood (2005) 36,100 cu m, of which fuelwood 86%; fisheries production (2005) 4,757 (from aqua-culture 3%). Mining and quarrying: gravel and sand for local use. Manufacturing (value added in F ’000,000; 1997): food and beverages 1,019, of which meat and milk products 268; construction materials (mostly cement) 394; fabricated metals 258. Energy production (consumption):electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 1,620,000,000 (1,620,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2005) none (721,000). Population economically active (2006): total 321,700; activity rate of total population 40.8% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 60.9%; female [2005] 43.4%; unemployed [April-June 2006] 29.1%). Households. Average household size (2004) 3.0; average annual income per capita of household (2003) €11,446 (US$14,456); sources of income (1997): wages and salaries and self-employment 41.8%, transfer payments 41.3%; expenditure (2001): housing and energy 24.0%, transportation and communications 20.0%, food and beverages 17.0%, recreation and culture 10.0%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 384. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 14%, in permanent crops 2%, in pasture 5%; overall forest area (2005) 34%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006): €3,911,679,000 (machinery and equipment 18.4%; food and agricultural products 16.2%; transport equipment 13.2%; mineral fuels 12.1%; chemicals and chemical products 10.9%). Major import sources: France 42.2%; Singapore 8.6%; China 4.0%; Germany 3.8%; Italy 3.2%. Exports (2006): €238,039,000 (food products 69.8%, of which sugar 41.0%; machinery and apparatus 9.3%; transportation equipment and parts 7.6%). Major export destinations: France 59.6%; Mayotte 8.0%; Japan 5.3%; Madagascar 5.2%; Mauritius 3.0%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2001): total length 1,214 km (paved [1991] 79%). Vehicles (1999): passenger cars 190,300; trucks and buses 44,300. Air transport (Air Austral only): passenger-km (2006) 2,859,000,000; metric ton-km cargo (2005) 48,547,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 74,000 (95); televisions (2002): 138,000 (185); telephone landlines (2001): 300,000 (410); cellular telephone subscribers (2004): 579,000 (753); personal computers (2004): 278,000 (351); total Internet users (2005): 220,000 (282); broadband Internet subscribers (2004): 57,000 (74).
Education and health
Educational attainment (1999). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling through incomplete secondary education 83.0%; complete secondary 7.4%; some higher 3.9%; complete higher 5.7%. Literacy (2003): total population ages 15 and over literate 88.9%; males literate 87.0%; females literate 90.8%. Health (2005): physicians 1,902 (1 per 413 persons); hospital beds 2,674 (1 per 295 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2004) 6.8.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2004): 3,600 French army and navy personnel.
Background
The island of Reunion was settled in the 17th century by the French, who brought slaves from eastern Africa to work on coffee and sugar plantations there. It was a French colony until 1946, when it became an overseas territory of France. Its economy is based almost entirely on the export of sugar.
Recent Developments
Reunion’s economy rebounded in 2007 from the effects of an outbreak of chikungunya, a usually nonfatal viral disease spread by mosquitoes. In 2007, 380,500 tourists visited the island, a 36.5% increase from the year before.
Romania
Official name: Romania. Form of government: unitary republic with two legislative houses (Senate [137]; Assembly of Deputies [332]). Chief of state: President Traian Basescu (from 2004). Head of government: Prime Minister Calin Popescu Tariceanu (from 2004). Capital: Bucharest. Official language: Romanian. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Romanian (new) leu (plural lei) = 100 bani; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = 2.30 (new) lei (the leu was re-denominated 1 Jul 2005, at the rate of 1 [new] leu [RON] = 10,000 [old] lei [ROL]).
Demography
Area: 92,043 sq mi, 238,391 sq km. Population (2007): 21,549,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 234.1, persons per sq km 90.4. Urban (2005): 53.7%. Sex distribution (2005): male 48.71%; female 51.29%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 15.7%; 15-29, 23.8%; 30-44, 21.5%; 45-59, 19.7%; 60-74, 13.8%; 75-84, 4.8%; 85 and over, 0.7%. Ethnic composition (2002): Romanian 89.5%; Hungarian 6.6%; Rom (Gypsy) 2.5%; Ukrainian 0.3%; German 0.3%; other 0.8%. Religious affiliation (2002): Romanian Orthodox 86.7%; Protestant 6.3%; Roman Catholic 4.7%; Greek Catholic 0.9%; Muslim 0.3%; other 1.1%. Major cities (2004): Bucharest 1,927,559; Iasi 317,812; Constanta 307,447; Timisoara 307,265; Galati 298,941. Location: southeastern Europe, bordering Ukraine, Moldova, the Black Sea, Bulgaria, Serbia, and Hungary.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 10.2 (world avg. 20.3); (2005) within marriage 71.5%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 12.0 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.32. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 68.2 years; female 75.4 years.
National economy
Budget (in ROL ’000,000,000,000; 2004). Revenue: 322.0 (VAT 35.0%; excise tax 24.7%; tax on profits 20.0%). Expenditures: 340.7 (economic affairs 26.7%; social assistance 14.0%; police 11.9%; defense 10.5%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$13,341,000,000. Population economically active (2006): total 10,041,600; activity rate of total population 46.5% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 63.7%; female 45.0%; unemployed 7.3%). Households. Average household size (2003) 2.8; average annual income per household (2004) ROL 130,295,388 (US$3,992); sources of income (2003): wages and salaries 44.8%, nonmonetary equivalent for consumption of own agricultural produce 23.4%, transfers 19.2%; expenditure (2004): food and nonalcoholic beverages 46.4%; housing and energy 14.7%; clothing and footwear 6.3%. Production (metric tons). Agriculture (2005): corn (maize) 10,388,000, wheat 7,341,000, potatoes 3,739,000, sunflower seed 1,341,000; livestock (number of live animals) 7,425,000 sheep, 6,495,000 pigs, 2,808,000 cattle; roundwood 14,501,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 20%; fisheries production 13,352 (from aquaculture 55%). Mining (2005): copper (metal content) 14,868; zinc (metal content) 13,784; lead (metal content) 11,610. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2004): wearingapparel 1,015; iron and steel 883; food products 782. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2006) 61,829,000,000 ([2004] 55,321,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2004) negligible (3,025,000); lignite (metric tons; 2006) 32,400,000 ([2004] 32,600,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006) 35,900,000 ([2004] 94,100,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 11,512,000 (8,705,000); natural gas (cu m; 2006) 10,231,000,000 ([2004] 16,269,000,000). Gross national income (2006): US$118,368,000,000 (US$5,500 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 1,044; remittances (2006) 4,733; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 3,484. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 878; remittances (2006) 34; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 19. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 40.8%, in permanent crops 2.0%, in pasture 21.6%; overall forest area (2005) 27.7%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004; f.o.b. in trading partners and c.i.f. in commodities): US$32,664,000,000 (chemicals and chemical products 10.4%; textile yarn and fabrics 10.2%; nonelectrical machinery 10.0%; road vehicles 8.0%; electrical machinery 7.8%; petroleum [all forms] 7.2%). Major import sources (2005): Italy 15.5%; Germany 14.0%; Russia 8.3%; France 6.8%; Turkey 4.9%. Exports (2004): US$23,485,000,000 (clothing and accessories 20.1%; iron and steel 9.2%; electrical machinery and parts 7.9%; nonelectrical machinery and parts 7.1%; footwear 6.4%; petroleum products 6.1%). Major export destinations (2005): Italy 19.4%; Germany 14.0%; Turkey 7.9%; France 7.4%; UK 5.5%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2004): route length (2003) 11,053 km; passenger-km 8,638,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 17,022,000,000. Roads (2004; public roads only): length 79,454 km (paved 26%). Vehicles (2004): cars 3,225,367; trucks and buses 525,617. Air transport (2006; TAROM, Carpatair, Blue Air, and Romavia airlines only): passenger-km 2,306,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 4,981,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 1,148,000 (53); televisions (2003): 15,150,000 (697); telephone landlines (2006): 4,204,000 (195); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 17,400,000 (806); personal computers (2005): 2,800,000 (129); total Internet users (2006): 7,000,000 (324); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 1,769,000 (82).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2002). Percentage of population ages 10 and over having: no formal schooling 5.5%; primary education 20.1%; lower secondary 27.6%; upper secondary/vocational 36.7%; higher vocational 3.0%; university 7.1%. Literacy (2004): total population ages 15 and over literate 97.3%; males literate 98.4%; females literate 96.3%. Health (2004): physicians 48,150 (1 per 450 persons); hospital beds 142,029 (1 per 153 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 15.0.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 69,600 (army 59.3%, navy 10.5%, air force 15.1%, other 15.1%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 2.0%; per capita expenditure US$90.
The Transylvanian Alps are a mountainous region of south-central Romania. It consists of that section of the Carpathian Mountain arc from the Prahova River valley (east) to the gap in which flow the Timis and Cerna rivers.
Background
Romania was formed in 1862 by the unification of the principalities Moldavia and Walachia, which had once been part of the ancient country of Dacia. During World War I, Romania sided with the Allies and doubled its territory in 1918 with the addition of Transylvania, Bukovina, and Bessarabia. Allied with Germany in World War II, it was occupied by Soviet troops in 1944 and became a satellite country of the USSR in 1948. During the 1960s Romania’s foreign policy was frequently independent of the Soviet Union’s. The communist regime of Nicolae Ceausescu was overthrown in 1989, and free elections were held in 1990. Throughout the 1990s Romania struggled with rampant corruption and organized crime as it tried to stabilize its economy.
Recent Developments
Romania joined the European Union on 1 Jan 2007. With its membership came both benefits and difficulties. The country’s GDP grew 17.5% in 2007, and its industrial output increased by 5.4%. The rate of registered unemployment dropped from 5.2% in 2006 to 4.1%, and the average monthly wage increased as well. Relations with neighboring Moldova, the poorest country in Europe and until World War II a part of Romania, remained strained. After Romania’s entrance into the EU, hundreds of thousands of Moldovans, eager for better financial opportunities, took advantage of existing Romanian laws to apply for joint Ro-manian-Moldovan citizenship. Moldova accused Romania of attempting to undermine its national security by luring away its people, while Romania, which itself was the poorest member of the EU, struggled with the social and economic costs of an influx in population.
Russia
Official name: Rossiyskaya Federatsiya (Russian Federation). Form of government: federal multiparty republic with two legislative houses (Federation Council [172]; State Duma [450]). Head of state: President Dmitry Medvedev (from 2008). Head of government: Prime Minister Vladimir Putin (from 2008). Capital: Moscow. Official language: Russian. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 ruble (RUB) = 100 kopecks; valuation (1 Jul 2008) market rate, US$1 = RUB 23.42.
Demography
Area: 6,592,800 sq mi, 17,075,400 sq km. Population (2007): 141,378,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 21.4, persons per sq km 8.3. Urban (2006): urban 73.0%. Sex distribution (2004): male 46.49%; female 53.51%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 14.9%; 15-29, 24.7%; 30-44, 21.5%; 45-59, 21.9%; 60-69, 8.4%; 70 and over, 8.6%. Ethnic composition (2002): Russian 79.82%; Tatar 3.83%; Ukrainian 2.03%; Bashkir 1.15%; Chuvash 1.13%; Chechen 0.94%; Armenian 0.78%; Mordvin 0.58%; Belarusian 0.56%; Avar 0.52%; Kazakh 0.45%; Udmurt 0.44%; Azerbaijani 0.43%; Mari 0.42%; German 0.41%; Kabardinian 0.36%; Osset-ian 0.35%; Dargin 0.35%; Buryat 0.31%; Sakha 0.31%; other 4.83%. Religious affiliation (2005): Christian 58.4%, of which Russian Orthodox 53.1%, Roman Catholic 1.0%, Ukrainian Orthodox 0.9%, Protestant 0.9%; Muslim 8.2%; traditional beliefs 0.8%; Jewish 0.6%; nonreligious 25.8%; atheist 5.0%; other 1.2%. Major cities (2005): Moscow 10,425,075; St. Petersburg 4,580,620; Novosibirsk 1,397,015; Yekaterinburg 1,308,441; Nizhny Novgorod 1,283,553; Samara 1,143,346; Omsk 1,138,822; Kazan 1,112,673; Chelyabinsk I,092,958; Rostov-na-Donu 1,054,865. Location: eastern Europe and northern Asia, bordering the Arctic Ocean, the Pacific Ocean, North Korea, China, Mongolia, Kazakhstan, the Caspian Sea, Azerbaijan, Georgia, the Black Sea, Ukraine, Belarus, Latvia, Estonia, Finland, and Norway; the exclave of Kaliningrad on the Baltic Sea borders Lithuania and Poland. Migration (2006): immigrants 186,380; emigrants 54,061. Refugees (2002): 828,784, of which from Kazakhstan 301,137, Uzbekistan 106,299, Tajikistan 86,041, Georgia 62,868. Households (2004). Total households 51,209,000; average household size 2.8; distribution by size (1995): 1 person 19.2%; 2 persons 26.2%; 3 persons 22.6%; 4 persons 20.5%; 5 persons or more II.5%.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 10.3 (world avg. 20.3); (2005) within marriage 70.0%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 15.2 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): -4.9 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 1.38. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 58.9 years; female 72.4 years.
Social indicators
Educational attainment (2002). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: no formal schooling 2.1%; primary education 7.7%; some secondary 18.1%; complete secondary/basic vocational 53.0%; incomplete higher 3.1%; complete higher 16.0%, of which advanced degrees 0.3%. Quality of working life (2006). Average workweek (2004) 40 hours. Annual rate per 100,000 workers of: injury or accident 290; industrial illness 16.0; death 11.8. Average working days lost to labor strikes per 1,000 employees 0.2. Social participation. Trade union membership in total workforce (2003) 45%. Social deviance. Offense rate per 100,000 population (2006) for: murder and attempted murder 19.4; rape and attempted rape 6.3; serious injury 36.2; theft 1,180.4. Incidence per 100,000 population of: alcoholism (1992) 1,727.5; substance abuse (2000) 25.6; suicide (2006) 30.0. Material well-being (2002). Durable goods possessed per 100 households: automobiles 27; personal computers 7; television receivers 126; refrigerators and freezers 113; washing machines 93; VCRs 50; motorcycles 26; bicycles 71.
National economy
Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$75,359,000,000. Budget (2006). Revenue: RUB 6,276,300,000,000 (VAT 24.1%; taxes on natural resources 17.8%; corporate taxes 8.1%; single social tax 5.0%). Expenditures: RUB 4,281,300,000,000 (transfers 21.4%; defense 15.9%; social and cultural services 14.4%; law enforcement 12.9%; debt service 3.9%). Gross national income (2006): US$956,557,000,000 (US$6,679 per capita). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): wheat 45,006,300, potatoes 38,572,640, sugar beets 30,861,230, barley 18,153,550, sunflower seeds 6,752,860, oats 4,880,270, cabbages 4,073,240, corn (maize) 3,668,560, rye 2,965,060, tomatoes 2,414,860, carrots and turnips 1,918,370, onions 1,788,750, apples 1,617,000, cucumbers 1,423,210, peas 1,157,640; livestock (number of live animals) 21,473,926 cattle, 16,074,449 sheep, 13,454,876 pigs; roundwood (2005) 186,500,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 25%; fisheries production (2005) 3,305,698 (from aquaculture 3%); aquatic plants production (2005) 50,507. Mining and quarrying (2005): nickel (metal content) 315,000 (world rank: 1); mica 101,500 (world rank: 1); platinum-group metals 123,000 (world rank: 2); gem diamonds 21,400,000 carats (world rank: 2); industrial diamonds 10,400,000 carats (world rank: 3); vanadium (metal content) 9,000 (world rank: 3); iron ore (metal content; 2004) 56,200,000 (world rank: 5); cobalt 5,000 (world rank: 5); copper ore (metal content) 675,000 (world rank: 6); gold 165,000 kg (world rank: 6); tin (metal content) 3,000 (world rank: 7); molybdenum (metal content) 3,000 (world rank: 7). Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2004): refined petroleum products 14,329; iron and steel 11,801; food products 8,933; chemicals and chemical products 7,709; nonferrous base metals 7,600; beverages 4,446; transportation equipment 4,255; general purpose machinery 3,369; cement, bricks, and ceramics 3,266; fabricated metal products 1,949; wood products (excluding furniture) 1,922; printing and publishing 1,648; paper products 1,508; textiles and wearing apparel 1,374; rubber products 1,359; electrical equipment 1,165; tobacco products 1,055. Energy production (consumption):electricity (kW-hr; 2006-07) 989,017,000,000 ([2005] 940,000,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2006-07) 237,700,000 ([2004] 144,978,000); lignite (metric tons; 2006-07) 70,300,000 ([2004] 75,460,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006-07) 3,482,900,000 ([2005] 1,022,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 175,486,000 (94,312,000); natural gas (cu m; 2006-07) 865,524,000,000 ([2005] 402,100,000,000). Population economically active (2006): total 74,146,000; activity rate of total population 52.0% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 73.0%; female 49.4%; unemployed 7.2%). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 7.5%, in permanent crops 0.1%, in pasture 5.6%; overall forest area (2005) 47.9%. Households. Average household size (2004) 2.8; income per household: RUB 52,400 (US$1,692); sources of monetary income (2006): wages 66.4%, transfers 13.2%, self-employment 11.2%, property income 7.2%; expenditure (2002): food 41.7%, clothing 13.3%, housing 6.2%, furniture and household appliances 5.7%, alcohol and tobacco 3.2%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 5,466; remittances (2006) 3,308; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 8,842. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 17,804; remittances (2006) 11,438; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 8,541.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; c.i.f.): US$137,548,000,000 (machinery, apparatus, and transportation equipment 47.7%; chemicals and chemical products 15.8%; food, beverages, and tobacco 15.7%; nonferrous metals and iron and steel 7.7%). Major import sources: Germany 13.4%; China 9.4%; Ukraine 6.7%; Japan 5.7%; Belarus 5.0%; US 4.7%; France 4.3%; Italy 4.2%; Kazakhstan 2.8%. Exports (2006; f.o.b.): US$301,976,000,000 (fuels and lubricants 65.9%; nonferrous metals and iron and steel 16.4%; machinery, apparatus, and transportation equipment 5.8%; chemicals and chemical products 5.6%). Major export destinations: The Netherlands 11.9%; Italy 8.3%; Germany 8.1%; China 5.2%; Ukraine 5.0%; Turkey 4.8%; Belarus 4.3%; Switzerland 4.0%; Poland 3.8%; UK 3.4%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2005): length (2006) 85,000 km; passenger-km 171,600,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 1,858,000,000,000. Roads (2006): total length 854,000 km (paved 85%). Vehicles (2002): passenger cars 22,342,000; trucks and buses (1999) 5,021,000. Air transport (2006-07): passen-ger-km 97,510,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 2,980,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 15,075,000 (105); televisions (2003): 50,599,000 (351); telephone landlines (2005): 40,100,000 (281); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 120,000,000 (840); personal computers (2005): 17,400,000 (121); total Internet users (2006): 25,689,000 (181); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 2,900,000 (20).
Education and health
Health (2005): physicians 690,000 (1 per 206 persons); hospital beds 1,575,000 (1 per 90 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 10.2. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,363 (vegetable products 79%, animal products 21%); 170% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 1,027,000 (army 38.5%, navy 13.8%, air force 15.6%, strategic deterrent forces 7.8%, command and support 24.3%); an additional 415,000 personnel in paramilitary forces include railway troops, special construction troops, federal border guards, interior troops, and other federal guard units. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 4.1%; per capita expenditure US$217.
Background
The region between the Dniester and Volga rivers was inhabited from ancient times by various peoples, including the Slavs. The area was overrun from the 8th century bc to the 6th century ad by successive nomadic peoples, including the Sythians, Sarmatians, Goths, Huns, and Avars. Kievan Rus, a confederation of principalities ruled from Kiev, emerged c. the 10th century. It lost supremacy in the 11th and 12th centuries to independent principalities, including Novgorod and Vladimir. Novgorod ascended in the north and was the only Russian principality to escape the domination of the Mongol Golden Horde in the 13th century. In the 14th-15th centuries the princes of Moscow gradually overthrew the Mongols. Under Ivan IV, Russia began to expand. The Romanov dynasty arose in 1613. Expansion continued under Peter I (the Great) and Catherine II (the Great). The area was invaded by Napoleon in 1812; after his defeat, Russia received most of the grand duchy of Warsaw (1815). Russia annexed Georgia, Armenia, and other Caucasus territories in the 19th century. The Russian southward advance against the Ottoman Empire was of key importance to Europe. Russia was defeated in the Crimean War. It sold Alaska to the US in 1867. Russia’s defeat in the Russo-Japanese War led to an unsuccessful uprising in 1905. In World War I it fought against the Central Powers.
The Russian Revolution that overthrew the czarist regime in 1917 marked the beginning of a government of soviets (councils). The Bolsheviks brought the main part of the former empire under communist control and organized it as the Russian Soviet Federated Socialist Republic (RSFSR; coextensive with present-day Russia). The Russian SFSR joined other soviet republics in 1922 to form the USSR. Although it fought with the Allies in World War II, after the war tensions with the West led to the decades-long Cold War.
Upon the dissolution of the USSR in 1991, the Russian SFSR was renamed Russia and became the leading member of the Commonwealth of Independent States. It adopted a new constitution in 1993. During the 1990s it struggled on several fronts, beset with economic difficulties, political corruption, and independence movements. Vladimir Putin was elected president in 2000, with economic reform, governmental reorganization, cutbacks in the military, and rooting out corruption and favoritism as his chief goals.
Recent Developments
Russian Pres. Vladimir Putin, Time magazine’s 2007 Person of the Year, was constitutionally barred from running for a third consecutive presidential term in 2008. However, in March 2008 First Deputy Prime Minister Dmitry Medvedev, a Putin protege, won election to succeed him and immediately asked Putin to take the post of prime minister. Many feared that this spelled the continuation of Putin’s hold on power in Russia.
Russia in 2007 recorded its ninth year of strong economic growth. The economy grew 8.1% in 2007, and there were large budget surpluses accompanied by high and rising foreign-exchange reserves. Russia’s overall foreign debt remained modest. High world oil prices and a relatively cheap ruble played key roles in this economic resurgence. Living standards improved, wages rose, and both unemployment and the population living below the official poverty line declined.
International concern grew over the reliability of Russia, which held massive petroleum reserves and one-third of the world’s natural gas reserves, as an energy supplier. In early 2007 Russia briefly suspended crude oil deliveries to Belarus after a dispute in which Gazprom, the state natural gas company, insisted Belarus accept a large increase in the price of Russian gas. In October Gazprom also threatened to cut gas supplies to Ukraine in what some interpreted as a political move following the return to power in Kiev of a Western-leaning administration, and in March 2008 it briefly did cut deliveries before the two sides agreed on a debt-repayment plan.
Relations between Russia and the US grew increasingly strained as the year wore on. Russia strongly objected to US plans to install antimissile defenses in Poland and the Czech Republic, arguing that the installations would undermine Russian national security. In August 2008, Georgian troops entered South Osse-tia, and Russia responded by invading. Several weeks of fighting and Russian occupation ensued, leaving hundreds dead. Russia withdrew most of its forces to the two separatist regions of South Ossetia and Abkhazia by the end of the month, but on 26 August Moscow recognized the independence of both.
Rwanda
Official name: Repubulika y’u Rwanda (Rwanda); Republique Rwandaise (French); Republic of Rwanda (English). Form of government: multiparty republic with two legislative bodies (Senate [26]; Chamber of Deputies [80]). Head of state and government: President Maj. Gen. Paul Kagame (from 2000), assisted by Prime Minister Bernard Makuza (from 2000). Capital: Kigali. Official languages: Rwanda; French; English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Rwanda franc (RF); valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = RF 540.61.
Demography
Area: 10,185 sq mi, 26,379 sq km. Population (2007): 9,725,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 995.0, persons per sq km 384.2. Urban (2006): 23.6%. Sex distribution (2005): male 48.16%; female 51.84%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 43.5%; 15-29, 32.0%; 30-44, 13.4%; 45-59, 7.4%; 60-74, 2.9%; 75-84, 0.7%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Ethnic composition (2002): Hutu 85%; Tutsi 14%; Twa 1%. Religious affiliation (2005): Roman Catholic 44%; Protestant 25%; Muslim 13%; other 18%. Major cities (2002): Kigali (2003) 656,153; Gitarama 84,669; Butare 77,449; Ruhengeri 71,511; Gisenyi 67,766. Location: east-central Africa, bordering Uganda, Tanzania, Burundi, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 40.3 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 15.4 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 24.9 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 5.43. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 47.2 years; female 49.3 years.
National economy
Budget (2004). Revenue: RF 271,900,000,000 (grants 46.2%; taxes on goods and services 25.8%; income tax 13.5%; import and export duties 9.7%). Expenditures:RF 253,300,000,000 (current expenditures 64.7%, of which wages 13.1%, defense 9.4%, debt payment 4.7%; capital expenditure 35.3%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$1,420,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): plantains 2,653,000, potatoes 1,285,000, sweet potatoes 777,000; livestock (number of live animals) 1,339,740 goats, 1,004,100 cattle, 464,330 sheep; roundwood (2005) 5,495,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 91%; fisheries production (2005) 8,186 (from aquaculture 5%). Mining and quarrying (2005): cassiterite (tin content) 700; tungsten (wolframite content) 200; niobium 80,000 kg. Manufacturing (value added in RF ’000,000; 2002): food products, beverages, and tobacco products 61,073; cement, bricks, and ceramics 4,326; chemicals and chemical products 3,201. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 173,000,000 (283,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (169,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 179,000 (179,000). Population economically active (2002): total 3,418,047; activity rate of total population 42.0% (participation rates: ages 6 and over 52.1%; female 55.2%; officially unemployed 0.9%). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 48.6%, in permanent crops 10.9%, in pasture 18.8%; overall forest area (2005) 19.5%. Households. Average household size (2004) 3.4; expenditure (2003): food and nonalcoholic beverages 37.1%, housing and energy 15.8%, transportation 9.9%, household furnishings 7.6%. Gross national income (2006): US$2,295,000,000 (US$242 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2004) 44; remittances (2006) 21; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 5.6; official development assistance (2005) 576. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2004) 31; remittances (2006) 35.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): US$354,180,000 (intermediate goods 31.4%; capital goods 31.0%; energy products 22.1%; food 10.0%). Major import sources (2002): Kenya 21.9%; Germany 8.4%; Belgium 7.9%; Israel 4.3%; US 3.5%. Exports (2005): US$124,980,000 (coffee 30.6%; tea 19.5%; pyrethrum extract 16.2%; tin 14.3%; tantalite 13.5%; gold 3.8%). Major export destinations (2002): Indonesia 30.8%; Germany 14.6%; Hong Kong 8.9%; South Africa 5.5%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2004): total length 14,008 km (paved 19%). Vehicles (2000): passenger cars 10,726; trucks 15,828. Air transport (2000; Kigali airport only): passengers embarked and disembarked 101,000; cargo loaded and unloaded 4,300 metric tons. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2004): 70,000 (7.4); telephone landlines (2006): 17,000 (1.8); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 314,000 (34); personal computers (2005): 19,000 (2.1); total Internet users (2006): 65,000 (7); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 1,700 (0.2).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2000). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal education/unknown 45.5%; incomplete primary education 30.1%; complete primary 14.4%; secondary 9.1%; higher 0.9%. Literacy (2006): percentage of total population ages 15 and over literate 64.9%; males literate 71.4%; females literate 59.8%. Health: physicians (2005) 450 (1 per 19,054 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 87.2. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 1,936 (vegetable products 96%, animal products 4%); 111% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 35,000 (army 91.4%, air force 2.9%, national police 5.7%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 2.9%; per capita expenditure US$7.
Background
Originally inhabited by the Twa, a Pygmy people, Rwanda became home to the Hutu, who were well established there when the Tutsi appeared in the 14th century. The Tutsi conquered the Hutu and in the 15th century founded a kingdom near Kigali. The Belgians occupied Rwanda in 1916, and the League of Nations created Ruanda-Urundi as a Belgian mandate in 1923. The Tutsi retained their dominance until shortly before Rwanda reached independence in 1962, when the Hutu took control of the government and stripped the Tutsi of much of their land. Many Tutsi fled Rwanda, and the Hutu dominated the country’s political system, waging sporadic civil wars until mid-1994, when the death of the country’s leader in a plane crash—apparently shot down—led to massive violence. The Tutsi-led Rwandan Patriotic Front (FPR) took over the country by force after the massacre of almost 500,000 Tutsi by Hutu. Two million refugees, mostly Hutu, fled to neighboring countries after the FPR’s victory.
Recent Developments
Genocide and its aftermath continued to dominate Rwandan domestic and foreign policy in 2007. In February about 8,000 prisoners accused of war crimes, many of them sick or elderly, were released because of prison congestion and calls for greater efforts toward reconciliation. In April Pres. Paul Kagame pardoned former president Pasteur Bizimungu, who had served just under 3 years of his 15-year prison sentence for setting up a militia, inciting ethnic violence, and committing financial fraud. In June the parliament abolished the death penalty, an important step in the country’s efforts to extradite genocide suspects from European countries that had hitherto refused such requests because they objected to capital punishment.
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Official name: Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis. Form of government: federated constitutional monarchy with one legislative house (National Assembly [15]). Chief of state: British Queen Elizabeth II (from 1952), represented by Governor-General Sir Cuthbert Sebastian (from 1996). Head of government: Prime Minister Denzil Douglas (from 1995). Capital: Basseterre. Official language: English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Eastern Caribbean dollar (EC$) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = EC$2.70.
Demography
Area: 104.0 sq mi, 269.4 sq km. Population (2007): 50,400. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 484.6, persons per sq km 187.1. Urban (2005): 33%. Sex distribution (2001): male 49.70%; female 50.30%. Age breakdown (2000): under 15, 30.7%; 15-29, 26.5%; 30-44, 21.1%; 45-59, 10.8%; 60-74, 6.1%; 75-84, 2.9%; 85 and over, 1.9%. Ethnic composition (2000): black 90.4%; mulatto 5.0%; Indo-Pakistani 3.0%; white 1.0%; other/unspecified 0.6%. Religious affiliation (2005): Protestant 75%, of which Anglican 24%, Methodist 23%; Roman Catholic 11%; other 14%. Major towns (2006): Basseterre 12,900; Charlestown 1,500; St. Paul’s 1,200. Location: islands in the Caribbean Sea, between Puerto Rico and Trinidad and Tobago.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 18.1 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 8.5 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 2.33. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 69.3 years; female 75.2 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue: EC$524,600,000 (tax revenue 71.3%, of which taxes on international trade 33.6%, taxes on domestic goods and services 17.3%, company taxes 12.7%; nontax revenue 22.4%; grants 5.2%; other 1.1%). Expenditures: EC$551,200,000 (current expenditure 86.0%, of which interest payments 19.1%; development expenditure 14.0%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): sugarcane 100,000, tropical fruit 1,300, coconuts 1,000; livestock (number of live animals) 16,000 goats, 12,500 sheep, 4,800 cattle; fisheries production 450. Mining and quarrying: excavation of sand and crushed stone for local use. Manufacturing (2003): raw sugar 22,000; carbonated beverages (2002) 32,000 hectoliters; beer (2002) 20,000 hectoliters; other manufactures include electronic components, garments, and cement. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 130,000,000 (130,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (41,000). Gross national income (2006): US$453,000,000 (US$9,110 per capita). Households. Average household size (2001) 2.9; average annual income per wage earner (1994) EC$9,940 (US$3,681); expenditure (2001): food, beverages, and tobacco 28.8%, education 19.3%, health 14.1%, housing 13.0%, clothing and footwear 9.3%, fuel and light 4.4%. Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$299,300,000. Population economically active (1995): total 18,170; activity rate of total population 41.7% (participation rates [1991]: ages 15-64, 70.5%; female 44.4%). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 107; remittances (2006) 3; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 70; official development assistance (2005) 12 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 11; remittances (2006) 2. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 19%, in permanent crops 3%, in pasture 6%; overall forest area (2005) 15%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2003; c.i.f.): US$204,800,000 (machinery and apparatus 22.0%; food 13.6%; refined petroleum 8.1%; chemicals and chemical products 6.9%; transport equipment 6.6%). Major import sources: US 53.3%; Trinidad and Tobago 12.9%; Canada 9.2%; UK 9.1%; Japan 3.2%. Exports (2003): US$48,300,000 (electrical switches and capacitors 73.1%; raw sugar 14.9%). Major export destinations: US 78.5%; UK 17.0%; Netherlands Antilles 1.2%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2003): length 58 km. Roads (2002): total length 383 km (paved [2001] 44%). Vehicles (2002): passenger cars 6,900; trucks and buses 2,500. Air transport (2001; Saint Kitts airport only): passenger arrivals 135,237, passenger departures 134,937; cargo handled 1,802 metric tons. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2001): 11,000 (239); telephone landlines (2004): 25,000 (513); cellular telephone subscribers (2004): 10,000 (205); personal computers (2004): 11,000 (226); total Internet users (2002): 10,000 (214); broadband Internet subscribers (2002): 500 (11).
Education and health
Educational attainment (1991). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling/unknown 6.8%; primary education 45.9%; secondary 38.4%; higher 8.9%. Literacy (2004): total population ages 15 and over literate 97.8%. Health (2005): physicians 62 (1 per 796 persons); hospital beds 247 (1 per 200 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 14.5.
Military
Total active duty personnel: the defense force includes coast guard and police units.
Background
Saint Kitts became the first British colony in the West Indies in 1623. Anglo-French rivalry grew in the 17th century and lasted more than a century. In 1783, by the Treaty of Versailles, the islands became wholly British possessions. They were united with Anguilla from 1882 to 1980 but became an independent federation within the British Commonwealth in 1983. In 1997 Nevis considered becoming independent.
Recent Developments
Foreign citizenship held by members of the Saint Kitts and Nevis government became an issue in August 2007 when it was alleged that those who fell into that category were in violation of the constitution. At least four members of the National Assembly, including Dwyer Astaphan, the national security minister, were identified as having dual citizenship.
Saint Lucia
Official name: Saint Lucia. Form of government: constitutional monarchy with two legislative houses (Senate [11]; House of Assembly [17]). Chief of state: British Queen Elizabeth II (from 1952), represented by Governor-General Dame Pearlette Louisy (from 1997). Head of government: Prime Minister Stephenson King (from 2007). Capital: Castries. Official language: English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Eastern Caribbean dollar (EC$) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = EC$2.70.
Demography
Area: 238 sq mi, 617 sq km. Population (2007): 168,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 705.9, persons per sq km 272.3. Urban (2005): 28.0%. Sex distribution (2005): male 48.91%; female 51.09%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 28.4%; 15-29, 28.4%; 30-44, 21.5%; 45-59, 12.3%; 60-74, 6.5%; 75 and over, 2.9%. Ethnic composition (2000): black 50%; mulatto 44%; East Indian 3%; white 1%; other 2%. Religious affiliation (2001): Roman Catholic 67.5%; Protestant 22.0%, of which Seventh-day Ad-ventist 8.4%, Pentecostal 5.6%; Rastafarian 2.1%; nonreligious 4.5%; other/unknown 3.9%. Major towns (2004): Castries (2001) 10,634 (urban area 37,962); Vieux Fort 4,900; Micoud 4,000; Soufriere 3,600. Location: island between the Caribbean Sea and North Atlantic Ocean, north of Trinidad and Tobago.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 15.1 (world avg. 20.3); within marriage 15.0%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 7.2 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 2.21. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 70.0 years; female 77.4 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:EC$575,700,000 (tax revenue 93.9%, of which taxes, duties, and service charges on imports 47.7%, taxes on domestic goods and services 15.5%, taxes on company profits 10.5%; nontax revenue 6.1%). Expenditures: EC$663,200,-000 (current expenditures 74.9%, of which interest payments 10.6%; development expenditures 25.1%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$248,900,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2004): bananas 42,326, coconuts 14,000, citrus and tropical fruits 7,500; livestock (number of live animals) 14,950 pigs, 12,500 sheep, 12,400 cattle; fisheries production (2005) 1,386, of which tuna 33.6%. Mining and quarrying: excavation of sand for local construction and pumice. Manufacturing (value of production in EC$’000; 2005): food, beverages (significantly alcoholic beverages), and tobacco products 78,002; electrical products 28,279; paper products and cardboard boxes 21,567. Energy production (consumption):electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 309,000,000 (309,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (119,000). Population economically active (2004): total 80,600; activity rate of total population 49.7% (participation rates: ages 15 and over 68.6%; female [2000] 47.2%; unemployed [2005] 17.0%). Households. Average household size (2001) 3.2; expenditure (1984): food 46.8%; housing 13.5%; clothing and footwear 6.5%; transportation and communication 6.3%. Gross national income (2006): US$872,000,000 (US$5,349 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 345; remittances (2004) 26; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 86; official development assistance (2005) 36 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 40; remittances (2004) 3.6. Land use as % of total land area (2000): in temporary crops 7%, in permanent crops 23%, in pasture 3%; overall forest area 15%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004; c.i.f.): US$430,800,000 (machinery and transport equipment 19.3%; food 18.8%; mineral fuels 17.2%; chemicals and chemical products 7.5%). Major import sources: US 35.1%; Trinidad and Tobago 14.2%; UK 7.7%; Japan 3.3%; Barbados 3.3%. Exports (2004): US$103,145,000 (reexports 46.0%, of which mineral fuels 30.6%; domestic exports 43.8%, of which bananas 19.5%, beverages (significantly beer) and tobacco products 11.4%; ships’ stores and bunkers 10.2%). Major export destinations: UK 46.0%; Trinidad and Tobago 11.8%; Barbados 10.4%; US 9.2%; Dominica 8.4%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (1999): total length 1,210 km (paved 5%). Vehicles (2001): passenger cars 22,453; trucks and buses 8,972. Air transport (2001; Castries and Vieux Fort airports only): passenger arrivals and departures 679,000; cargo unloaded and loaded 3,500 metric tons. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2001): 46,000 (291); telephone landlines (2002): 51,000 (336); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 106,000 (657); personal computers (2004): 26,000 (173); total Internet users (2004): 55,000 (339).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2004). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: no formal schooling/unknown 9.8%; incomplete primary education 7.4%; complete primary 45.0%; secondary 28.6%; higher vocational 6.2%; university 3.0%. Literacy (2000): 90.2%. Health (2002): physicians 92 (1 per 1,740 persons); hospital beds 285 (1 per 562 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 18.9.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2004): a 300-member police force includes a specially trained paramilitary unit and a coast guard unit.
Background
Caribs replaced early Arawak inhabitants on the island c. ad 800-1300. Settled by the French in 1650, it was ceded to Great Britain in 1814 and became one of the Windward Islands in 1871. It became fully independent as Saint Lucia in 1979. The economy is based on agriculture and tourism.
Recent Developments
The United Workers Party (UWP) government in April 2007 made the controversial decision to reestablish diplomatic relations with Taiwan, much to the annoyance of China. The former Saint Lucia Labour Party government had switched diplomatic recognition to China in the mid-1990s, after a postindependence period during which Taiwan was the preferred choice. The UWP insisted that it could recognize both Beijing and Taiwan, but a Chinese spokesman rejected this option.
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Official name: Saint Vincent and the Grenadines. Form of government: constitutional monarchy with one legislative house (House of Assembly [22]). Chief of state: British Queen Elizabeth II (from 1952), represented by Governor-General Sir Frederick Ballan-tyne (from 2002). Head of government: Prime Minister Ralph Gonsalves (from 2001). Capital: Kingstown.
Official language: English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Eastern Caribbean dollar (EC$) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = EC$2.70.
Demography
Area: 150.3 sq mi, 389.3 sq km. Population (2007): 106,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 705.3, persons per sq km 272.3. Urban (2006): 46.3%. Sex distribution (2005): male 50.85%; female 49.15%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 27.1%; 15-29, 30.0%; 30-44, 22.1%; 45-59, 12.1%; 60-74, 5.8%; 75 and over, 2.9%. Ethnic composition (1999): black 65.5%; mulatto 23.5%; Indo-Pakistani 5.5%; white 3.5%; black-Amerindian 2.0%. Religious affiliation (2000): Protestant 47.0%; unaffiliated Christian 20.3%; independent Christian 11.7%; Roman Catholic 8.8%; Hindu 3.4%; Spiritist 1.8%; Muslim 1.5%; nonreligious 2.3%; other 3.2%. Major cities (2004): Kingstown 13,044; Georgetown 1,700; Byera 1,400; Barrouallie 1,400. Location: islands in the Caribbean Sea, north of Trinidad and Tobago.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 20.0 (world avg. 20.3); (2003) within marriage 15.6%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 6.7 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 2.20. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 69.0 years; female 74.6 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue:EC$399,240,000 (tax revenue 90.6%, of which taxes on international trade and transactions 40.6%, income tax 12.4%, corporate taxes 10.9%, stamp duty 9.6%; nontax revenue 9.4%). Expenditures: EC$456,740,000 (current expenditure 77.8%, of which wages and salaries 37.5%; development expenditure 22.2%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): bananas 50,000, sugarcane 20,000, starchy roots and tubers (significantly eddoes and dasheens) 13,945; livestock (number of live animals) 12,000 sheep, 9,150 pigs, 7,200 goats; fisheries production 2,745. Mining and quarrying: sand and gravel for local use. Manufacturing (value added in EC$’000,000; 2000): beverages and tobacco products 17.4; food 15.6; paper products and publishing 3.6. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005)132,000,000 ([2004] 110,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (65,000). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2006) 113; remittances (2006) 5.0; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 42; official development assistance (2005) 7.4 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 14; remittances (2006) 2.0. Gross national income (2006): US$424,000,000 (US$3,537 per capita). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$248,300,000. Population economically active (2006): total 58,000; activity rate of total population 48.3% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 75.3%; female 41.4%; unemployed [2004] 12.0%). Households. Average household size (1991) 3.9; income per household (1988) EC$4,579 (US$1,696); expenditure (2001): food and beverages 53.6%; housing and energy 12.8%; clothing and footwear 8.9%. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 18%, in permanent crops 18%, in pasture 5%; overall forest area (2005) 27%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004; c.i.f.): US$226,290,000 (machinery and transport equipment 22.7%; food products 18.8%; mineral fuels 11.4%; chemicals and chemical products 8.4%). Major import sources: US 36.5%; Caricom (Caribbean Community and Common Market) countries 28.9%, of which Trinidad and Tobago 21.7%, Barbados 3.9%; UK 10.4%; Japan 3.7%. Exports (2004; f.o.b.): US$36,030,000 (domestic exports 90.3%, of which bananas 36.2%, packaged flour 13.6%, packaged rice 7.5%, eddoes and dasheens 6.1%; reexports 9.7%). Major export destinations: Caricom countries 58.5%, of which Barbados 13.3%, St. Lucia 11.7%, Trinidad and Tobago 10.0%; UK 34.1%; US 5.1%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2004): total length 829 km (paved 70%). Vehicles (2003): passenger cars 12,196; trucks and buses 4,447. Air transport (2003): passenger arrivals 133,769; passenger departures 137,899. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2000): 50,000 (446); telephone landlines (2006): 23,000 (218); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 88,000 (834); personal computers (2005): 16,000 (152); total Internet users (2005): 10,000 (102); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 5,600 (53).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2001). Percentage of employed population having: no formal schooling/unknown 1.7%; primary education 55.6%; secondary 27.3%; higher vocational 15.1%; university 0.3%. Literacy (2004): total population ages 15 and over literate 88.1%. Health (2005): physicians 72 (1 per 1,458 persons); hospital beds 472 (1 per 222 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 15.7. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,623 (vegetable products 79%, animal products 21%); 138% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): no regular military forces; the paramilitary includes coast guard and police units.
Background
The French and the British contested for control of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines until 1763, when it was ceded to England by the Treaty of Paris. The original inhabitants, the Caribs, recognized British sovereignty but revolted in 1795. Most of the Caribs were deported; many who remained were killed in volcanic eruptions in 1812 and 1902. In 1969 Saint Vincent and the Grenadines became a self-governing state in association with the United Kingdom, and in 1979 it achieved full independence.
Recent Developments
In June 2007 Prime Minister Ralph Gonsalves defended the growing assistance provided by Cuba and Venezuela. He stressed that Saint Vincent and the Grenadines was also pursuing closer relations with Taiwan, Turkey, and Brazil and insisted that a small state had to take advantage of all opportunities for links with larger countries.
Samoa
Official name: Malo Sa’oloto Tuto’atasi o Samoa (Samoan); Independent State of Samoa (English). Form of government: mix of parliamentary democracy and constitutional monarchy with one legislative house (Legislative Assembly [49]). Chief of state: Head of State Tuiatua Tupua Tamasese Efi (from 2007). Head of government: Prime Minister Tuila’epa Sa’ilele Malielegaoi (from 1998). Capital: Apia. Official languages: Samoan; English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 tala (plural tala; SAT) = 100 sene; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = SAT 2.51.
Demography
Area: 1,093 sq mi, 2,831 sq km. Population (2007): 180,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 164.7, persons per sq km 63.6. Urban (2006): 20.8%. Sex distribution (2006): male 51.88%; female 48.12%. Age breakdown (2001): under 15, 40.7%; 15-29, 25.5%; 30-44, 17.8%; 45-59, 9.3%; 60-74, 5.0%; 75-84, 1.3%; 85 and over, 0.2%; unknown 0.2%. Ethnic composition (2000): Samoan (Polynesian) 88.1%; Euronesian (European and Polynesian) 10.1%; European and US white 1.2%; other 0.6%. Religious affiliation (2001): Congregational 34.8%; Roman Catholic 19.6%; Methodist 15.0%; Mormon 12.7%; Assemblies of God 6.6%; other Christian 9.6%; other/unknown 1.7%. Major towns (2006): Apia 37,237 (urban agglomeration 60,702); Vaitele 6,294; Faleasi’u 3,548; Vailele 3,174; Le’auva’a 3,015. Location: group of islands in the South Pacific Ocean, about halfway between Hawaii (US) and New Zealand.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 27.1 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 5.6 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 21.5 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 4.17. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 67.8 years; female 74.2 years.
National economy
Budget (2005-06). Revenue:SAT 387,200,000 (tax revenue 70.5%, of which VAT 28.0%, excise taxes 17.8%, income tax 12.2%; grants 18.6%; nontax revenue 10.9%). Expenditures: SAT 391,700,000 (current expenditure 72.0%, of which general services 22.9%, economic services 14.4%, education 14.1%, health 12.1%; development expenditure 22.0%; net lending 6.0%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): coconuts 152,826, bananas 24,275, taro 17,000; livestock (number of live animals) 201,000 pigs, 29,000 cattle, 450,000 chickens; roundwood 131,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 53%; fisheries production 4,501. Manufacturing (value of manufactured exports in SAT ’000; 2006-07): beer 3,520; noni (fruit known locally as nonu;also known as Indian mulberry) juice 3,130; coconut cream 2,130. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2006) 113,000,000 (90,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (49,000). Households. Average household size (2004) 7.2; sources of income (1997): wages and salaries 44%, other 56%; expenditure (2002): food 50.3%, transportation and communications 14.4%, alcohol and tobacco products 12.2%, household furnishings and operation 11.1%. Population economicallyactive (2003): total 64,000; activity rate of total population 35% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 63%; female 32%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$177,000,000. Gross national income (2006): US$409,000,000 (US$2,210 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2006-07) 86; remittances (2006-07) 119; foreign direct disinvestment (2001-05 avg.) -2.6; official development assistance (2005) 44. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 13; remittances (2005) 11. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 21.2%, in permanent crops 24.4%, in pasture 0.7%; overall forest area (2005) 60.4%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005-06; c.i.f.): SAT 549,500,000 (petroleum products 19.0%; unspecified 81.0%). Major import sources: New Zealand 29.3%; Australia 18.8%; US 10.6%; Fiji 7.0%; China 5.3%. Exports (2005-06; f.o.b.): SAT 29,600,000 (fresh fish 42.8%; beer 14.6%; coconut cream 7.6%; taro 2.0%). Major export destinations: American Samoa 49.1%; US 32.6%; New Zealand 9.4%; Australia 3.4%; Japan 3.1%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2001): total length 2,337 km (paved 14%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 4,638; trucks and buses 4,894. Air transport (2004; Polynesian Airlines only): passenger-km 326,090,000; metric ton-km cargo 2,709,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 4,500 (25); televisions (2003): 27,000 (152); telephone landlines (2005): 19,000 (106); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 24,000 (134); personal computers (2005): 4,000 (22); total Internet users (2006): 8,000 (45); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 100 (0.5).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2002). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling 1.8%; incomplete/complete primary education 32.4%; incomplete/complete secondary 55.4%; higher 10.4%. Literacy (2003): total population ages 16 and over literate: virtually 100%. Health (2005): physicians 50 (1 per 3,570 persons); hospital beds 229 (1 per 780 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 27.7. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,605 (vegetable products 76%, animal products 24%); 193%of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
No military forces are maintained; informal defense ties exist with New Zealand per 1962 Treaty of Friendship.
Background
Polynesians inhabited the islands oftheSamoan archipelago for thousands of years before they were visited by Europeans in the 18th century. Control of the islands was contested by the US, Britain, and Germany until 1899, when they were divided between the US and Germany. In 1914 Western Samoa was occupied by New Zealand, which received it as a League of Nations mandate in 1920. After World War II, it became a UN trust territory administered by New Zealand, and it achieved independence in 1962. In 1997 the word Western was dropped from the country’s name.
Recent Developments
The Samoan government continued its economic and institutional restructuring programs and was rewarded with low inflation and stable external debt in 2007. The economy grew about 6%, due in part to increased returns from fishing, agriculture, tourism, and manufacturing. The UN Economic and Social Council removed Samoa from its list of least developed countries. The government remained dependent, however, on remittances from some 200,000 Samoans living abroad.
San Marino
Official name: Repubblica di San Marino (Republic of San Marino). Form of government: unitary multiparty
republic with one legislative house (Great and General Council [60]). Heads of state and government: two captains-regent who serve six-month terms beginning in April and October. Capital: San Marino. Official language: Italian. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 euro (€) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = €0.63.
Demography
Area: 23.63 sq mi, 61.20 sq km. Population (2007): 30,500. Density(2007): persons persq mi 1,291, persons per sq km 498.4. Urban (2005): 96%. Sex distribution (2007): male 49.16%; female 50.84%. Age breakdown (2004): under 15,15.3%; 15-29,16.1%; 30-44, 27.3%; 45-59, 19.6%; 60-74, 14.1%; 75-84, 6.0%; 85 and over, 1.6%. Ethnic composition (2002): Sammarinesi 85.7%; Italian 13.0%; other 1.3%. Religious affiliation (2000): Roman Catholic 88.7%; other Christian 3.5%; nonreligious 5.1%; other 2.7%. Major municipalities (2007): Serravalle 9,908; Borgo Maggiore 6,082; San Marino 4,402. Location: southern Europe, completely surrounded by Italy.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 9.5 (world avg. 20.3); within marriage 90.1%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 7.3 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 2.2 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.11. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 79.4 years; female 85.1 years.
National economy
Budget (2003). Revenue: €288,000,000 (direct taxes 34.7%; import taxes 33.0%; nontax revenue 22.0%). Expenditures: €272,400,000 (current expenditures 92.0%; capital expenditures 8.0%). Public debt (2003): US$52,900,000. Tourism: number of tourist arrivals (2006) 2,135,589. Population economically active (2006): total 21,272; activity rate of total population 70.4% (participation rates: ages 15-64 [2002] 72.1%; female 42.1%; unemployed 3.3%). Households. Average household size (2002) 2.5; expenditure (2004): food and beverages 22.0%, housing 13.8%, transportation 10.6%, vacation and recreation 10.1%, restaurants 9.3%. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): small amounts of wheat, grapes, and barley; livestock (number of live animals) 991 cattle, 91 sheep, 32 pigs. Quarrying: building stone is an important export product. Manufacturing (2005): processed meats 283,674 kg, of which beef 270,616 kg, veal 8,549 kg, pork 3,615 kg; cheese 56,610 kg; butter 8,110 kg; other major products include electrical appliances, musical instruments, printing ink, paint, cosmetics, furniture, floor tiles, gold and silver jewelry, clothing, and postage stamps. Energy production (consumption): all electrical power is imported via electrical grid from Italy (kW-hr; consumption [2004] 212,000,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) none (56,000,000). Gross national income (at 2006 market prices): US$1,257,000,000 (US$41,044 per capita). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 17%; overall forest (2005) 2%.
Foreign trade
Major import source (2004): significantly Italy. Exports (2005): US$2,531,000,000 (goods include electronics, postage stamps, leather products, ceramics, wine, wood products, and building stone). Major export destinations (2004): Italy 90%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2001): total length 252 km. Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 32,263; trucks and buses 3,262. Air transport: a heliport provides passenger and cargo service between San Marino and Rimini, Italy, during the summer months. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2003): 25,000 (893); telephone landlines (2006): 21,000 (696); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 17,000 (576); personal computers (2003): 23,000 (819); total Internet users (2006): 15,000 (510); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 1,500 (50).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2002). Percentage of population ages 14 and over having: basic literacy or primary education 41.0%; some secondary 25.0%; secondary 27.0%; higher degree 7.0%. Literacy (2001): total population ages 15 and over literate 98.7%; males literate 98.9%; females literate 98.4%. Health (2002): physicians 117 (1 per 230 persons); hospital beds 134 (1 per 191 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2004) 3.4.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): defense is the responsibility of Italy.
San Marino is a small republic situated on the slopes of Mount Titano, on the Adriatic side of central Italy between the Romagna and the Marche regions and surrounded on all sides by Italy.
Background
According to tradition, San Marino was founded in the early 4th century ad by St. Marinus. By the 12th century it had developed into a commune and remained independent despite challenges from neighboring rulers, including the Malatesta family in nearby Rimini, Italy. San Marino survived the Renaissance as a relic of the self-governing Italian city-state and remained an independent republic after the unification of Italy in 1861. It is one of the smallest republics in the world, and it may be the oldest one in Europe.
Recent Developments
The economy of San Marino was strong overall; the IMF reported in April 2007 that GDP growth in 2006 was about 5%, with unemployment hovering at about 2%. Some economic experts suggested further growth potential because San Marino would make an attractive location for the head offices of multinational enterprises, which could be enticed to relocate through tax incentives and improved financial services.
Sao Tome and Principe
Official name: Republica Democratica de Sao Tome e Principe (Democratic Republic of Sao Tome and Principe). Form of government: multiparty republic with one legislative house (National Assembly [55]). Chief of state: President Fradique de Menezes (from 2003). Head of government: Prime Minister Patrice Trovoada (from 2008). Capital: Sao Tome. Official language: Portuguese. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 dobra (Db) = 100 centimos; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = Db 14,650.99.
Demography
Area: 386 sq mi, 1,001 sq km. Population (2007): 158,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 409.3, persons per sq km 157.8. Urban (2004): 37.9%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.34%, female 50.66%. Age breakdown (2001): under 15, 42.1%; 15-29, 30.3%; 30-44, 14.4%; 45-59, 6.9%; 60-74, 4.7%; 75-84,1.3%; 85 and over, 0.3%. Ethnic composition (2000): black-white admixture 79.5%; Fang 10.0%; Angolares (descendants of former Angolan slaves) 7.6%; Portuguese 1.9%; other 1.0%. Religious affiliation (2005): Roman Catholic 80%; Protestant 15%; Muslim 3%; other 2%. Major urban areas (2001): Sao Tome 49,957; Neves 6,635; Santana 6,228; Trindade 6,049; Santo Antonio 1,010. Location: islands in the Gulf of Guinea, straddling the Equator west of Gabon.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 40.8 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 6.7 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 34.1 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 5.71. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 65.4 years; female 68.6 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: Db 972,100,000,000 (petroleum exploration bonuses 57.8%; grants 18.9%; taxes 18.9%, of which consumption taxes 7.1%; nontax revenue 4.4%). Expenditures: Db 545,500,000,000 (current expenditure 58.7%; capital expenditure 35.5%; other 5.8%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$293,700,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing(2006): oil palm fruit 43,460, taro 28,000, bananas 27,000; livestock (number of live animals) 5,000 goats, 4,600 cattle, 3,000 sheep; roundwood (2005) 9,000 cu m; fisheries production (2005) 3,600. Mining and quarrying: some quarrying to support local construction industry. Manufacturing (value in Db; 1995): beer 880,000; clothing 679,000; lumber 369,000. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 37,200,000 (25,600,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (30,000). Households. Average household size (2004) 5.5; expenditure (1995): food, beverages, and tobacco 71.9%, housing and energy 10.2%, transportation and communications 6.4%. Population economically active (2006): total 53,266; activity rate of total population 35.1% (participation rates: ages 10 and over (2001) 43.7%; female 41.6%; unemployed 30%). Gross national income (2006): US$55,000,000 (US$356 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 14; remittances (2006) 1; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 2.4; official development assistance (2005) 32. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2002) 0.6; remittances (2006) 1. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 8%, in permanent crops 49%, in pasture 1%; overall forest area (2005) 28%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006): US$70,853,000 (food and beverages 30.1%; petroleum products 20.4%; machinery and equipment 13.5%; construction materials 8.7%; transportation equipment 8.2%). Major import sources: Portugal 63.6%; Angola 18.3%; Belgium 4.6%; Gabon 3.5%. Exports (2006): US$3,820,000 (cocoa beans 64.9%; coffee 24.2%; remainder 10.9%). Major export destinations: Portugal 33.3%; The Netherlands 27.1%; Belgium 14.3%; France 8.9%; US 5.3%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2000): total length 320 km (paved 68%). Vehicles (1996): passenger cars 4,040; trucks and buses 1,540. Air transport (2001): passenger-km 7,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2003): 19,000 (128); telephone landlines (2006): 7,600 (47); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 18,000 (115); personal computers (2005): 6,000 (38); total Internet users (2006): 29,000 (181).
Education and health
Unknown 22.9%; primaryeducation 41.4%; lower secondary 25.0%; upper secondary/vocational 8.8%; higher 1.9%. Literacy (2006): total population ages 15 and over literate 85%; males literate 92%; females literate 78%. Health: physicians (2004) 81 (1 per 1,803 persons); hospital beds (1991) 532 (1 per 211 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 43.1. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,418 (vegetable products 95%, animal products 5%); 193% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2005): 460 (army/coast guard 65.2%; presidential guard 34.8%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.2%; per capita expenditure US$4.
Background
First visited by European navigators in the 1470s, the islands of Sao Tome and Prfncipe were colonized by the Portuguese in the 16th century and were used in the trade and transshipment of slaves. Sugarcane and cacao were the main cash crops. The islands became an overseas province of Portugal in 1951 and achieved independence in 1975. During recent decades the country’s economy was heavily dependent on international assistance.
Recent Developments
While Sao Tome and Prfncipe waited for the bonanza promised by the discovery of oil in its offshore waters, it was rewarded for its good governance and stable economy by the IMF, which offered debt relief in March 2008 under its Heavily Indebted Poor Countries initiative. Though no oil had yet been pumped from the country’s waters, an estimated US$80 million had been earned for prospecting rights, and most of that money had been invested (on international advice) in interest-bearing securities.
Saudi Arabia
Official name: Al-Mamlakah al-’Arabiyah al-Sa’udiyah (Kingdom of Saudi Arabia). Form of government: monarchy (assisted by the Consultative Council consisting of 150 appointed members). Head of state and government: King Abdullah (from 2005). Capital: Riyadh. Official language: Arabic. Official religion: Islam. Monetary unit: 1 Saudi riyal (SR) = 100 ha-lalah; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = SR 3.75.
Demography
Area: 830,000 sq mi, 2,149,690 sq km. Population (2007): 24,209,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 29.2, persons per sq km 11.3. Urban (2005): 81.0%. Sex distribution (2006): male 54.64%; female 45.36%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 38.2%; 15-29, 29.5%; 30-44, 22.9%; 45-59, 5.9%; 60-74, 2.7%; 75 and over, 0.8%. Ethnic composition (2005): Saudi Arab 74%; expatriates 26%, of which Indian 5%, Bangladeshi 3.5%, Pakistani 3.5%, Filipino 3%, Egyptian 3%, Palestinian 1%, other 7%. Religious affiliation (2000): Muslim 94%, of which Sunni 84%, Shi’i 10%; Christian 3.5%, ofwhich Roman Catholic 3%; Hindu 1%; nonreligious/other 1.5%. Major cities (2005; urban agglomerations): Riyadh 4,193,000; Jiddah 2,860,000; Mecca 1,319,000; Medina 944,000; Al-Dammam 766,000. Location: the Middle East, bordering Iraq, Kuwait, the Persian Gulf, Qatar, the UAE, Oman, Yemen, the Red Sea, the Gulf of Aqaba, and Jordan.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 29.3 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 2.6 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 26.7 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 4.00. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 73.7 years; female 77.8 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue: SR 673,682,000,000 (oil revenues 89.7%). Expenditures:SR 393,322,000,000 (current expenditures 82.0%; capital expenditures 18.0%). National debt (domestic only; end of 2004): US$150,000,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): wheat 2,400,000, alfalfa 1,644,661, dates 970,488; livestock (number of live animals) 7,000,000 sheep, 2,200,000 goats, 352,000 cattle, 260,000 camels; fisheries production (2005) 74,778 (from aquaculture 19%). Mining and quarrying (2005): gypsum 713,000; silver 13,501 kg; gold 7,456 kg. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 1998): industrial chemicals 3,349; refined petroleum 1,806; cement, bricks, and tiles 1,505. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 176,124,000,000 ([2006] 163,151,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006-07) 3,286,000,000 ([2004] 609,600,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 112,228,000 (67,300,000); natural gas (cu m; 2005) 81,350,000,000 ([2004] 65,679,000,000). Population economically active (2006): total 8,024,885, of which 3,900,591 Saudi workers and 4,124,294 foreign nationals; activity rate of total population 33.9% (participation rates: ages 15-64 [2003] 54%; female 15.5%; unemployed 6.3%). Gross national income (at current market prices; 2006): US$365,786,000,000 (US$15,131 per capita). Households. Average household size (2004) 5.7; expenditure (1998-99): food and nonalcoholic beverages 37.3%, transportation 18.9%, housing and energy 15.7%, household furnishings 9.7%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 5,181; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 1,661; official development assistance (2005) 13 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 4,764; remittances (2006) 14,318; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 301. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 1.7%, in permanent crops 0.1%, in pasture 79.1%; overall forest area (2005) 1.3%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): SR 222,985,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 24.6%; transport equipment 20.7%; food and live animals 13.6%; base and fabricated metals 10.6%; chemicals and chemical products 9.7%). Major import sources: US 14.8%; Japan 9.0%; Germany 8.2%; China 7.4%; UK 4.7%. Exports (2005; f.o.b.): SR 677,144,000,000 (crude and refined petroleum 86.2%; other mineral fuels [mostly natural gas] 3.3%; organic chemicals 2.6%). Major export destinations: Japan 15.6%; US 15.5%; South Korea 8.5%; China 6.0%; India 5.9%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2003): route length (2006) 1,392 km; passenger-km 232,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 778,000,000. Roads (2006): total length 174,429 km (paved 100%). Vehicles (2001): passenger cars 4,452,793; trucks and buses 4,110,271. Air transport (2006; Saudi Arabian Airlines only): pas-senger-km 28,722,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 1,092,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 1,093,000 (48); televisions (2004): 6,576,000 (292); telephone landlines (2006): 3,951,000 (167); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 19,663,000 (830); personal computers (2005): 8,184,000 (354); total Internet users (2006): 4,700,000 (198); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 218,000 (9.2).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2000). Percentage of Saudi (non-Saudi) population ages 10 and over who: are illiterate 19.9% (12.1%); are literate/have primary education 39.5% (40.6%); have some/completed secondary 34.2% (36.0%); have at least begun university 6.4% (11.3%). Literacy (2005): percentage of total population ages 15 and over literate 80.4%; males literate 85.8%; females literate 73.3%. Health (2005): physicians 43,348 (1 per 533 persons); hospital beds 53,192 (1 per 435 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 12.8. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,527 (vegetable products 86%, animal products 14%); 190% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 124,500 (army 60.2%, navy 12.4%, air force 14.5%, air defense forces 12.9%); US troops (2007) 274. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 8.2%; per capita expenditure US$1,092.
Background
Saudi Arabia is the historical home of Islam, founded by Muhammad in Medina in 622. During medieval times, local and foreign rulers fought for control of the Arabian Peninsula; in 1517 the Ottomans prevailed. In the 18th-19th centuries Islamic leaders supporting religious reform struggled to regain Saudi territory, all of which was restored by 1904. The British held Saudi lands as a protectorate from 1915 to 1927; then they acknowledged the sovereignty of the Kingdom of the Hejazand Najd. The two kingdoms were unified as the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia in 1932. Since World War II, it has supported the Palestinian cause in the Middle East and maintained close ties with the US.
Recent Developments
Saudi liberals welcomed a royal decree in October 2007 overhauling the kingdom’s judicial system—the reforms would preserve the centrality of the Shari’ah (Islamic law) but would take away many powers exercised by the Supreme Judicial Council, which was controlled by conservative clerics. In lateSeptemberSaudi Arabia’s grand mufti, Sheikh ‘Abd al-Aziz al-Sheikh, issued a fatwa (religious edict) prohibiting Saudi youth from traveling abroad under the pretext of jihad. It was understood that the fatwa was aimed at discouraging young Saudis from going to Iraq to fight US and other foreign forces there. The Saudi Arabian economy continued to perform extremely well, especially since the price of crude oil remained robust and, by mid-2008, had soared to over US$125 per barrel. The country enjoyed a massive trade surplus, and GDP grew by 7.1% in 2007. Saudi Arabia was to be the largest purchaser in a US$20 billion arms deal that was reached between the US and the Arab Gulf states, and inSeptem-berSaudi Arabia signed a US$8.8 billion deal with the UK to buy and service 72 Eurofighter aircraft.
Senegal
Official name: Republique du Senegal (Republic of Senegal). Form of government: multiparty republic with two legislative houses (Senate [100]; National Assembly [150]). Head of state and government: President Abdoulaye Wade (from 2000), assisted by Prime Minister Cheikh Hadjibou Soumare (from 2007). Capital: Dakar. Official language: French. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 CFA franc (CFAF) = 100 centimes; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = CFAF 414.60.
Demography
Area: 75,955 sq mi, 197,021 sq km. Population (2007): 12,522,000. Density (2007): persons persq mi 164.9, persons per sq km 63.7. Urban (2005): 41.6%. Sex distribution (2006): male 49.99%; female 50.01%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 42.2%; 15-29, 28.4%; 30-44, 16.0%; 45-59, 8.7%; 60-74, 3.9%; 75-84, 0.7%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Ethnic composition (2000): Wolof 34.6%; Peul (Fulani) and Tukulor 27.1%; Serer 12.0%; Malinke (Mandingo) 9.7%; other 16.6%. Religious affiliation (2005): Muslim 94%, of which Shi’i 5%; Christian (mostly Roman Catholic) 4%; other 2%. Major cities (2007): Dakar 2,243,400; Touba 529,200; Thies 263,500; Kaolack 186,000; Mbour 181,800. Location: western Africa, bordering Mauritania, Mali, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, the North Atlantic Ocean, and The Gambia.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 38.3 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 11.2 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 27.1 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 5.13. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 55.0 years; female 57.7 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:CFAF 955,800,000,000 (tax revenue 89.0%, of which taxes on domestic goods and services 28.7%, income taxes 21.4%, taxes on imports 19.7%; grants 7.9%; nontax revenue 3.1%). Ex-penditures:CFAF 1,084,400,000,000 (currentexpen-ditures 58.0%, of which public debt interest payments 4.3%; development expenditure 42.0%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$3,467,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): sugarcane (2006) 829,500, peanuts (groundnuts) 703,400, millet 608,600; livestock (number of live animals) 4,863,000 sheep, 4,144,000 goats, 3,091,000 cattle; roundwood 6,070,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 87%; fisheries production 405,263. Mining and quarrying: calcium phosphate (crude rock; 2005) 1,451,000. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2002): food and food products 108; industrial chemicals 70; cement, bricks, and ceramics 31. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 2,351,000,000 (2,351,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) negligible (8,583,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 1,127,000 (1,309,000); natural gas (cu m; 2005) 13,000,000 ([2004] 13,000,000). Population economically active (2003): total 4,383,000; activity rate of total population 39.4% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 71.5%; female 42.0%; unemployed [2005] 40%). Households. Average household size (2005) 8.7; sources of income (1997-2000): agricultural 45%; other 55%; expenditure (2005): food and nonalcoholic beverages 54.8%, household furnishings 6.9%, housing and energy 6.3%, communications 6.0%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2004) 212; remittances (2006) 633; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 59; official development assistance (2005)689. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2004) 57; remittances (2006) 77; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 15. Gross national income (2006): US$9,335,000,000 (US$770 per capita). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 12.8%, in permanent crops 0.2%, in pasture 29.3%; overall forest area (2005) 40.0%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): CFAF 1,697,000,000,000 (petroleum [all forms] 19.2%; food and live animals 19.2%, of which rice 7.8%; machinery and apparatus 12.4%; transport equipment 8.5%). Major import sources (2005): France 22.8%; Nigeria 11.4%; Brazil 4.5%; Thailand 4.2%; US 4.2%. Exports (2004): CFAF 697,000,000,000 (petroleum [all forms] 19.3%; phosphorous pentoxide and phosphoric acids 13.6%; fresh fish 12.6%; crustaceans and mollusks 9.0%; manufactured fertilizers 4.7%). Major export destinations (2005): Mali 16.9%; India 13.1%; France 9.5%; Spain 6.1%; Italy 5.5%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2004): route length (2005) 906 km; passenger-km 122,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 358,000,000. Roads (2003): total length 13,576 km (paved 29%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 147,000; trucks and buses 46,000. Air transport (2006; Air Senegal International only): passenger-km 937,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 70,000 (6.5); televisions (2003): 869,000 (77); telephone landlines (2006): 283,000 (23); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 2,983,000(245); personal computers (2005): 250,000 (21); total Internet users (2006): 650,000 (53); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 29,000 (2.4).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2005). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling/unknown 70.0%; incomplete primary education 13.0%; complete primary 3.7%; incomplete sec-ondary9.5%; complete secondary 1.4%; higher 2.4%. Literacy (2003): percentage of total population ages 15 and over literate 40.2%; males literate 49.9%; females literate 30.8%. Health: physicians (2005) 693 (1 per 17,115 persons); hospital beds (1998) 3,582 (1 per 2,500 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 61.4. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,513 (vegetable products 92%, animal products 8%); 136% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 13,620 (army 87.4%, navy 7.0%, air force 5.6%); French troops (2006) 840. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.5%; per capita expenditure US$11.
Background
Links between the peoples of Senegal and North Africa were established in the 10th century ad. Islam was introduced in the 11th century, although animism retained a hold on the country into the 19th century. The Portuguese explored the coast in 1445, and in 1638 the French established a trading post at the mouth of the Senegal River. Throughout the 17th and 18th centuries, Europeans exported slaves, ivory, and gold from Senegal. The French gained control over the coast in the early 19th century and moved inland, checking the expansion of the Tukulor empire; in 1895 Senegal became part of French West Africa. Its inhabitants were made French citizens in 1946, and it became an overseas territory of France. It became an autonomous republic in 1958 and was federated with Mali in 1959-60. It became an independent state in 1960. In 1982 it entered a confederation with The Gambia, called Senegambia, which was dissolved in 1989.
Recent Developments
The government of Senegal threatened in early 2007 to withdraw its 500 men from the African Union (AU) peacekeeping force in the Darfur region of The Sudan after 5 of them were killed there in April. In August, however, after a series of meetings with AU and UN authorities, the government committed Senegal to tripling the size of its contingent.
Serbia
Many of these statistics include Kosovo, which declared its independence in February 2008. Official name: Republika Srbija (Republic of Serbia). Form of government: republic with National Assembly (250). Chief of state: President Boris Tadic (from 2004). Head of government: Prime Minister Mirko Cvetkovic (from 2008). Capital: Belgrade. Official language: Serbian. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Serbian dinar (CSD) = 100 paras; valuation (1 Jul 2008) $1 = 49.97 CSD.
Demography
Area: 34,128 sq mi, 88,391 sq km. Population (2007): 7,402,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 247.4, persons per sq km 95.5. Urban (2002): 56.4%. Sex distribution (2005): male 48.62%; female 51.38%. Age breakdown (2002): under 15, 15.7%; 15-29, 20.2%; 30-44, 19.9%; 45-59, 21.1%; 60-74, 17.2%; 75-84, 4.7%; 85 and over, 0.6%; unknown 0.6%. Ethnic composition (2002): Serb 82.9%; Hungarian 3.9%; Bosniac 1.8%; Rom (Gypsy) 1.4%; Yugoslav 1.1%; Croat 0.9%; Montenegrin 0.9%; other 7.1%. Religious affiliation (2002): Orthodox 85.0%; Roman Catholic 5.5%; Muslim 3.2%; Protestant 1.1%; other/unknown 5.2%. Major cities (2002): Belgrade 1,120,092; Novi Sad 191,405; Nis 173,724; Kragujevac 146,373. Location: southeastern Europe, bordering Romania, Bulgaria, Macedonia, Kosovo, Montenegro, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, and Hungary.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 9.7 (world avg. 20.3); within marriage 77.8%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 14.3 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2004): 1.60. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 69.9 years; female 75.4 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:CSD 701,200,000,000 (tax revenue 91.2%, of which VAT 30.8%, excises and customs duties 15.7%, personal and corporate income tax 14.9%; nontax revenue 8.8%). Expenditures: CSD 669,600,000,000 (current expenditure 95.1%; capital expenditure 4.9%). Population economically active (2006): total 3,323,716; activity rate of total population 44.0% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 63.6%; female 43.0%; unemployed 20.9%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): corn (maize) 6,017,000, sugar beets 3,189,000, wheat 1,875,000; livestock (number of live animals) 3,211,597 pigs, 1,609,239 sheep, 1,096,185 cattle; roundwood (data for Serbia and Montenegro; 2005) 3,170,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 58%; fisheries production (data for Serbia and Montenegro; 2005) 7,022 (from aquaculture 65%). Mining and quarrying (2005): copper (metal content) 27,000; lead (metal content) 2,000. Manufacturing (value added in CSD ’000,000 in constant prices of 2002; 2004): food products and beverages 48,970; chemicals and chemical products 21,862; cement, bricks, and ceramics 11,445. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 33,874,000,000 (22,911,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) 424,000 (303,000); lignite (metric tons; 2004) 34,400,000 (30,900,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) 4,840,000 (29,419,000; data for Serbia and Montenegro); petroleum products (metric tons; data for Serbia and Montenegro; 2004) 3,150,000 (3,150,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 317,000,000 (794,000,000). Gross national income (2006): US$34,927,000,000 (US$4,700 per capita). Public debt (external, outstanding; August 2007): US$8,697,300,000. Households. Average household size (2006) 3.2; average annual income per household CSD 394,740 (US$5,620); sources of income: wages and salaries 47.7%, transfers 26.5%, self-employment 5.5%; expenditure: food and nonalcoholic beverages 35.1%, housing and energy 18.9%, transportation 11.2%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2004) 220; remittances (2005) 2,400; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 822 (data for Serbia and Montenegro); official development assistance (2005) 1,260 (data for Serbia and Montenegro; commitments). Land use as % of total land area (2002): in temporary crops 43.3%, in permanent crops 4.1%, in pasture 18.2%; overall forest area 25.2%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): US$10,575,700,000 (mineral fuels 18.9%; chemicals and chemical products 13.6%; machinery and apparatus 10.3%; transportation equipment 8.2%; base metals 7.6%). Major import sources: Russia 15.9%; Germany 10.3%; Italy 8.6%; China 4.8%; US 3.6%. Exports (2005): US$4,553,-400,000 (base metals 15.4%; food and food products 14.7%; chemicals and chemical products 8.8%; rubber and plastic products 6.4%). Major export destinations: Bosnia and Herzegovina 16.4%; Italy 14.4%; Germany 9.8%; Macedonia 5.8%; Russia 5.0%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2006): route length (2004) 3,809 km; passenger-km 684,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 4,232,000,000. Roads (2004): total length 38,507 km (paved 62%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 1,497,418; trucks and buses 257,642. Air transport (2006): passenger-km 1,252,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 5,470,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2002): 1,015,000 (95); televisions (2000): 2,980,000 (279); telephone landlines (2006): 2,719,000 (259); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 6,644,000 (633); personal computers (2005): 446,000 (55); total Internet users (2006): 1,400,000 (133); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 122,000 (16).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2002). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: no formal education/unknown 7.8%; incomplete primary education 16.2%; complete primary 23.9%; secondary 41.1%; higher 11.0%. Literacy (2002): total population ages 10 and over literate 96.6%. Health (2004): physicians (2003) 19,900 (1 per 379 persons); hospital beds 45,283 (1 per 166 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 8.0.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 39,686 (army 83.6%, air force 16.4%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2006) 2.3%; per capita expenditure US$99.
Background
The Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes was created after the collapse of Austria-Hungary at the end of World War I. The country signed treaties with Czechoslovakia and Romania in 1920-21, marking the beginning of the Little Entente. In 1929 an absolute monarchy was established, the country’s name was changed to Yugoslavia, and it was divided into regions without regard to ethnic boundaries. Axis powers invaded Yugoslavia in 1941, and German, Italian, Hungarian, and Bulgarian troops occupied it for the rest of World War II. In 1945 the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia was established; it included the republics of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, and Slovenia. Its independent form of communism under Josip Broz Tito’s leadership provoked the USSR. Internal ethnic tensions flared up in the 1980s, causing the country’s ultimate collapse. In 1991-92 independence was declared by Croatia, Slovenia, Macedonia, and Bosnia and Herzegovina; the new Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (containing roughly 45% of the population and 40% of the area of its predecessor) was proclaimed by Serbia and Montenegro. Still fueled by long-standing ethnic tensions, hostilities continued into the 1990s. Despite the approval of the Dayton Peace Agreement (1995), sporadic fighting continued and was followed in 1998-99 by Serbian repression and expulsion of ethnic populations in the province of Kosovo. In September-October 2000, the battered nation of Yugoslavia ended the autocratic rule of Pres. Slobodan Milosevic. In April 2001 he was arrested and in June extradited to The Hague to stand trial for war crimes, genocide, and crimes against humanity committed during the fighting in Kosovo. In February 2003 both houses of the Yugoslav federal legislature voted to accept a new state charter and change the name of the country from Yugoslavia to Serbia and Montenegro. Henceforth, defense, international political and economic relations, and human rights matters would be handled centrally, while all other functions would be run from the republican capitals, Belgrade and Podgorica, respectively. The move was seen as an acknowledgment that Serbia and Montenegro had little in common, and a provision was included for both states to vote on independence after three years; Serbia declared its independence in June 2006, shortly after Montenegro severed its federal union with Serbia.
Recent Developments
Serbia’s restive province of Kosovo declared its independence on 17 Feb 2008. Serbia’s parliament had passed a resolution condemning any such attempt while rejecting any role the EU planned to take in Kosovo if the EU recognized the province’s independence, and Prime Minister Vojislav Kostunica had suggested Hong Kong’s “two systems, one state” arrangement with China as a model for relations between Serbia and Kosovo. The Kosovar declaration was backed by the US, Turkey, and most EU member states, including the UK, France, and Germany. It was rejected by several states that experienced their own struggles with independence movements, however, including Russia, China, Greece, Spain, Cyprus, and, obviously, Serbia. Economic growth was 7.5% in 2007, while inflation stood at 8.5%. In July 2008 Radovan Karadzic, former president of Bosnia, was captured in Serbia. He had been wanted to stand trial on charges of war crimes for more than a decade, stemming from atrocities committed by Bosnian Serb forces in the mid-1990s.
Seychelles
Official name: Repiblik Sesel (Creole); Republic of Seychelles (English); Republique des Seychelles (French). Form of government: multiparty republic with one legislative house (National Assembly [34]). Head of state and government: President James Michel (from 2004). Capital: Victoria. Official languages: none; Creole, English, and French are national languages. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Seychelles rupee (SR) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = SR 8.00.
Demography
Area: 176 sq mi, 455 sq km. Population (2007): 84,300. Density (2007): persons persq mi 479.8, persons persq km 185.3. Urban (2005): 53%. Sexdistribution (2006): male 50.68%; female 49.32%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 23.8%; 15-29, 26.4%; 30-44, 24.4%; 45-59, 15.1%; 60-74, 7.0%; 75 and over, 3.3%. Ethnic composition (2000): Seychellois Creole (mixture of Asian, African, and European) 93.2%; British 3.0%; French 1.8%; Chinese 0.5%; Indian 0.3%; other unspecified 1.2%. Religious affiliation (2002): Roman Catholic 82.3%; Anglican 6.4%; other Christian 4.5%; Hindu 2.1%; Muslim 1.1%; other 2.1%; unknown 1.5%. Major towns (2004): Victoria 23,200; Anse Royale 3,800. Location: groupof islands in the Indian Ocean, northeast of Madagascar.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 17.3 (world avg. 20.3); (2005) within marriage 23.6%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 7.8 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 2.11. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 68.9 years; female 75.7 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue: SR 2,476,000,000 (current revenue 97.1%, of which dividends and interest 14.0%, income and business tax 12.0%, indirect taxes on services 9.5%, trades tax 9.1%; grants 2.9%). Expenditures: SR 2,302,000,000 (current expenditure 82.5%, of which public debt interest charges 17.6%, education 8.6%, health 8.4%; development expenditure 17.5%). Public debt (2006): US$1,035,000,000. Gross national income (2006): US$659,000,000 (US$7,660 per capita). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): coconuts 2,529, bananas 2,046, tea 189; livestock (number of live animals) 18,500 pigs, 5,150 goats, 570,000 chickens; fisheries production 107,327 (from aquaculture 1%). Mining and quarrying (2006): granite 93,000. Manufacturing (2006): canned tuna 40,222; fish meal 14,821; copra 253. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2006) 251,000,000 ([2004] 220,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (178,000). Population economically active (2002): total 43,859; activity rate of total population 53.6% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 80.1%; female [1997] 47.6%; unemployed [2006] 2.6%). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2006) 227; remittances (2006) 11; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 58; official development assistance (2005) 10 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 39; remittances (2006) 10; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 8.4. Households. Average household size (2004) 3.5; sources of income (1997): wages and salaries 77.2%, self-employment 3.8%, transfer payments 3.2%; expenditure (2001): food 25.5%, housing and energy 14.8%, beverages 13.3% (of which alcoholic 10.7%), clothing and footwear 6.7%. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 2%, in permanent crops 13%; overall forest area (2005) 89%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; c.i.f.): SR 4,180,000,000 (mineral fuels 26.7%; food and beverages 24.1%, of which fish, crustaceans, and mollusks 12.6%; machinery and apparatus 11.0%; iron and steel 5.5%; vehicles 4.3%). Major import sources: Saudi Arabia 26.4%; Singapore 11.3%; France 8.0%; Spain 8.0%; South Africa 7.3%. Exports (2006; f.o.b.): SR 2,100,000,000 (domestic exports 56.5%, of which canned tuna 49.5%, medicaments and medical appliances 3.9%, crustaceans 1.2%, fish meal 1.2%; reexports 43.5%, of which petroleum products to ships and aircraft 42.4%). Major export destinations (domestic exports only): UK 42.0%; France 26.1%; Italy 18.0%; Germany 3.7%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2006): total length 502 km (paved 96%). Vehicles (2006): passenger cars 7,070; trucks and buses 2,796. Airtransport (2006; Air Seychelles only): passenger-km 1,089,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 22,502,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 3,500 (42); televisions (2003): 22,000 (266); telephone landlines (2006): 22,000 (260); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 72,000 (851); personal computers (2005): 16,000 (193); total Internet users (2006): 29,000 (343); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 1,300 (15).
Education and health
Primary education 23.2%; secondary 73.4%; higher 3.4%. Literacy (2005): total population ages 12 and over literate 96.0%; males literate 96.0%; females literate 96.0%. Health (2006): physicians 83 (1 per 1,019 persons); hospital beds 417 (1 per 203 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 9.5. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,547 (vegetable products 81%, animal products 19%); 141% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 200 (army 100%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.8%; per capita expenditure US$157.
Background
The first recorded landing on the uninhabited Seychelles was made in 1609 by an expedition of the British East India Co. The archipelago was claimed by the French in 1756 and surrendered to the British in 1810. Seychelles became a British crown colony in 1903 and a republic within the Commonwealth in 1976. A one-party socialist state since 1979, Seychelles began moving toward democracy in the 1990s; it adopted a new constitution in 1993.
Recent Developments
In 2007 Seychelles continued efforts to strengthen its economy (one of the strongest in Africa) by forging foreign-trade agreements. In February Chinese Pres. Hu Jintao concluded his eight-country African tour in Victoria, where he met with Pres. James Michel, signed a number of cooperation agreements, canceled a debt, and pledged US$12 million in aid.
Sierra Leone
Official name: Republic of Sierra Leone. Form of government: republic with one legislative body (Parliament [124]). Head of state and government: President Ernest Bai Koroma (from 2007). Capital: Freetown. Official language: English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 leone (Le) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = Le 2,969.80.
Demography
Area: 27,699 sq mi, 71,740 sq km. Population (2007): 5,866,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 211.8, persons per sq km 81.8. Urban (2005): 40.7%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.23%; female 50.77%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 42.8%; 15-29, 26.1%; 30-44, 16.0%; 45-59, 9.6%; 60-74, 4.7%; 75-84, 0.7%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Ethnic composition (2000): Mende 26.0%; Temne 24.6%; Limba 7.1%; Kuranko 5.5%; Kono 4.2%; Fu-lani 3.8%; Bullom-Sherbro 3.5%; other 25.3%. Religious affiliation (2005): Muslim 65%; Christian 25%; traditional beliefs/other 10%. Major cities (2004): Freetown 772,873; Bo 149,957; Kenema 128,402; Yoni 87,627; Makeni 82,840. Location: western Africa, bordering Guinea, Liberia, and the North Atlantic Ocean.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 46.1 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 23.4 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 22.7 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 6.15. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 37.7 years; female 42.1 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: Le 765,762,000,000 (grants 46.0%; import taxes 22.4%; corporate taxes 8.1%). Expenditures: Le 830,410,000,000 (current expenditures 75.2%, of which wages and salaries 27.6%, goods and services 24.8%, debt service 15.1%; capital expenditures 24.8%). Gross national income (2006): US$1,791,000,000 (US$312 per capita). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): rice 1,062,000, cassava 350,000, oil palm fruit 166,100; livestock (number of live animals) 540,000 goats, 470,000 sheep, 350,000 cattle; roundwood (2005) 5,546,391 cu m, of which fuelwood 98%; fisheries production 145,993. Mining and quarrying (2006): bauxite 1,071,140; rutile 73,600; diamonds 582,330 carats. Manufacturing (2006): soap 467,360; cement 234,440; paint 142,730 gallons. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 244,000,000 (244,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) none (1,942,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 178,000 (248,000). Households. Average household size (2004) 6.0. Public debt (external, outstanding; January 2006): US$1,467,100,000. Population economically active (2003-04): total 2,005,900; activity rate of total population 40.0% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 68.2%; female 53.6%). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 64; remittances (2006) 2; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 14; official development assistance (2005) 343. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 32; remittances (2006) 2. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 8.0%, in permanent crops 1.0%, in pasture 30.7%; overall forest area (2005) 38.5%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; c.i.f.): Le 1,169,446,800,000 (fuels 37.3%; machinery and transport equipment 17.5%; food and live animals 14.2%; chemicals and chemical products 6.1%). Major import sources: Cote d’Ivoire 9.7%; US 8.1%; China 8.0%; UK 7.0%; The Netherlands 5.8%. Exports (2006; f.o.b.): Le 684,311,100,000 (diamonds 54.1%; rutile 12.3%; bauxite 10.2%; cacao 5.0%; reexports 12.3%). Major export destinations: Belgium 51.7%; US 19.0%; The Netherlands 6.7%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2002; Marampa Mineral Railway; there are no passenger railways): length 84 km. Roads (2002): total length 11,300 km (paved 8%). Vehicles (2003): passenger cars 17,439; trucks and buses 12,428. Air transport: passenger-km (2001) 73,000,000; metric ton-km cargo (2004) 8,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 16,000 (3.3); televisions (2003): 63,000 (13); telephone land-lines (2002): 24,000 (4.8); cellular telephone subscribers (2003): 113,000 (23); personal computers (1999): 100; total Internet users (2004): 10,000 (2).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2004): percentage of total population having: no formal schooling 62.2%; incomplete/complete primary 24.6%; lower secondary 6.4%; upper secondary 4.2%; vocational 2.0%; incomplete/complete higher 0.6%. Literacy (2004): total population ages 10 and over literate 39%; males literate 49%; females literate 29%. Health: physicians (2004) 162 (1 per 30,384 persons); hospital beds (2001) 2,770 (1 per 1,680 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 162.6. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 1,875 (vegetable products 95%, animal products 5%); 102% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 12,500 (army 98%, navy 2%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.0%; per capita expenditure US$2.
Background
The earliest inhabitants of Sierra Leone were probably the Buloms; the Mende and Temne peoples arrived in the 15th century. The coastal region was visited by the Portuguese in the 15th century, and by 1495 there was a Portuguese fort on the site of modern Freetown. European ships visited the coast regularly to trade for slaves and ivory, and the English built trading posts on offshore islands in the 17th century. British abolitionists and philanthropists founded Freetown in 1787 as a private venture for freed and runaway slaves. In 1808 the coastal settlement became a British colony. The region became a British torate in 1896. It achieved independence in 1961 and became a republic in 1971. It was marked by political and economic turmoil in the late 20th century as successive military regimes tried to assume power. UN peacekeeping forces were stationed there but were ineffectual in preventing bloodletting and atrocities.
Recent Developments
Six years after the end of a decadelong civil war, the increasingly disillusioned people of Sierra Leone yearned for the implementation of an effective policy to end poverty in their mineral-rich country, which ranked last out of 177 countries in the United Nations Development Programme’s human development index for 2007-08. Major priorities for the new regime of businessman Ernest Bai Koroma, inaugurated as Sierra Leone’s president in September 2007, were to defuse ethnic tensions, stem unemployment, restore electricity, and continue the crackdown on the “blood diamonds” trade that had disrupted international trade and investment.
Singapore
Official name: Xinjiapo Gongheguo (Chinese); Re-publik Singapura (Malay); Cingkappur Kudiyarasu (Tamil); Republic of Singapore (English). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with one legislative house (Parliament [94]). Head of state: President Sellapan Rama (S.R.) Nathan (from 1999). Head of state government: Prime Minister Lee Hsien Loong (from 2004). Capital: Singapore. Official languages: Chinese; Malay; Tamil; English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Singapore dollar (S$) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = S$1.36.
Demography
Area: 271.8 sq mi, 704.0 sq km. Population (2007): 4,564,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 16,792, persons per sq km 6,483. Urban: 100%. Sex distribution (2007): male 49.48%; female 50.52%. Age breakdown (2007): under 15, 18.9%; 15-29, 20.2%; 30-44, 25.8%; 45-59, 22.7%; 60-74, 9.1%; 75-84, 2.6%; 85 and over, 0.7%. Ethnic composition (2007): Chinese 74.8%; Malay 13.5%; Indian 9.0%; other 2.7%. Religious affiliation (2000): Buddhist/Taoist/Chinese folk-religionist 51.0%; Muslim 14.9%; Christian 14.6%; Hindu 4.0%; traditional beliefs 0.6%; nonreligious 14.9%. Location: southeastern Asia, islands between Malaysia and Indonesia.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 10.1 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 4.3 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 1.26. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 78.0 years; female 81.8 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue: S$31,072,000,000 (income tax 48.1%; goods and services tax 12.7%; fees and charges 6.8%; assets taxes 6.6%; customs and excise duties 6.3%). Expenditures: S$29,875,-000,000 (security and external relations 42.8%; education 21.3%; transportation 6.8%; health 6.2%; trade and industry 5.6%). Public debt (2006): US$122,000,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): vegetables 5,800,orchids (15% of the world market) and other ornamental plants are cultivated for export; livestock (number of live animals) 250,000 pigs, 2,000,000 chickens; fisheries production 7,837 (from aquaculture 76%); aquarium fish farming is also an important economic pursuit; Singapore produces 30% of the world’s ornamental fish. Manufacturing (value added in S$’000,000; 2005): pharmaceuticals 8,204; semiconductors 7,636; computer-related electronics 7,218. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 38,213,000,000 (34,761,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) none (324,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 31,094,000 (8,794,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) none (6,303,000,000). Gross national income (2006): US$127,980,000,000 (US$29,210 per capita). Households (2003). Average household size 3.6; income per household S$58,404 (US$33,523); sources of income: wages and salaries 82.5%, self-employment 12.3%; expenditure: housing costs and furnishings 22.4%, transportation and communications 21.4%, food 21.3%, education 7.8%. Population economically active (2006): total 1,880,800; activity rate of total population 52.1% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 71.3%; female 42.5%; unemployed 3.6%). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 5,736; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 13,653. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 9,853; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 7,926. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 0.9%, in permanent crops 0.3%; overall forest area (2005) 3.4%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; c.i.f.): S$378,924,000,000 (machinery and apparatus [including parts] and transport equipment 54.7%; crude and refined petroleum 19.7%; chemicals and chemical products 6.0%). Major import sources (2005): Malaysia 14.4%; US 12.4%; China 10.8%; Japan 10.1%; Indonesia 5.5%. Exports (2006; f.o.b.):S$431,559,000,000(domestic exports 52.7%, of which electronics 18.2%, petroleum [all forms] 13.8%, chemicals and chemical products 9.2%; reexports 47.3%, of which electronics, nonelectrical machinery and transport equipment 34.6%). Major export destinations (2005): Malaysia 14.7%; US 11.5%; Indonesia 10.7%; Hong Kong 10.4%; China 9.5%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2006): length 39 km. Roads (2005): total length 3,234 km (paved [2004] 99%). Vehicles (2006): passenger cars 476,333; trucks and buses 158,586. Air transport (2006; Singapore Airlines, Singapore Airlines Cargo, and SilkAir only): pas-senger-km 90,288,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 12,809,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 1,624,000 (383); televisions (2005): 1,847,000 (425); telephone landlines (2006): 1,854,000 (413); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 4,789,000 (1,068); personal computers (2005): 2,960,000 (682); total Internet users (2006): I,717,000 (383); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 797,000 (178).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2005). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: no schooling 16.4%; primary education 22.0%; lower secondary 21.3%; upper secondary 15.1%; technical 8.2%; university 17.0%. Literacy (2004): 94.6% Health (2006): physicians 6,931 (1 per 647 persons); hospital beds II,545 (1 per 388 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 2.6.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 72,500 (army 69.0%, navy 12.4%, air force 18.6%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 4.7%; per capita expenditure US$1,274.
Background
Long inhabited by fishermen and pirates, Singapore was an outpost of the Sumatran empire of Srivijaya until the 14th century, when it passed to Java and then Siam. It became part of the Malacca empire in the 15th century. In the 16th century the Portuguese controlled the area; they were followed by the Dutch in the 17th century. In 1819 Singapore was ceded to the British East India Co., becoming part of the Straits Settlements and the center of British colonial activity in Southeast Asia. The Japanese occupied the islands in 1942-45. In 1946 it became a crown colony. It achieved full internal self-government in 1959, became a part of Malaysia in 1963, and gained independence in 1965. It is influential in the affairs of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations. The country’s dominant voice in politics for 30 years after independence was Lee Kuan Yew.
Recent Developments
In Singapore in 2007 the property market finally awoke—with a vengeance—from a five-year slumber. Lured by the prospect of becoming millionaires overnight, many property owners put their buildings on the market for collective sale. Proceeds from these collective sales were estimated to hit S$6 billion (about US$4.1 billion) in 2008. Even as the property marketsurged in 2007 (private housing prices increased 31.2% for the year), so too did inflation, which was projected to rise to as much as 5.5% in 2008, on the back of higher oil and food prices. The overall economy grew by 7.8% in 2007.
Slovakia
Official name: Slovenska Republika (Slovak Republic). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with one legislative house (National Council [150]). Chief of state: President Ivan Gasparovic (from 2004). Head of government: Prime Minister Robert Fico (from 2006). Capital: Bratislava. Official language: Slovak. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Slovak koruna (Sk) = 100 halura; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = Sk 19.15.
Demography
Area: 18,933 sq mi, 49,035 sq km. Population (2007): 5,396,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 285.0, persons per sq km 110.0. Urban (2006): 55.4%. Sex distribution (2005): male 48.54%; female 51.46%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 16.7%; 15-29, 24.5%; 30-44, 21.8%; 45-59, 20.7%; 60-74, 11.3%; 75-84, 4.2%; 85 and over, 0.8%. Ethnic composition (2001): Slovak 85.8%; Hungarian 9.7%; Rom (Gypsy) 1.7%; Czech 0.8%; Ruthenian and Ukrainian 0.7%; other 1.3%. Religious affiliation (2001): Roman Catholic 68.9%; Protestant 9.2%, of which Lutheran 6.9%, Reformed Christian 2.0%; Greek Catholic 4.1%; Eastern Orthodox 0.9%; nonreligious 13.0%; other/unknown 3.9%. Major cities (2004): Bratislava 425,155; Kosice 235,006; Presov 91,767; Nitra 85,742; Zilina 85,268. Location: central Europe, bordering Poland, Ukraine, Hungary, Austria, and the Czech Republic.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 10.0 (world avg. 20.3); (2004) within marriage 75.2%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 9.9 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 0.1 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2004): 1.25. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 70.1 years; female 77.9 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: Sk 466,400,000,000 (tax revenue 46.6%, of which taxes on goods and services 37.2%; social security contributions 39.9%; nontax revenue 10.4%; grants 3.1%). Expenditures: Sk 515,900,000,000 (social protection 32.4%; general administration 21.8%; health 18.5%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): sugar beets 1,370,908, wheat 1,342,693, corn (maize) 838,000; livestock (number of live animals) 1,108,265 pigs, 527,889 cattle; roundwood (2005) 9,302,000 cu m, of which fuel-wood 3%; fisheries production (2005) 2,648 (from aquaculture 36%). Mining and quarrying (2005): magnesite 447,700; iron ore (metal content) 300,000; kaolin 85,000. Manufacturing (value added in Sk ’000,000; 2004): base and fabricated metals 54,558; transportation equipment 26,251; electrical equipment 26,146. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 30,567,000,000 (28,705,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2004) none (5,151,000); lignite (metric tons; 2005) 2,511,000 ([2004] 3,589,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) 279,000 (41,876,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 5,569,000 (2,337,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 169,000,000 (6,555,000,000). Population economically active (2006): total 2,654,800; activity rate of total population 49.2% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 68.9%; female 45.8%; unemployed [March 2006-February 2007] 10.0%). Households (2003). Average household size 2.9; average annual gross income per household Sk 288,388 (US$7,842); sources of income: wages and salaries 73.9%, transfers 19.6%; expenditure: food and nonalcoholic beverages 25.7%, energy 18.8%, transportation 9.0%, recreation 7.5%, clothing and footwear 7.3%. Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$3,340,000,000. Gross national income (2006): US$52,921,000,000 (US$9,820 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 1,210; remittances (2006) 424; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 1,921. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 486; remittances (2006) 16. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 29.4%, in permanent crops 0.6%, in pasture 16.5%; overall forest area (2005) 40.1%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): US$34,292,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 25.8%; mineral fuels 15.4%; road vehicles 12.3%; base and fabricated metals 10.0%). Major import sources: Germany 25.1%; Czech Republic 19.3%; Russia 10.5%; Austria 6.1%; Poland 4.7%. Exports (2004): US$27,603,000,000 (machinery, apparatus, and parts 21.2%; passenger vehicles 15.4%; iron and steel 9.1%; parts and accessories of passenger vehicles 7.5%; chemicals and chemical products 5.4%; refined petroleum 5.2%). Major export destinations (2005): Germany 26.2%; Czech Republic 14.1%; Austria 7.1%; Italy 6.7%; Poland 6.3%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2005): length 3,658 km; pas-senger-km 2,181,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 9,463,000,000. Roads (2004): total length 43,000 km (paved 87%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 1,337,425; trucks and buses 179,412. Airtransport (2006; SkyEurope and Slovak airlines only): passen-ger-km 2,596,207,000; metric ton-km cargo 29,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 894,000 (166); televisions (2004): 2,285,000 (425); telephone landlines (2006): 1,167,000 (216); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 4,893,000 (908); personal computers (2005): 1,929,000 (358); total Internet users (2006): 2,256,000 (418); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 317,000 (59).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2002). Percentage of population ages 25-64 having: primary education 1%; complete lower secondary 13%; complete upper secondary 75%; higher 11%. Literacy (2001): total population ages 15 and over literate: virtually 100%. Health (2005): physicians 20,158 (1 per 267 persons); hospital beds 48,622 (1 per 111 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 6.4. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,592 (vegetable products 73%, animal products 27%); 128% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 15,223 (army 39.7%, air force 24.0%, headquarters staff 17.2%, support/training 19.1%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.7%; per capita expenditure US$153.
Background
Slovakia was inhabited in the first centuries ad by Il-lyrian, Celtic, and Germanic tribes. Slovaks settled there around the 6th century. It became part of Great Moravia in the 9th century but was conquered by the Magyars c. 907. It remained in the kingdom of Hungary until the end of World War I, when the Slovaks joined the Czechs to form the new state of Czechoslovakia in 1918. In 1938 Slovakia was declared an autonomous unit within Czechoslovakia; it was nominally independent under German protection in 1939-45. After the expulsion of the Germans, Slovakia joined a reconstituted Czechoslovakia, which came under Soviet domination in 1948. In 1969 a partnership between the Czechs and Slovaks established the Slovak Socialist Republic. The fall of the communist regime in 1989 led to a revival of interest in autonomy, and Slovakia became an independent nation in 1993.
Recent Developments
The Slovak economy surged at a record pace in 2007 (GDP grew 13.2% during the year) as strong foreign demand contributed to a sharp narrowing of external deficits. Moreover, productivity gains continued to outpace real wage growth (though average monthly wages rose by 7.4%), keeping concerns about economic overheating to a minimum. The value of construction in the country grew by 9.8%. By the standards of Eurostat’s Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices, Slovakia’s inflation fell to about 2%, well within the Maastricht Treaty limit for entry to the euro zone. Thus, Slovakia appeared to be on track to adopt the euro in January 2009. On the downside, Slovakia recorded the highest unemployment rate (11.0%) in the EU during the year, falling behind Poland.
Slovenia
Official name: Republika Slovenija (Republic of Slovenia). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with two legislative houses (National Council [40]; National Assembly [90]). Head of state: President Danilo Turk (from 2007). Head of government: Prime Minister Janez Jansa (from 2004). Capital: Ljubljana. Official language: Slovene. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 euro (€) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = €0.63 (the euro replaced the Slovenian tolar [SIT] 1 Jan 2007, at the rate of €1 = SIT 239.64).
Demography
Area: 7,827 sq mi, 20,273sq km. Population (2007): 2,011,000. Density(2007): persons persq mi 256.9, persons per sq km 99.2. Urban (2005): 51.0%. Sex distribution (2006): male 49.09%; female 50.91%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 14.0%; 15-29, 20.3%; 30-44, 22.5%; 45-59, 22.3%; 60-74, 14.1%; 75-84, 5.6%; 85 and over, 1.2%. Ethnic composition (2002): Slovene 91.2%; Serb 2.2%; Croat 2.0%; Bosniac (ethnic Muslim) 1.8%; other 2.8%. Religious affiliation (2002): Roman Catholic 57.8%; Muslim 2.4%; Orthodox 2.3%; Protestant 0.8%; non-religious/atheist 10.2%; other/unknown/unspecified 26.5%. Major cities (2005; populations of municipalities): Ljubljana 266,941; Maribor 111,073; Kranj 52,938; Koper 49,479; Celje 48,607. Location: southeastern Europe, bordering Austria, Hungary, Croatia, the Adriatic Sea, and Italy.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 9.4 (world avg. 20.3); within marriage 52.8%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 9.1 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 0.3 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 1.31. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 74.8 years; female 81.9 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:SIT 2,739,000,000,000 (tax revenue 51.7%, of which taxes on goods and services 33.1%, personal income tax 9.4%; social security contributions 38.3%; nontax revenue 7.4%; grants 2.6%). Expenditures: SlT 2,846,000,000,000 (social protection 40.8%; health 14.6%; general administration 12.6%; education 12.6%). Public debt (2006): US$9,900,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): corn (maize) 276,106, sugar beets 262,031, wheat 134,449; livestock (number of live animals) 547,430 pigs, 452,517 cattle; roundwood (2005) 2,732,822 cu m, of which fuelwood 35%; fisheries production (2005) 2,759 (from aquaculture 56%). Mining and quarrying (2005): sand and gravel 11,000,000; salt 125,000. Manufacturing (value added in SlT ’000,000; 2005): chemicals and chemical products 189,495; fabricated metal products 177,195; nonelectrical machinery 153,770. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2006) 14,117,000,000 (13,298,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2004) none (45,000); lignite (metric tons; 2006) 4,522,000 ([2004] 5,329,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2005) 2,200 ([2004] negligible); petroleum products (metric tons; 2006) none (2,269,000); natural gas (cu m; 2006) 4,000,000 (1,105,000,000). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 8.6%, in permanent crops 1.4%, in pasture 15.3%; overall forest area (2005) 62.8%. Households (2005). Average household size 2.7; average annual income per household SlT 4,151,377 (US$21,542); sources of income: wages and salaries 53.4%, transfers 27.9%, self-employment 5.1%; expenditure: housing and energy 20.1%, transportation 16.2%, food and nonalcoholic beverages 15.9%, recreation and culture 9.2%. Gross national income (at current market prices; 2006): US$38,197,000,000 (US$19,020 per capita). Population economically active (2006): total 1,030,000; activity rate of total population 51.4% (participation rates: ages 15-64,71.3%; female 46.7%; unemployed [April 2006-March 2007] 5.6%). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 1,894; remittances (2006) 282; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 732. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 1,019; remittances (2006) 119; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 377.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; c.i.f.): €18,341,000,000 (machinery and transport equipment 32.5%, of which road vehicles 11.2%; chemicals and chemical products 12.2%; mineral fuels 11.2%, of which petroleum and petroleum products 7.0%; iron and steel 5.7%). Major import sources:Germany 20.4%; Italy 18.6%; Austria 12.2%; France 6.2%; Croatia 4.0%. Exports (2006; f.o.b.): €16,757,000,000 (machinery and transport equipment 38.2%, of which road vehicles 13.6%, electrical machinery and apparatus 9.9%; chemicals and chemical products 13.7%, of which medicines and pharmaceuticals 6.9%; furniture and parts 5.1%). Major export destinations: Germany 19.7%; Italy 12.9%; Croatia 8.7%; Austria 8.7%; France 6.8%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2006): length 1,228 km; pas-senger-km 793,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 3,373,000,000. Roads (2006): total length 38,562 km (paved 100%). Vehicles (2006): passenger cars 980,261; trucks and buses 72,409. Air transport (2006): passenger-km 1,043,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 3,436,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 362,000 (181); televisions (2005): 559,000 (279); telephone landlines (2006): 837,000 (417); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 1,820,000 (907); personal computers (2005): 808,000 (404); total Internet users (2006): 1,251,000 (623); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 264,000(132).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2004). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: no formal schooling 0.6%; incomplete and complete primary education 28.6%; secondary 6.0%; vocational 50.2%; some higher 5.0%; undergraduate 8.7%; advanced degree 0.9%. Literacy (2006): virtually 100%. Health: physicians (2005) 4,620 (1 per 433 persons); hospital beds (2004) 9,584 (1 per 208 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 3.4. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,756 (vegetable products 65%, animal products 35%); 139% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 6,550 (army 100%). Military expenditure as percentage of GNI (2005): 1.5%; per capita expenditure US$257.
Background
The Slovenes settled the region in the 6th century ad. In the 8th century it was incorporated into the Frank-ish empire of Charlemagne, and in the 10th century it came under Germany as part of the Holy Roman Empire. Except for 1809-14, when Napoleon ruled the area, most of the lands belonged to Austria until the formation of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes in 1918. It became a constituent republic of Yugoslavia in 1946 and received a section of the former Italian Adriatic coastline in 1947. In 1990 Slovenia held the first contested multiparty elections in Yugoslavia since before World War II. In 1991 itseceded from Yugoslavia; its independence was internationally recognized in 1992.
Recent Developments
Slovenia in 2007 became the 13th country in the European Union to adopt the euro as its currency, replacing the tolar. The country assumed the presidency of the European Union during the first half of 2008. Thus, Slovenia, the first of the 10 states that joined the EU in 2004 to adopt the euro, was also the first of that group to accede to the EU rotating presidency. A third major step came in December 2007, when extension of the Schengen Agreement abolished Slovenia’s border controls with fellow members Italy, Austria, and Hungary and made Slovenia’s border with Croatia an external border of the EU.