Cuba
Official name: República de Cuba (Republic of Cuba).Form of government: unitary socialist republic with one legislative house (National Assembly of the People’s Power [609]). Head of state and government: President Raul Castro Ruz (from 2008). Capital: Havana. Official language: Spanish. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Cuban peso (CUP) = 100 cen-tavos; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = 1.00 CUP.
Demography
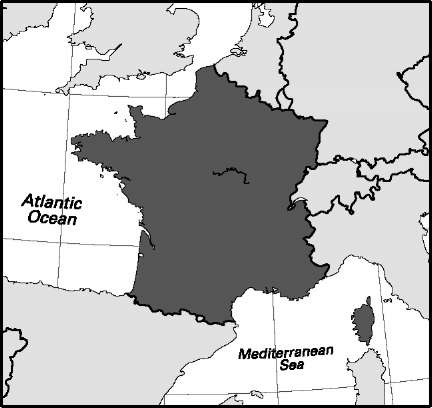
Area: 42,804 sq mi, 110,861 sq km. Population (2007): 11,238,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 264.9, persons per sq km 102.3. Urban (2005): 75.5%. Sex distribution (2006): male 50.08%; female 49.92%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 19.2%; 15-29, 20.5%; 30-44, 27.6%; 45-59, 17.0%; 60-74,10.8%; 75-84, 3.6%; 85 and over, 1.3%. Ethnic composition (1994): mixed 51.0%; white 37.0%; black 11.0%; other 1.0%. Religious affiliation (2005): Roman Catholic 47%; Protestant 5%; nonreligious 22%; other 26% (up to 70% of the population also practices Santerfa). Major cities (2002): Havana 2,201,610; Santiago de Cuba 423,392; Camaguey 301,574; Holguin 269,618; Santa Clara 210,220. Location: island southeast of Florida (US), between the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 9.9 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 7.2 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 2.7 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 1.40. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 75.1 years; female 79.0 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue: CUP 30,012,400,000 (tax revenue 73.6%; nontax revenue 26.4%). Expendi-tures:CUP 31,742,400,000 (current revenue 84.2%, of which education 14.8%, social security contributions 11.2%, health 9.7%, housingand communityser-vices 7.2%; capital expenditure 15.8%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2004): US$12,000,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): raw sugar (2006) 1,300,000, tomatoes 802,600, plantains 770,000; livestock (number of live animals) 3,950,000 cattle, 2,361,000 sheep, 1,626,000 pigs; roundwood 2,579,000 (2005) cu m, of which fuelwood 70%; fisheries production 52,387 (from aquaculture 43%). Mining and quarrying (2004): nickel (metal content) 71,944; cobalt (metal content) 4,055. Manufacturing (2006): cement 1,713,900; steel 257,200; cigarettes (2004) 12,800,000,000 units. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2006) 16,468,500,000 ([2004] 13,270,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) none (13,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) 24,500,000 (31,300,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 1,896,000 (5,104,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 704,000,000 (704,000,000). Population economically active (2004): total 4,729,386; activity rate 42.1% (participation rates: ages 15 and over, 52.3%; female 36.5%; unemployed [2006] 1.9%). Gross national income (2006): US$51,504,000,000 (US$4,571 per capita). Households. Average household size (2002) 3.2. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) I,920; remittances (2003) 1,200; official development assistance (2005) 83 (commitments). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 27.9%, in permanent crops 6.6%, in pasture 26.1%; overall forest area (2005) 24.7%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2001; f.o.b. in trading partners and c.i.f. for balance of trade and commodities): US$4,838,-700,000 (machinery and transport equipment 25.5%, of which motor vehicles and parts 5.0%; food and live animals 15.7%, of which cereals 6.5%; refined petroleum 13.1%; crude petroleum 6.6%). Major import sources (2004): Spain 15.4%; Venezuela 13.7%; US II.5%; China 8.0%; Canada 6.6%. Exports (2001): US$1,660,600,000 (raw sugar 32.6%; nickel [all forms] 27.8%; raw tobacco and tobacco products 15.8%; fresh and frozen fish 4.6%; medicinal and pharmaceutical products 2.4%). Major export destinations (2004): The Netherlands 23.5%; Canada 21.9%; China 8.3%; Russia 7.8%; Spain 6.6%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2003; Cuban Railways only; length of railways exclusively for the transport of sugar equals 7,742 km): length 4,226 km; passenger-km (2001) 1,766,600; metric ton-km cargo 806,900,000. Roads (1999): total length 60,858 km (paved 49%). Vehicles (1998): passenger cars 172,574; trucks and buses 185,495. Air transport (2003; Cubana only): passenger-km 2,044,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 40,933,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 400,000 (36); televisions (2004): 3,000,000 (267); telephone landlines (2006): 983,000 (101); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 153,000 (14); personal computers (2005): 377,000 (33); total Internet users (2006): 240,000 (21).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2002): Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling 14.1%; primary education 17.2%; secondary 26.6%; vocational/technical/teacher training 32.8%; university 9.3%. Literacy (2004): total population ages 15 and over literate 96.9%; males literate 97.0%; females literate 96.8%. Health (2006): physicians 70,594 (1 per 160 persons); hospital beds (2004) 70,079 (1 per 160 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 5.3. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,547 (vegetable products 88%, animal products 12%); 183% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 49,000 (army 77.6%, navy 6.1%, air force 16.3%); US military forces at Naval Base Guantanamo Bay (2005) 950. Military expenditure as percentage of GdP (2005): 3.8%; per capita expenditure US$151.
Background
Several Indian groups, including the Ciboney, the Taino, and the Arawak, inhabited Cuba at the time of the first Spanish contact. Christopher Columbus claimed the island for Spain in 1492, and the Spanish conquest began in 1511, when the settlementofBara-coa was founded. The native Indians were eradicated over the succeeding centuries, and African slaves, from the 18th century until slavery was abolished in 1886, were imported to work the sugar plantations. Cuba revolted unsuccessfully against Spain in the Ten Years’ War (1868-78); a second war of independence began in 1895. In 1898 the US entered the war; Spain relinquished its claim to Cuba, which was occupied by the US for three years before gaining its independence in 1902. The US invested heavily in the Cuban sugar industry in the first half of the 20th century, and this, combined with tourism and gambling, caused the economy to prosper. Inequalities in the distribution of wealth persisted, however, as did political corruption. In 1958-59 the communist revolutionary Fidel Castro overthrew Cuba’s longtime dictator, Fulgencio Batista, and established a socialist state aligned with the Soviet Union, abolishing capitalism and nationalizing foreign-owned enterprises. Relations with the US deteriorated, reaching a low point with the 1961 Bay of Pigs invasion and the 1962 Cuban missile crisis. In 1980 about 125,000 Cubans, including many that their government officially labeled “undesirables,” were shipped to the US in the so-called “Mariel boat lift.” When communism collapsed in the USSR, Cuba lost important financial backing and its economy suffered greatly. The latter gradually improved in the 1990s with theencouragementoftourism,though diplomatic relations with the US were not resumed.
Recent Developments
Following a severe stomach illness, longtime Cuban leader Fidel Castro had stepped down from power in July 2006, and in February 2008 he was officially succeeded as president by his brother Raul Castro, who had been acting president. Cuba’s relations with Venezuelan Pres. Hugo Chavez continued to deepen. Chavez met with Fidel several times, and in February 2007 the two countries signed agreements for US$1.5 billion in projects, including the development of 11 ethanol plants. In August the Venezuelan state oil company announced that it would explore for offshore oil in Cuban waters. Honduras named its first full ambassador to Cuba in 45 years, and in April Spain’s foreign minister became the highest-level Spanish official to have visited Cuba in nearly a decade. Top Chinese officials also met with Raul to pledge continuing political and economic cooperation, and Russia announced in November that it was restructuring Cuba’s US$166 million debt. US-Cuban relations remained frozen, however. In the US Congress, a new Democratic majority introduced several proposals to repeal trade and travel sanctions, but none were passed.
Cyprus
Two de facto states currently exist on the island of Cyprus: the Republic of Cyprus (ROC), predominantly Greek in character, occupying the southern two-thirds of the island, which is the original and still the internationally recognized de jure government of the whole island; and the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus (TRNC), proclaimed unilaterally 15 Nov 1983, on territory originally secured for the Turkish Cypriot population by the 20 Jul 1974 intervention of Turkey. Only Turkey recognizes the TRNC, and the two ethnic communities have failed to reestablish a single state. Provision of separate data below does not imply recognition of either state’s claims but is necessitated by the lack of unified data.
Area: 3,572 sq mi, 9,251 sq km. Population (2007): 1,047,000; includes 150,000-160,000 “settlers” from Turkey; excludes 3,300 British military in the Sovereign Base Areas (SBA) in the ROC and 850 UN peacekeeping forces. Location: the Middle East, island in the Mediterranean Sea, south of Turkey.
Republic of Cyprus
Official name: Kipriakf Dhimokratfa (Greek); Kibris Cumhuriyeti (Turkish) (Republic of Cyprus). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with a uni-cameral legislature (House of Representatives [80]). Head of state and government: President Dimitris Christofias (from 2008). Capital: Lefkosia (Nicosia). Official languages: Greek; Turkish. Monetary unit: 1 euro (€) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = €0.63.
Demography
Area (includes 99 sq mi [256 sq km] of British mili-tarySBAand 107 sq mi (278 sq km) of the UN Buffer Zone): 2,276 sq mi, 5,896 sq km. Population (2007): 781,000. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 18.4%; 15-29, 23.9%; 30-44, 21.8%; 45-59, 19.2%; 60-74,11.7%; 75-84, 3.9%; 85 and over, 1.1%. Ethnic composition (2000): Greek Cypriot 91.8%; Armenian 3.3%; Arab 2.9%, of which Lebanese 2.5%; British 1.4%; other 0.6%. Religious affiliation (2001): Greek Orthodox 94.8%; Roman Catholic 2.1%, of which Maronite 0.6%; Anglican 1.0%; Muslim 0.6%; other 1.5%. Urban areas (2004): Lefkosia (ROC only) 219,200; Limassol 172,500; Larnaca 77,000.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 11.2 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 6.8 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005) 1.42. Life expectancy at birth (2004-05): male 77.0 years; female 81.7 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: £C 3,273,700,000 (excises and import duties 41.4%; income tax 22.3%; social security contributions 19.9%). Expenditures: £C 3,459,300,000 (current expenditures 91.3%; development expenditures 8.7%). Gross national income (at 2006 market prices): US$18,191,000,000 (US$23,735 per capita). Production. Agriculture (in ’000 metric tons; 2005): potatoes 116.0, grapes 80.9, olives 27.5. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2005): food products, beverages, and tobacco 281; cement, bricks, and ceramics 98; base metals and fabricated metal products 67. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 4,338,000,000 (3,931,000,000). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2006) 2,240; remittances (2006) 154; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 1,027. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 932; remittances (2006) 278; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 450. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 12.4%, in permanent crops 4.4%, in pasture 0.4%; overall forest area (2005) 18.9%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): £C 2,967,000,000 (consumer goods 33.0%; fuels and lubricants 16.2%; motor vehicles 10.2%; capital goods 9.1%). Major import sources: Greece 17.1%; Italy 10.1%; UK 8.8%; Germany 8.3%; Israel 7.0%. Exports (2005; f.o.b.): £C 672,000,000 (reexports 49.1%; domestic exports 35.7%, of which fresh vegetables, fruits, and nuts 8.1%, pharmaceuticals 7.5%; ships’ stores 15.2%). Major export destinations: France 16.9%; UK 16.8%; Greece 11.4%; Germany 5.3%; UAE 2.6%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2004): total length 12,059 km (paved 65%). Vehicles (2004): cars 335,634; trucks and buses 121,024. Air transport (2005; Cyprus Airways only): passenger-km 3,187,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 46,607,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 77,000 (104); televisions (2003): 276,000 (384); telephone landlines (2006): 408,000 (483); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 778,000 (921); personal computers (2004): 249,000 (309); total Internet users (2006): 357,000 (422); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 50,000 (59).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2004). Percentage of population ages 20 and over having: no formal schooling/incomplete primary education 10%; complete primary 20%; secondary 45%; higher education 25%. Health (2004): physicians 1,965 (1 per 375 persons); hospital beds 3,075 (1 per 240 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 4.6.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 10,000 (national guard 100%); Greek troops 950. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.4%; per capita expenditure US$241.
Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus
Official name: Kuzey KibrisTurk Cumhuriyeti (Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus). Capital: Lefkosa (Nicosia). Official language: Turkish. Monetary unit: 1 new Turkish lira (YTL) = 100 kurush; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = YTL 1.25. Population (2007; includes 150,000-160,000 “settlers” from Turkey; excludes 3,300 British military in the Sovereign Base Areas (SBA) in the ROC and 850 UN peacekeeping forces): 266,000 (Lefkosa [TRNC only; 2006] 49,237; Ma-gusa [Famagusta; 2006] 34,803; Girne [Kyrenia; 2006] 24,122; Guzelyurt [Morphou; 2006] 12,425). Ethnic composition (2006): Turkish Cypriot/Turkish 96.8%; other 3.2%. Budget (2004). Revenue: US$885,187,000 (indirect taxes 21.4%; direct taxes 18.8%; foreign aid 13.9%; loans 11.8%). Expenditures: US$885,187,000 (wages 29.7%; social transfers 22.9%; investments 10.3%; defense 6.2%). Imports (2004; c.i.f.): US$853,100,000 (machinery and transport equipment 35.7%; food 9.4%). Major import sources:Turkey 60.1%; UK 10.7%. Exports (2004; f.o.b.): US$62,000,000 (citrus fruits 32.4%; clothing 18.9%). Major export destinations: Turkey 46.3%; UK 21.8%. Health (2004): physicians 422 (1 per 573 persons); hospital beds 1,291 (1 per 186 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 10.0.
Background
Cyprus was inhabited by the early Neolithic Age; by the late Bronze Age it had been visited and settled by Mycenaeans and Achaeans, who introduced Greek culture and language, and it became a trading center. By 800 bc Phoenicians had begun to settle there. Ruled over the centuries by the Assyrian, Persian, and Ptolemaic empires, it was annexed by Rome in 58 BC. It was part of the Byzantine empire in the 4th-12th centuries ad. Cyprus was conquered by the English king Richard I in 1191. A part of the Venetian empire from 1489, it was taken by Ottoman Turks in 1571. In 1878 the British assumed control, and Cyprus became a British crown colony in 1925. It gained independence in 1960. Conflict between Greek and Turkish Cypriots led to the establishment of a UN peacekeeping mission in 1964. In 1974, fearing a movement to unite Cyprus with Greece, Turkish soldiers occupied the northern third of the country, and Turkish Cypriots established a functioning government, which obtained recognition only from Turkey. Conflict has continued to the present, and the UN peacekeeping mission has remained in place. Reunification talks have remained deadlocked.
The city of Nicosia is the capital ofthe Republic of Cyprus. It lies along the Pedieos River, in the center ofthe Mesaoria Plain between the Kyrenia Mountains
Recent Developments
Cypriots from both sides routinely crossed the border to shop and work in 2007, though the UN’s peacekeeping operations there remained. The Turkish Cypriots removed a controversial footbridge, and the Cyprus government dismantled a wall in Nicosia—both removals signifying a step toward establishing a pedestrian buffer zone—and in April 2008 officials opened a popular street in the capital as another border crossing. Problems persisted, however; title to confiscated real estate remained vexatious, for instance, and Turkish Cypriots protested the shipping of goods out of Greek Cypriot ports. European Union membership enhanced prosperity and provided economic stimulus to both zones, however, and tourism revenue increased on both sides.
Czech Republic
Official name: Ceska Republika (Czech Republic). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with two legislative houses (Senate [81]; Chamber of Deputies [200]). Chief of state: President Vaclav Klaus (from 2003). Head of government: Prime Minister Mirek Topolanek (from 2006). Capital: Prague. Official language: Czech. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 koruna (Kc) = 100 halura; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = 15.06 Kc.
Demography
Area: 30,450 sq mi, 78,866 sq km. Population (2007): 10,302,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 338.3, persons per sq km 130.6. Urban (2003): 74.3%. Sex distribution (2006): male 48.83%; female 51.17%. Age breakdown (2004): under 15, 14.9%; 15-29, 22.1%; 30-44, 21.3%; 45-59, 22.0%; 60-74,13.6%; 75-84, 5.2%; 85 and over, 0.9%. Ethnic composition (2001): Czech 90.4%; Moravian 3.7%; Slovak 1.9%; Polish 0.5%; German 0.4%; Silesian 0.1%; Rom (Gypsy) 0.1%; other 2.9%. Religious affiliation (2000): Christian 63.0%, of which Roman Catholic 40.4%, unaffiliated Christian 16.0%, Protestant (mostly Lutheran) 3.1%, independent Christian (mostly independent Catholic [Hussite Church ofthe Czech Republic]) 2.6%; atheist 5.0%; Jewish 0.1%; nonreligious 31.9%. Major cities (2005): Prague 1,181,610; Brno 366,757; Ostrava 310,078; Plzen 162,759; Olomouc 100,381. Location: central Europe, bordering Germany, Poland, Slovakia, and Austria.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 10.3 (world avg. 20.3); (2005) within marriage 68.3%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 10.2 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 0.1 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.28. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 72.9 years; female 79.1 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: Kc 1,279,628,000,000 (tax revenue 82.8%, of which social security contributions 32.5%, taxes on goods and services 26.8%, taxes on income and profits 22.4%; nontax revenue 4.5%; grants 2.5%; other 10.2%). Expenditures:Kc 1,279,054,000,000 (social security and welfare 29.1%; health 14.5%; transportation and communications 9.8%; education 9.6%; defense 4.4%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): wheat 4,145,000, sugar beets 3,496,000, barley 2,195,000; livestock (number of live animals) 2,877,000 pigs, 1,397,000 cattle; roundwood 15,510,000 cu m, of which fuel-wood 8%; fisheries production 24,697 (from aquaculture 83%). Mining and quarrying (2004): kaolin 4,100,000; feldspar 400,000. Manufacturing (value added in Kc ’000,000; 2003): base and fabricated metals 93,380; food, beverages, and tobacco products 81,440; electrical and optical equipment 70,800. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 84,333,000,000 (57,118,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2005) 13,248,000 ([2004] 9,860,000); lignite (metric tons; 2005) 48,780,000 ([2004] 48,430,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) 2,074,000 (45,500,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 4,806,000 (6,578,000); natural gas (cu m; 2005) 202,000,000 ([2004] 10,969,000,000). Households (2004). Average household size 2.5; average annual income per household Kc 295,011 (US$11,479); sources of income: wages and salaries 66.7%, transfer payments 20.6%, self-employment 8.8%, other 3.9%; expenditure: food and nonalcoholic beverages 21.3%, housing and energy 19.3%, transportation 11.0%, recreation and culture 10.9%, household furnishings 6.5%. Population economically active (2005): total 5,174,000; activity rate of total population 50.6% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 70.4%; female 44.1%; unemployed [2006] 7.1%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2004): US$12,020,000,000. Gross national income (2006): US$134,001,000,000 (US$13,152 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 4,631; remittances (2006) 1,058; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 6,438. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 2,405; remittances (2006) 2,645; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 490. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 39.6%, in permanent crops 3.1%, in pasture 12.6%; overall forest area (2005) 34.3%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004): Kc 1,746,671,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 31.1%; chemicals and chemical products 10.4%; motor vehicles 9.8%; base metals 7.6%; fabricated metals 4.5%). Major import sources: Germany 31.7%; Slovakia 5.4%; Italy 5.3%; China 5.2%; Poland 4.8%. Exports (2004): Kc 1,723,731,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 34.1%, of which telecommunications equipment 6.6%, office machinery and computers 6.1%; motor vehicles 15.7%; fabricated metal products 6.6%; base metals 6.4%). Major export destinations: Germany 36.2%; Slovakia 8.5%; Austria 6.0%; Poland 5.3%; UK 4.7%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2005): route length (2004) 9,441 km; passenger-km 6,667,000; metric ton-km cargo 14,866,000,000. Roads (2003): total length 127,672 km (paved 100%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 3,958,708; trucks and buses 435,235. Air transport (2005): passenger-km 9,735,710,000; metric ton-km cargo 44,668,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 1,861,000 (182); televisions (2003): 5,488,000 (538); telephone landlines (2006): 3,541,000 (345); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 12,150,000 (1,190); personal computers (2004): 5,100,000 (500); total Internet users (2006): 3,541,000 (347); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 1,087,000 (106).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2001). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: no formal schooling 0.2%; primary education 21.6%; secondary 68.7%; higher 9.5%. Literacy (2001): 99.8%. Health (2005): physicians 36,381 (1 per 282 persons); hospital beds 65,022 (1 per 158 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 3.3. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,303 (vegetable products 75%, animal products 25%); 163% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 22,272 (army 74.8%, air force 25.2%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.8%; per capita expenditure US$216.
Background
Until 1918 the history of what is now the Czech Republic was largely that of Bohemia. In that year the independent republic of Czechoslovakia was born through the union of Bohemia and Moravia with Slovakia. Czechoslovakia came under the domination of the Soviet Union after World War II, and from 1948 to 1989 it was ruled by a communist government. Its growing political liberalization was suppressed by a Soviet invasion in 1968. After communist rule collapsed in 1989-90, separatist sentiments emerged among the Slovaks, and in 1992 the Czechs and Slovaks agreed to break up their federated state. On 1 Jan 1993 the Czechoslovakian republic was peacefully dissolved and replaced by two new countries, the Czech Republic and Slovakia, with the region of Moravia remaining in the former. In 1999 the Czech Republic entered NATO and in 2004 the EU.
Recent Developments
Public finance reform was the most important policy issue in the Czech Republic in 2007. The government’s proposed fiscal package included a shift to a flat tax on personal income, a reduction in corporate tax rates, and the introduction of fees for health care services. Critics emerged on both ends of the spectrum; while the left argued that the reforms would help only the rich, the right claimed that the measures failed to simplify the taxation system. In the end, however, the package was approved. From an international perspective, an incredibly controversial issue was the decision by the US to build a radar base in the Czech Republic as part of a missile-defense shield, an action most Czechs opposed. In April 2008 NATO approved the shield, setting in motion plans to begin construction, though Russia vehemently protested.
Denmark
Official name: Kongeriget Danmark (Kingdom of Denmark). Form of government: constitutional monarchy with one legislative house (Folketing [179]). Chief of state: Queen Margrethe II (from 1972). Head of government: Prime Minister Anders Fogh Rasmussen (from 2001). Capital: Copenhagen. Official language: Danish. Official religion: Evangelical Lutheran. Monetary unit: 1 Danish krone (DKK; plural kroner) = 100 0re; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = DKK 4.72.
Demography
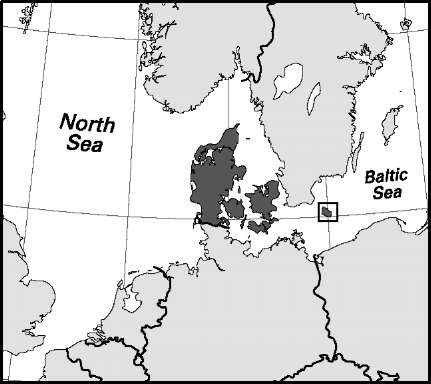
Area: 16,640 sq mi, 43,098 sq km (excludes the Faroe Islands and Greenland). Population (2007): 5,454,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 327.8, persons per sq km 126.5. Urban (2004): 85.4%. Sex distribution (2006): male 49.51%; female 50.49%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 18.6%; 15-29, 17.3%; 30-44, 21.9%; 45-59, 20.2%; 60-74, 15.0%; 75-84, 5.1%; 85 and over, 1.9%. Ethnic composition (2006): Danish 91.9%; Turkish 0.6%; German 0.5%; Iraqi 0.4%; Swedish 0.4%; Norwegian 0.3%; Bosnian 0.3%; other 5.6%. Religious affiliation (2006): Evangelical Lutheran 83.0%; other Christian 1.3%; Muslim 3.7%; nonreli-gious 5.4%; atheist 1.5%; other 5.1%. Major urban areas (2005): Greater Copenhagen 1,084,855; Arhus 228,764; Odense 152,060; Alborg 100,617; Fred-eriksberg 92,234. Location: northern Europe, bordering the North Sea, the Baltic Sea, and Germany.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 12.0 (world avg. 20.3); (2005) within marriage 54.3%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 10.3 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): I.7 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.80. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 75.6 years; female 80.2 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:DKK 882,940,000,000 (income/wealth taxes 54.4%; import/production taxes 31.0%; other 14.6%). Expenditures: DKK 821,539,000,000 (social protection 41.9%; education 15.2%; health 13.4%; economic affairs 6.6%; defense 2.9%). National debt (December 2006): US$57,887,-000,000. Population economically active (2005): total 2,876,100; activity rate of total population 53.1% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 80.2%; female 47.0%; unemployed [July 2005-June 2006] 5.0%). Households. Average household size (2005) 2.2; average annual disposable income per household (2003) DKK 270,176 (US$41,010); sources of gross income (2003): wages and salaries 63.8%, transfers 24.6%, property income 6.8%, self-employment 3.9%; expenditure (2003): housing 22.5%, transportation and communications 15.7%, food II.1%, recreation and entertainment 11.1%, energy 7.5%. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): wheat 4,826,000, barley 3,730,000, sugar beets 2,800,000; livestock (number of live animals) 13,466,000 pigs, 1,544,000 cattle; roundwood 2,285,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 55%; fisheries production 949,625 (from aquaculture 4%). Mining and quarrying (2005): sand and gravel 29,000,000 cu m; chalk 1,950,000. Manufacturing (value of sales in DKK ’000,000; 2005): food products 121,040; nonelectrical machinery and apparatus 66,050; computer and telecommunications equipment 49,078. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 40,260,000,000 (68,616,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2006) none (9,436,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006) 129,000,000 ([2005] 59,300,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 7,948,000 (7,050,000); natural gas (cu m; 2006) 10,358,000,000 (4,918,000,000). Gross national income (2006): US$278,800,000,000 (US$51,344 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 4,493; remittances (2006) 869; foreign direct investment (FDI; 2001-05 avg.) 3,067. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 5,690; remittances (2006) 1,792; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 3,830. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 53.4%, in permanent crops 0.2%, in pasture 9.1%; overall forest area (2005) 11.8%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): DKK 452,304,000,000 (machinery and apparatus [including parts] 23.1%; transport equipment and parts 16.9%; food, beverages, and tobacco 8.6%; chemical products 6.6%; fuels 6.6%; clothing and footwear 4.3%). Major import sources:Germany 20.7%; Sweden 13.7%; The Netherlands 6.6%; UK 6.0%; China 4.8%. Exports (2005; f.o.b.): DKK 506,920,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 26.4%; agricultural products 16.7%, of which swine meat 4.6%; mineral fuels and lubricants 10.3%; pharmaceuticals 7.6%; textiles and clothing 5.0%; furniture 3.2%). Major export destinations: Germany 17.3%; Sweden 13.3%; UK 9.0%; US 6.5%; Norway 5.3%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2004): route length 2,644 km; passenger-km 6,132,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 1,976,000,000. Roads (2006): total length 72,362 km (paved 100%). Vehicles (2006): passenger cars 2,020,013; trucks and buses 508,788. Airtransport (Danish share of Scandinavian Airlines System only): passenger-km (2005) 5,940,000,000; metric ton-km cargo (2004) 170,352,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 1,328,000 (246); televisions (2003): 5,264,000 (977); telephone landlines (2006): 3,098,000 (569); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 5,841,000 (1,073); personal computers (2004): 3,543,000 (659); total Internet users (2006): 3,171,000 (582); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 1,728,000 (317).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2004). Percentage of population ages 25-69 having: complete lower secondary/unknown 30.3%; complete upper secondary or vocational 43.9%; undergraduate 19.6%; graduate 6.2%. Literacy: 100%. Health: physicians (2002) 15,692 (1 per 342 persons); hospital beds (2004) 20,638 (1 per 262 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 4.4. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,494 (vegetable products 67%, animal products 33%).
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 21,180 (army 59.0%, air force 19.8%, navy 18.0%, other 3.2%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.8%; per capita expenditure US$640.
Background
The Danes, a Scandinavian branch of the Teutons, settled the area c. the 6th century AD. During the Viking period the Danes expanded their territory, and by the 11th century the united Danish kingdom included parts of what are now Germany, Sweden, England, and Norway. Scandinavia was united under Danish rule from 1397 until 1523, when Sweden became independent; a series of debilitating wars with Sweden in the 17th century resulted in the Treaty of Copenhagen (1660), which established the modern Scandinavian frontiers. Denmark gained and lostvar-ious other territories, including Norway, in the 19th and 20th centuries; it went through three constitutions between 1849 and 1915 and was occupied by Nazi Germany in 1940-45. A founding member of NATO (1949), Denmark adopted its current constitution in 1953. It became a member of the European Community in 1973 and modified its membership during the 1990s. The island of Zealand, on which Copenhagen stands, was connected to the central island of Funen by a rail tunnel and bridge in 1997. This ended more than 100 years of ferry service and cut the crossing time from an hour to under 10 minutes.
Recent Developments
With polls showing persistent opposition among Danes to their country’s continued presence in Iraq, Denmark in August 2007 withdrew its 460-strong military force from southern Iraq, where it had been operating since 2003 under British command, and the remaining 55 troops in the Basra province were removed in late December 2007. However, the country enlarged its contingent in Afghanistan to 662 soldiers by early 2008 (most in the turbulent Helmand province). International disapproval of Denmark’s tight immigration policy continued, with the Council of Europe challenging the government to soften its contentious stipulations for family reunification, drop stiff bank guarantees for immigrants, and call off cuts in welfare benefits for newly arrived immigrants. Meanwhile, Denmark enjoyed a robust economy, with almost four years of uninterrupted growth, the lowest unemployment in 33 years (about 3%), no foreign debt, and a budget surplus in excess of 3% of GDP.
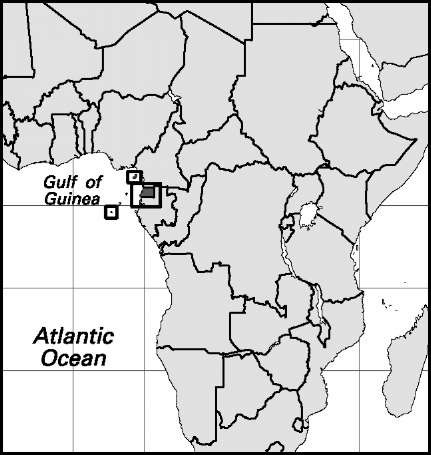
Djibouti
Official name: Jumhuriyah Jibuti (Arabic); Republique de Djibouti (French) (Republic of Djibouti). Form of government: multiparty republic with one legislative house (National Assembly [65]). Chief of state and head of government: President Ismail Omar Guelleh (from 1999), assisted by Prime Minister Dileita Muhammad Dileita (from 2001). Capital: Djibouti. Official languages: Arabic; French. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Djibouti franc (FDJ) = 100 centimes; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = FDJ 177.72.
Demography
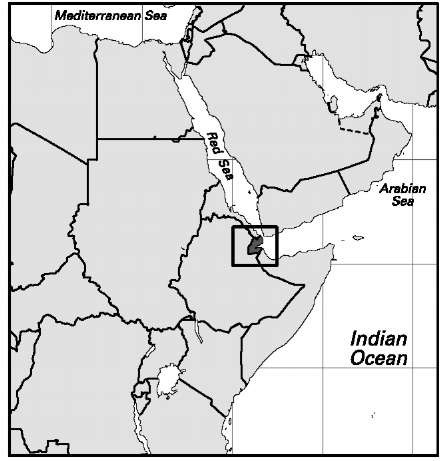
Area: 8,950 sq mi, 23,200 sq km. Population (2007): 496,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 55.4, persons persq km 21.4. Urban (2005): 86.1%. Sex distribution (2006): male 51.19%; female 48.81%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 43.3%; 15-29, 28.0%; 30-44, 13.7%; 45-59, 9.2%; 60-74, 5.1%; 75 and over, 0.7%. Ethnic composition (2000): Somali 46.0%; Afar 35.4%; Arab 11.0%; mixed African and European 3.0%; French 1.6%; other/unspecified 3.0%. Religious affiliation (2000): Muslim (nearly all Sunni) 94.1%; Christian 4.5%, of which Orthodox 3.0%, Roman Catholic 1.4%; nonreli-gious 1.3%; other 0.1%. Major city and towns: Djibouti (2006) 325,000; Dikhil (1991) 20,480; ‘Ali Sabih (1991) 16,423; Tadjoura (1991) 7,309. Location: eastern Africa, bordering Eritrea, the Red Sea, the Gulf of Aden, Somalia, and Ethiopia.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 39.5 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 19.3 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 20.2 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 5.31. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 41.9 years; female 44.5 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: FDJ 46,710,000,000 (tax revenue 65.8%, of which indirect taxes 26.3%, direct taxes 24.8%, transit taxes, harbor dues and other registration fees 14.7%; nontax revenue 17.5%; grants 16.7%). Expenditures: FDJ 46,378,000,000 (current expenditures 74.7%; capital expenditures 25.3%). Public debt (external, outstanding; February 2006): US$474,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): lemons and limes 1,800, dry beans 1,500, tomatoes 1,283; livestock (number of live animals) 512,000 goats, 466,000 sheep, 69,000 camels; fisheries production 260. Mining and quarrying: mineral production limited to locally used construction materials such as basalt and evaporated salt. Manufacturing (2003): products of limited value include furniture, nonalcoholic beverages, meat and hides, light electromechanical goods, and mineral water. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 303,000,000 (220,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (119,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) none (4,380,000); geothermal, wind, and solar resources are substantial but largely undeveloped. Population economically active (2003): total 299,000; activity rate of total population 39.1% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 69.0%; female 39.5%; unemployed [2006] 60%). Households. Average household size (2004) 6.4; expenditure (1999; Djibouti city only): food 36.2%, housing and energy 18.1%, tobacco and related products 14.4%, transportation 8.8%, household furnishings 7.7%. Gross national income (2006): US$792,000,000 (US$968 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 7.1; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 17; official development assistance (2005) 79. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 2.8. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 0.4%, in pasture 73.3%; overall forest area (2005) 0.2%.
Foreign trade
Imports (1999): US$152,700,000 (food and beverages 25.0%; machinery and electric appliances 12.5%; khat 12.2%; petroleum products 10.9%; transport equipment 10.3%). Major import sources (2004): Saudi Arabia 21.9%; India 18.7%; China 10.2%; Ethiopia 4.8%; France 4.7%. Exports (2001): US$10,200,000 (aircraft parts 24.5%; hides and skins of cattle, sheep, goats, and camels 20.6%; leather 7.8%; live animals 6.9%). Major export destinations (2005): Somalia 66.4%; Ethiopia 21.5%; Yemen 3.4%. until the 16th century; it became the French protectorate of French Somaliland in 1888. In 1946 it became a French overseas territory, and in 1977 it gained its independence. In the late 20th century, the country received refugees from the Ethiopian-Somali war and from civil conflicts in Eritrea. In the 1990s it suffered from political unrest.
Recent Developments
In January 2007 the United States military launched air raids on suspected al-Qaeda hideouts in southern Somalia from the Combined Joint Task Force-Horn of Africa, which was based at Camp Lemonier in Djibouti, the only official US military presence in Africa. Djibouti Pres. Ismail Omar Guelleh condemned the raids as being counterproductive to the diplomatic efforts being made to end the clashes in Somalia. An estimated 53,000 Djiboutians faced malnutrition and hunger when in April and May the UN World Food Programme halted its feeding programs due to a shortfall in funding.
Transport and communications
Transport. Rai/roads:length (2006) 100 km; passen-ger-km (1999) 81,000,000; metric ton-km cargo (2002) 201,000,000. Roads (2002): total length 2,890 km (paved 13%). Vehic/es (2002): passenger cars 15,700; trucks and buses 3,200. Air transport (2005): passenger arrivals and departures 219,119; metric tons of freight loaded and unloaded 10,973. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2004): 53,000 (114); telephone landlines (2005): 11,000 (23); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 44,000 (94); personal computers (2005): 19,000 (41); total Internet users (2006): 11,000 (23); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 40 (0.09).
Education and health
Literacy (2003): percentage of population ages 15 and over literate 68.0%; males literate 78.2%; females literate 58.6%. Health: physicians (2004) 129 (1 per 3,619 persons); hospital beds (2000) 694 (1 per 621 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 102.4. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,674 (vegetable products 90%, animal products 10%); 151% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 9,850 (army 81.3%, navy 2.0%, air force 2.5%, paramilitary 14.2%); foreign troops: French (2007) 2,700; US and German military personnel at Camp Lemonier (2006) 1,729 and 320, respectively. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2004): 4.0%; per capita expenditure US$52.
Background
Settled around the 3rd century bc by the Arab ancestors of the Afars, Djibouti was later populated by Somali Issas. In ad 825 Islam was brought to the area by missionaries. Arabs controlled the trade in this region.
Dominica
Official name: Commonwealth of Dominica. Form of government: multiparty republic with one legislative house (House of Assembly [31]). Chief of state: President Nicholas Liverpool (from 2003). Head of government: Prime Minister Roosevelt Skerrit (from 2004). Capital: Roseau. Official language: English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 East Caribbean dollar (EC$) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = EC$2.70.
Demography
Area: 290 sq mi, 750 sq km. Population (2007): 70,600. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 243.4, persons per sq km 94.1. Urban (2003): 72.0%. Sex distribution (2006): male 50.34%; female 49.66%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 26.1%; 15-29, 23.8%; 30-44, 27.4%; 45-59, 12.4%; 60-74, 7.0%; 75 and over, 3.3%. Ethnic composition (2000): black 88.3%; mulatto 7.3%; black-Amerindian 1.7%; British expatriates 1.0%; Indo-Pakistani 1.0%; other 0.7%. Religious affiliation (2001): Roman Catholic 61%; four largest Protestant groups (including Seventh-day Adventist, Pentecostal groups, and Methodist) 28%; nonreligious 6%; other 5%. Major towns (2004): Roseau 20,200; Berekua 4,000; Portsmouth 3,600; Marigot 2,900; Atkinson (1991) 2,518. Location: island in the southern Caribbean Sea, south of Guadeloupe and north of Martinique.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 15.3 (world avg. 20.3); (1991) within marriage 24.1%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 6.7 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 8.5 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 1.94. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 72.0 years; female 77.9 years.
National economy
Budget (2005-06). Revenue:EC$325,000,000 (tax revenue 73.7%, of which taxes on international trade and transactions 29.8%, taxes on goods and services 25.3%; grants 18.6%; nontax revenue 7.3%; development revenue 0.4%). Expenditures: EC$315,300,000 (current expenditures 76.2%, of which wages 33.4%, transfers 14.7%, debt payment 13.6%; development expenditures and net lending 23.8%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2004): US$186,700,000. Gross national income (2006): US$287,000,000 (US$4,242 per capita). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 7%, in permanent crops 21%, in pasture 3%; overall forest area (2005) 61%. Population economically active (2001): total 27,865; activity rate of total population 40.0% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 64.7%; female 38.9%; unemployed [2002] 25%). Households. Average household size (2003) 3.0; sources of income (2001): wages and salaries 68.2%, self-employment 24.4%, other 7.4%; expenditure (2001): food 32.9%, transportation and communications 19.4%, housing 11.2%, household furnishings 9.4%, clothing and footwear 8.2%. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): bananas 29,000, grapefruit and pomelos 17,000, taro 11,200; livestock (number of live animals) 13,400 cattle, 9,700 goats, 7,600 sheep; fisheries production 579. Mining and quarrying: pumice, limestone, and sand and gravel are quarried primarily for local consumption. Manufacturing (value of production in EC$’000; 2004): toilet and laundry soap 24,588; toothpaste 8,774; crude coconut oil (2001) 1,758. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 79,000,000 (79,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (35,000). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 56; remittances (2005) 4; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 24; official develop-mentassistance (2005) 37 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 10.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004; f.o.b. in balance of trade and c.i.f. in commodities and trading partners): US$144,200,-000 (machinery and apparatus 25.1%; food, beverages, and tobacco 19.1%; mineral fuels 11.1%; telecommunications equipment 7.3%). Major import sources (2003): Japan 21.6%; US 15.1%; China 14.8%; Trinidad and Tobago 12.0%; South Korea 7.7%. Exports (2004): US$42,200,000 (agricultural exports 31.8%, of which bananas 17.2%; manufactured exports 61.8%, of which coconut-based soaps 26.4%; reexports 4.0%). Major export destinations (2003): Japan 27.1%; UK 16.4%; Jamaica 15.1%; US 6.6%; Antigua and Barbuda 6.2%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (1999): total length 780 km (paved 50%). Vehicles (1998): passenger cars 8,700; trucks and buses 3,400. Airtransport (1997): passenger arrivals and departures 74,100; cargo loaded and unloaded 938 metric tons. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2000): 16,000 (220); telephone landlines (2004): 21,000 (295); cellular telephone subscribers (2004): 42,000 (589); personal computers (2004): 13,000 (182); total Internet users (2005): 26,000 (372); broadband Internet subscribers (2004): 3,300 (46).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2002). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: primary education 62%; secondary 31%; vocational/university 7%. Literacy (1996): total population ages 15 and over literate, 94.0%. Health (2004): physicians 38 (1 per 1,824 persons); hospital beds (2002) 270 (1 per 257 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 13.7. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,083 (vegetable products 78%, animal products 22%); 160% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2003): none.
Background
At the time of the arrival of Christopher Columbus in 1493, Dominica was inhabited by the Caribs. With its steep coastal cliffs and inaccessible mountains, it was one of the last islands to be explored by Europeans, and the Caribs remained in possession until the 18th century; it was then settled by the French and ultimately taken by Britain in 1783. Subsequent hostilities between the settlers and the native inhabitants resulted in the Caribs’ near extinction. Incorporated with the Leeward Islands in 1883 and with the Windward Islands in 1940, it became a member of the West Indies Federation in 1958. Dominica became independent in 1978.
Recent Developments
Dominica began talks in early 2007 with Venezuela concerning the building by Caracas of an $80 million, 1,600 bbl-per-day refinery in the country. The project would be funded under the PetroCaribe oil-assistance program introduced by Venezuelan Pres. Hugo Chavez to help Caribbean territories hard hit by rising oil costs. The political opposition insisted, however, that the government did not have a mandate to establish a refinery in Dominica.
Dominican Republic
Official name: Republica Dominicana (Dominican Republic). Form of government: multiparty republic with two legislative houses (Senate [32]; Chamber of Deputies [178]). Head of state and government: President Leonel Fernandez Reyna (from 2004). Capital: Santo Domingo. Official language: Spanish. Official religion: none (Roman Catholicism is the state religion per concordat with Vatican City). Monetary unit: 1 Dominican peso (RD$) = 100 centavos; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = RD$34.15.
Demography
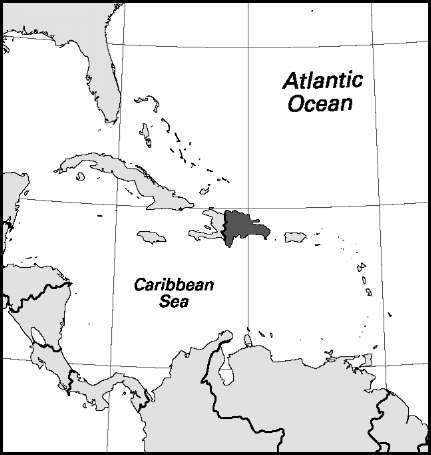
Area: 18,792 sq mi, 48,671 sq km. Population (2007): 9,366,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 498.4, persons per sq km 192.4. Urban (2005): 66.8%. Sex distribution (2005): male 50.18%; female 49.82%. Age breakdown (2002): under 15, 33.5%; 15-29, 26.6%; 30-44, 20.2%; 45-59, 11.7%; 60-74, 5.9%; 75-84, 1.6%; 85 and over, 0.5%. Ethnic composition (2003): mulatto 73%; white 16%; black 11%. Religious affiliation (2004): Roman Catholic 64.4%; other Christian 11.4%; nonreligious 22.5%; other 1.7%. Major urban centres (2002): Santo Domingo 1,887,586; Santiago 507,418; San Pedro de Macoris 193,713; La Romana 191,303; San Cristobal 137,422. Location: eastern two-thirds of the island of Hispaniola, bordered by the North Atlantic Ocean, the Caribbean Sea, and Haiti.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 23.2 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 5.4 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 2.83. Marriage/divorce rates per 1,000 population (2001): 2.8/1.0. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 71.0 years; female 74.5 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:RD$157,585,000,000 (tax revenue 94.2%, of which taxes on goods and services 49.0%, import duties 24.0%, income taxes 18.8%; nontax revenue 5.8%). EXpend/tures:RD$161,612,-000,000 (current expenditures 75.7%; development expenditures 24.3%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$6,093,000,000. Gross national income (2006): US$29,890,000,000 (US$3,109 per capita). Households (1997-98). Average household size (2002) 3.9; average annual household income RD$130,394 (US$8,745); sources of income: wages and salaries 32.1%, self-employment 31.0%, non-monetary income 22.8%, transfers 12.0%; expenditure: food, beverages, and tobacco 33.2%, transportation 16.0%, housing 9.3%, clothing and footwear 7.9%. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agr/culture, forestry, f/sh/ng (2005): sugarcane 4,950,000, rice 566,000, bananas 500,000; livestock (number of live animals) 2,200,000 cattle, 47,500,000 chickens; roundwood 562,300 cu m, of which fuelwood 99%; fisheries production 12,086 (from aquaculture 8%). M/n/ng (2005): nickel (metal content) 47,000; marble 10,384 cu m. Manufactur-/ng (2005): cement 2,779,000; refined sugar 139,203; beer 4,541,000 hectolitres. Energy product/on (consumpt/on): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 13,760,000,000 (13,760,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) none (777,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) none (33,500,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 1,993,000 (5,151,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) none (5,305,000). Population economically active (2004): total 3,701,804; activity rate of total population 43.1% (participation rates: ages 10 and over, 55.1%; female 38.7%; unemployed [2006] 16.2%). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2006) 3,792; remittances (2006) 2,911; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 853. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 352; remittances (2005) 26. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 22.7%, in permanent crops 10.3%, in pasture 43.4%; overall forest area (2005) 28.4%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006): US$8,745,000,000 (consumer goods 50.7%, ofwhich refined petroleum 21.0%, food products 5.8%; capital goods 15.4%; crude petroleum 10.9%). Major /mport sources (2005): US 50.0%; Colombia 6.2%; Mexico 5.8%. Exports (2006): US$6,440,000,000 (reexports from free zones 70.0%, of which assembled clothing 24.8%, electronics 10.3%, jewelry 9.8%; ferronickel 11.0%; fuels 5.6%; raw sugar 1.6%). Major export dest/nat/ons (2005): US 78.9%; The Netherlands 2.4%; Mexico 1.9%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Ra/lroads (2004): route length 615 km (includes 240 km of track that is privately owned and serves the sugar industry only). Roads (2002): total length 19,705 km (paved 51%). Vehicles (2001): passenger cars 561,300; trucks and buses 284,700. A/r transport: passenger-km (1999) 4,900,000; metric ton-km cargo (2003) 200,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 283,000 (30); televisions (2004): 1,950,000 (209); telephone landlines (2006): 897,000 (99); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 4,606,000 (511); personal computers (2005): 206,000 (22); total Internet users (2006): 2,000,000 (222); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 67,000 (7.1).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2002). Percentage of population ages 25 and older having: no formal education/unknown 4.1%; incomplete/complete primary education 53.1%; secondary 25.9%; undergraduate 15.9%; graduate 1.0%. Literacy (2003): total population ages 15 and over literate 84.7%. Health: physicians (2005; public sector only) 12,966 (1 per 730 persons); hospital beds (2005) 9,640 (1 per 982 persons); infant mortality rate (2006) 29.0. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,673 (vegetable products 84%, animal products 16%); 139% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 24,500 (army 61.2%, navy 16.3%, air force 22.5%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 0.5%; per capita expenditure US$20.
Background
The Dominican Republic was originally part of the Spanish colony of Hispaniola. In 1697 the western third of the island, which later became Haiti, was ceded to France; the remainderof the island passed to France in 1795. The eastern two-thirds of the island was returned to Spain in 1809, and the colony declared its independence in 1821. Within a matter of weeks it was overrun by Haitian troops and occupied until 1844. Since then the country has been under the rule of a succession of dictators, except for short interludes of democratic government, and the US has frequently been involved in its affairs. The termination of the dictatorship of Rafael Trujillo in 1961 led to civil war in 1965 and US military intervention. The country suffered from severe hurricanes in 1979 and 1998.
Recent Developments
In 2007 the Dominican Republic remained a country of economic and social contrasts. The burgeoning economy of the previous three years continued with an increase of 8.3% in GDP (one of the highest in Latin America), an improved fiscal regulatory system, better tax collection, and a manageable inflation rate of 6%. Business confidence was strengthened with the implementation in March of the Central America-Dominican Republic Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA-DR) with the US. However, the Dominican Republic ranked 79th out of 177 countries in the 2007-08 UN Human Development Reportand 26th outof 108 less-developed countries on the UN Poverty Index. The quality of public education and public health remained poor, and the government invested more in the capital’s subway project than in both of those sectors combined. Little discernible headway was made againstcorruption.
East Timor
Official name: Republika Demokratika Timor Lorosa’e (Tetum); Republica Democratica de Timor- Leste (Portuguese) (Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste). Form of government: republic with one legislative body (National Parliament [65]). Chief of State: President Jose Ramos-Horta (from 2007). Head of government: Prime MinisterXanana Gusmao (from 2007). Capital: Dili. Official languages: Tetum; Portuguese. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 US dollar (US$) = 100 centavos.
Demography
Area: 5,760sq mi, 14,919 sq km. Population (2007): 1,155,000. Density(2007): persons persq mi 200.5, persons per sq km 77.4. Urban (2005): 7.8%. Sex distribution (2006): male 50.86%; female 49.14%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 36.3%; 15-29, 28.9%; 30-44, 18.4%; 45-59, 11.2%; 60-74, 4.4%; 75 and over, 0.8%. Ethnic composition (1999): East Timorese 80%; other (nearly all Indonesian, and particularly West Timorese) 20%. Religious affiliation (2005): Roman Catholic 98%; Protestant 1%; Muslim 1%. Major urban areas (2004): Dili 151,026; Los Palos (Lospalos) 12,612; Same 9,966; Pante Macassar 9,754; Maliana 9,721. Location: southeast Asia, eastern end of the island of Timor plus an exclave on the western end, bordering the Timor Sea and Indonesia.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 27.0 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 6.2 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 20.8 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 3.53. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 64.0 years; female 68.7 years.
National economy
Budget (2005-06). Revenue:US$485,000,000 (oil and gas revenue 93.1%, of which taxes 74.8%, royalties 15.5%; domestic revenue 6.9%). Expenditures: US$93,000,000 (current expenditure 71.3%; capital expenditure 16.9%; previous year spending 11.8%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agricu/ture, forestry, fishing (2005): corn (maize) 80,000, rice 65,000, cassava 41,500; livestock (number of live animals) 346,000 pigs, 110,000 buffalo, 20,000 beehives; fisheries production 350. Mining and quarrying (2005): commercial quantities of marble are exported. Manufacturing (2001): principally the production of textiles, garments, handicrafts, bottled water, and processed coffee. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 300,000,000 (300,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) 990,000 (negligible); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 6,700,000 (57,000). Households. Average household size (2004) 4.7. Population economically active (2001): total 232,000; activity rate of total population 28% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 57%; unemployed 50%). Gross national income (2006): US$847,000,000 (US$761 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 19; official development assistance (2005) 185. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 8.2%, in permanent crops 4.6%, in pasture 10.1%; overall forest area (2005) 53.7%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004): US$146,100,000 (mineral fuels and oils 25.2%; vehicles and vehicle parts 10.1%; electrical machinery and equipment 6.7%; cereals 5.6%). Major import sources:Indonesia 42.8%; Australia 17.1%; Singapore 11.2%; Vietnam 3.6%; Portugal 3.0%. Exports (2004): US$6,972,000 (coffee 86.1%). Major export destinations: Australia 41.7%; Japan 22.8%; Portugal 13.0%; US 4.1%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads(2005): total length 5,000 km (paved 50%). Vehicles (1998): passenger cars 3,156; trucks and buses 7,140. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 600 (0.7); telephone landlines (1996): 6,600 (8); total Internet users (2004): 1,000(1.1).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2002). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: no formal education 54.3%; some primary education 14.4%; complete primary 6.2%; lower secondary 10.4%; upper secondary and higher 14.7%. Literacy (2005): percentage of population ages 15 and over literate 49%; males literate 54%; females literate 45%. Health: physicians (2002) 47 (1 per 17,355 persons); hospital beds (1999) 560 (1 per 1,277 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 45.9.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 1,250 (army 100%); UN peacekeeping personnel were withdrawn in May 2005, and 600 police personnel were reintro-duced in August 2006. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2003): 1.3%; per capita expenditure US$5.
Background
The Portuguese first settled on the island of Timor in 1520 and were granted rule over Timor’s eastern half in 1860. The Timor political party Fretilin declared East Timor independent in 1975 after Portugal withdrew its troops. It was invaded by Indonesian forces and was incorporated as a province of Indonesia in 1976. The takeover, which resulted in thousands of East Timorese deaths during the next two decades, was disputed by the UN. In 1999 an independence referendum won overwhelmingly; civilian militias, armed by the militaryand led bylocal supporters of integration, then rampaged through the province, killing 1,000-2,000 people. The Indonesian parliament rescinded Indonesia’s annexation of the territory, and East Timor was returned to its preannexation status as a non-self-governing territory, though this time under UN supervision. Preparation for independence got under way in 2001, with East Timorese voting by universal suffrage in August for a Constituent Assembly of 88 members. Independence was declared on 20 May 2002 and was followed by the swearing in of Xanana Gusmao as the first president of the country.
Recent Developments
Prime Minister Jose Ramos-Horta, corecipient of the 1996 Nobel Prize for Peace, won East Timor’s presidential runoff election in May 2007. Ramos-Horta swore in former president Xanana Gusmao as prime minister in August, even though Gusmao’s party had won fewer seats than the ruling party in parliamentary elections in June. Two days of rioting followed in which hundreds of buildings and cars were set on fire. In February 2008 Ramos-Horta was seriously wounded in an assassination attempt.
Ecuador
Official name: Republica del Ecuador (Republic of Ecuador). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with one legislative house (National Congress [100]). Head of state and government: President Rafael Correa Delgado (from 2007). Capital: Quito. Official language: Spanish (Quechua and Shuar are also official languages for the indigenous peoples). Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 US dollar (US$) = 100 cents.
Demography
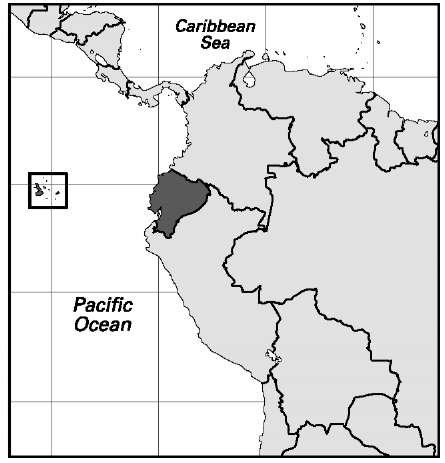
62.8% Sex distribution (2005): male 50.15%; female 49.85%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 32.6%; 15-29, 27.4%; 30-44, 19.5%; 45-59, 12.1%; 60-74, 6.1%; 75-84, 1.8%; 85 and over, 0.5%. Ethnic composition (2000): mestizo 42.0%; Amerindian 40.8%; white 10.6%; black 5.0%; other 1.6%. Religious affiliation (2005): Roman Catholic (practicing) 35%; Roman Catholic (nonpracticing) 50%; other (significantly Evangelical Protestant) 15%. Major cities (2003): Guayaquil (urban agglomeration) 2,387,000; Quito (urban agglomeration) 1,514,000; Cuenca 303,994; Machala 217,266; Santo Domingo de los Colorados 211,689. Location: northwestern South America, bordering Colombia, Peru, and the Pacific Ocean.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 22.1 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 5.0 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 2.70. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 71.7 years; female 77.6 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue:US$6,895,000,000 (non-petroleum revenue 75.1%, of which value-added tax 32.3%, income tax 15.5%, customs duties 9.0%; petroleum export revenue 24.9%). Expend/tures: US$7,011,000,000 (current expenditure 76.2%; capital expenditure 23.8%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, f/sh/ng (2005): bananas 5,878,000, sugarcane 5,657,000, oil palm fruit 1,930,000; livestock (live animals) 4,971,000 cattle, 1,281,000 pigs, 1,053,000 sheep; round-wood 6,638,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 82%; fisheries production 486,023 (from aquaculture 16%). M’/n’/ng and quarry/ ng (2004): limestone 5,160,000; gold 5,300 kg. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2004): refined petroleum 1,794; food products 870; beverages 845. Energy product on (consumpt on): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 11,702,000,000 (13,344,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2006) 197,000,000 (55,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 6,594,000 (5,777,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 352,000,000 (352,000,000). Population economically active (2005): total 4,225,400; activity rate of total population 47.9% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 70.6%; female 41.5%; unemployed [March 2006-February 2007] 10.1%). Households (2003; urban households only). Average household size 4.2; average annual income per household US$8,161; sources of income: wages 47.0%, self-employment 25.6%, transfer payments 15.7%, rent 11.7%; expenditure: food, beverages, and tobacco 23.8%, housing and energy 19.1%, transportation and communications 12.9%, restaurants and hotels 10.4%, clothing 8.1%. Public debt (external, outstanding; December 2006): US$10,215,000,000. Gross national income (2006): US$36,796,000,000 (US$2,787 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2006) 497; remittances (2006) 2,916; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 1,447; official development assistance (2005) 271 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2006) 466; remittances (2005) 38. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 4.7%, in permanent crops 4.3%, in pasture 17.2%; overall forest area (2005) 39.2%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004; f.o.b. in balance of trade and c.i.f. for commodities and trading partners): US$7,861,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 24.3%; road vehicles 10.6%; mineral fuels and lubricants 10.2%; food and live animals 7.4%). Major m-port sources (2004): US 16.8%; Colombia 14.1%; China 9.0%; Venezuela 7.1%; Brazil 6.5%. Exports (2006): US$12,658,000,000 (crude petroleum 54.8%; bananas and plantains 9.6%; refined petroleum 4.8%; shrimp 4.6%; cut flowers 3.5%). Major export destinations (2006): US 53.6%; Peru 8.2%; Colombia 5.6%; Chile 4.4%; Italy 3.3%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Ra/lroads (2004): route length (2005) 965 km; passenger-km 3,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 2,000. Roads (2004): total length 43,197 km (paved 15%). Veh cles (2004): passenger cars 413,432; trucks and buses 310,009. A/r transport (2005): pas-senger-km 867,100,000; metric ton-km cargo 5,400,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 901,000 (68); televisions (2004): 3,298,000 (253); telephone landlines (2006): 1,754,000 (131); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 8,485,000 (632); personal computers (2005): 866,000 (65); total Internet users (2006): 1,549,000 (115); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 27,000 (2).
Education and health
Educational attainment (1995). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling/incomplete primary education 18.8%; complete primary/incomplete secondary 47.2%; complete secondary 16.1%; higher 17.9%. Literacy (2003): total population ages 15 and over literate 92.5%; males literate 94.0%; females literate 91.0%. Health: physicians (2004) 21,625 (1 per 603 persons); hospital beds (2004) 21,200 (1 per 615 persons); infant mortality rate (2005) 23.0. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,770 (vegetable products 83%, animal products 17%); 152% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 46,500 (army 79.6%, navy 11.8%, air force 8.6%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 2.6%; per capita expenditure US$66.
Background
Ecuador was conquered by the Incas in ad 1450 and came under Spanish control in 1534. Under the Spaniards it was a part of the Viceroyalty of Peru until 1740, when it became a part of the Viceroyalty of New Granada. It gained its independence from Spain in 1822 as part of the republic of Gran Colombia, and in 1830 it became a sovereign state. A succession of authoritarian governments ruled into the mid-20th century, and economic hardship and social unrest prompted the military to take a strong role. Border disputes led to war between Peru and Ecuador in 1941; the two fought periodically until agreeing to a final demarcation in 1998. The economy, booming in the 1970s with petroleum profits, was depressed in the 1980s by reduced oil prices and earthquake damage. A new constitution was adopted in 1979. In the 1990s social unrest caused political instability and several changes of heads of state. In a controversial move to help stabilize the economy, the US dollar replaced the sucre as the national currency in 2000.
Recent Developments
The inauguration of Pres. Rafael Correa in January 2007 added Ecuador to the list of South American countries in which elected leftist leaders sought to implement major political, economic, and social change. His administration appeared to favor political reform as a priority over economic nationalism, and it moved swiftly to overhaul the constitution and Ecuador’s discredited political institutions. He said that he would disavow debts contracted corruptly or illegally and that the government would renegotiate agreements with private oil companies to increase its share of revenues. He spoke in favor of US legislation extending the Andean Trade Promotion and Drug Eradication Act (which gave trade preferences to Ecuador in exchange for antinarcotic aid) but opposed a bilateral free-trade agreement between Ecuador and the US.
Egypt
Official name: Jumhuriah Misr al-’Arabiyah (Arab Republic of Egypt). Form of government: republic with one legislative house (People’s Assembly [454]). Chief of state: President Hosni Mubarak (from 1981). Head of government: Prime Minister Ahmed Nazif (from 2004). Capital: Cairo. Official language: Arabic. Official religion: Islam. Monetary unit: 1 Egyptian pound (£E) = 100 piastres; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = £E 5.33.
Demography
Area: 385,229 sq mi, 997,739 sq km. Population (2007): 73,358,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 190.4, persons per sq km 73.5. Urban (2006): 42.6%. Sex distribution (2006): male 51.11%; female 48.89%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 33.0%; 15-29, 28.0%; 30-44, 19.8%; 45-59, 12.3%; 60-74, 5.7%; 75 and over, 1.2%. Ethnic composition (2000): Egyptian Arab 84.1%; Sudanese Arab 5.5%; Arabized Berber 2.0%; Bedouin 2.0%; Rom (Gypsy) 1.6%; other 4.8%. Religious affiliation (2000): Muslim (nearly all Sunni) 84.4%; Christian 15.1%, of which Orthodox 13.6%; nonreligious 0.5%. Major cities (’000; 2006): Cairo 7,787 ([2005 urban agglomeration] 11,128); Alexandria 4,110; Al-Jizah 2,950; Shubra al-Khaymah (1996) 871; Port Said (1996) 470. Location: northern Africa, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, the Gaza Strip, Israel, the Red Sea, The Sudan, and Libya.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 25.5 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 6.4 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 2.83. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 69.2 years; female 73.6 years.
National economy
Budget (2003-04). Revenue: £E 116,490,000,000 (income and profits taxes 28.3%; sales taxes 19.4%; customs duties 13.0%; Suez Canal fees 4.4%; petroleum revenue 3.5%). Expenditures: £E 159,600,000,000 (current expenditure 76.6%; capital expenditure 23.4%). Population economically active (2005): total 22,310,000; activity rate 31.3% (participation rates: ages 15-64 [2001] 46.9%; female 23.3%; unemployed [2006] 9.3%). Production (’000; metric tons except as noted). Agricu/ture, forestry, fishing (2005): sugarcane 16,335, wheat 8,185, corn (maize) 7,698; livestock (’000; number of live animals) 5,150 sheep, 4,500 cattle, 120 camels; roundwood 17,060,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 80%; fisheries production 889,302 (from aquacul-ture 61%). Mining and quarrying (2005): phosphate rock 2,730; iron ore 2,600; salt 1,400. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2002): chemicals (all forms) 2,823; food products 1,016; textiles and wearing apparel 618. Energy production (consumption): electricity (’000,000 kW-hr; 2004-05) 101,300 ([2004] 100,600); coal (’000 metric tons; 2004) 33 (1,850); crude petroleum (’000 barrels; 2004) 253,000 (240,000); petroleum products (’000 metric tons; 2004) 32,600 (28,000); natural gas (’000,000 cu m; 2003) 33,000 (29,400). Households. Average household size (2006) 4.2. Gross national income (2006): US$111,348,000,000 (US$1,501 per capita). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2006): US$28,000,000,000. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 2.9%, in permanent crops 0.5%; overall forest area (2005) 0.1%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 6,851; remittances (2005-06) 5,034; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 1,785; official development assistance (2005) 987 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 1,629; remittances (2005) 57.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005-06; c.i.f.): US$30,441,000,000 (petroleum 17.6%; machinery and apparatus 10.9%; food products 9.7%; metal products 7.3%; chemicals and chemical products 6.0%). Major mport sources (2004): free zones 11.3%; US 10.3%; Germany 6.6%; China 5.1%; Italy 4.9%. Exports (2005-06; f.o.b.): US$18,455,100,000 (petroleum 55.4%, of which crude petroleum 17.4%; finished goods 28.0%; semimanufactured goods 6.4%). Major export dest nat ons (2004): Italy 12.5%; bunkers and ships’ stores 9.8%; US 7.4%; free zones 5.7%; Spain 5.5%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Ra lroads (2005): length 9,525 km; pas-senger-km 54,853,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 4,234,000,000. Roads (2004): length 92,370 km (paved 81%). Veh/cles (2002): passenger cars 1,847,000; trucks and buses 650,000. Inland water (2006): Suez Canal, number of transits 18,664; cargo 742,708,000 metric tons. A/r transport (2005; EgyptAir only): passenger-km 10,048,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 287,561,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 3,577,000 (51); televisions (2004): 17,500,000 (253); telephone landlines (2006): 10,808,000 (143); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 18,001,000 (239); personal computers (2005): 2,800,000 (40); total Internet users (2006): 6,000,000 (80); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 206,000 (2.9).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2006). Percentage of population ages 10 and over having: no formal schooling 42.9%; incomplete primary 19.4%; complete primary 24.9%; secondary 3.2%; higher 9.6%. Literacy (2001): total population ages 15 and over literate 56.1%; males literate 67.2%; females literate 44.8%. Health (2006): physicians 161,000(1 per451 persons); hospital beds (2007) 185,000 (1 per 393 persons); infant mortality rate (2005) 20.5. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,274 (vegetable products 92%, animal products 8%); 172% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 468,500 (army 72.6%, navy 3.9%, air force [including air defense] 23.5%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 2.8%; per capita expenditure US$37.
Background
Egypt is home to one of the world’s oldest continuous civilizations. Upper and Lower Egypt were united c. 3000 bc, beginning a period of cultural achievement and a line of native rulers that lasted nearly 3,000 years. Egypt’s ancient history is divided into the Old, Middle, and New Kingdoms, spanning 31 dynasties and lasting to 332 bc. The pyramids date from the Old Kingdom; the cult of Osiris and the refinement of sculpture, from the Middle Kingdom; and the era of empire and the Exodus of the Jews, from the New Kingdom. An Assyrian invasion occurred in the 7th century bc, and the Persian Achaemenids established a dynasty in 525 bc. The invasion by Alexander the Great in 332 bc inaugurated the Macedonian Ptolemaic period and the ascendancy of Alexandria. The Romans held Egypt from 30 bc to ad 395; later it was placed under the control of Constantinople. Constantine’s granting of tolerance in 313 to the Christians began the development of a formal Egyptian (Coptic) church. Egypt came under Arab control in 642 and ultimately was transformed into an Arabic-speaking state, with Islam as the dominant religion. Held by the Umayyad and Ab-basid dynasties, in 969 it became the center of the Fa-timid dynasty. In 1250 the Mamluks established a dynasty that lasted until 1517, when Egypt fell to the Ottoman Turks. An economic decline ensued, and with ita decline in Egyptian culture. Egypt became a British protectorate in 1914 and received nominal independence in 1922, when a constitutional monarchy was established. A coup overthrew the monarchy in 1952, with Gamal Abdel Nasser taking power. Following three wars with Israel, Egypt, under Nasser’s successor, Anwar el-Sadat, ultimately played a leading role in Middle East peace talks. Sadat was succeeded by Hosni Mubarak, who followed Sadat’s peace initiatives and in 1982 regained Egyptian sovereignty (lost in 1967) over the Sinai Peninsula. Although Egypt took part in the coalition against Iraq during the Persian Gulf War (1991), it later made peace overtures to Iraq and other countries in the region.
Recent Developments
Egypt’s government intensified its campaign in 2007 to contain political dissent led by the banned Muslim Brotherhood. A number of amendments were passed, including a new antiterrorism law, which would provide the police with increased powers of arrest and surveillance; a new election law that would eliminate the need for judicial monitoring of each ballot box; and a ban on the creation of political parties based on religion. Though there was an estimated US$5 billion surplus and a decline in unemployment (from 9.5% in 2005-06 to 9.1% in 2006-07) and the rate of inflation (from 12.8% in March to 8.5% in August), there was a 10.5% rise in the cost of living. Nonetheless, 14 million Egyptians were classified as poor.
El Salvador
Official name: Republica de El Salvador (Republic of El Salvador). Form of government: republic with one legislative house (Legislative Assembly [84]). Chief of state and government: President Elfas Antonio Saca Gonzalez (from 2004). Capital: San Salvador. Official language: Spanish. Official religion: none (Roman Catholicism, although not official, enjoys special recognition in the constitution). Monetary unit: 1 colon (0)= 100centavos; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = 08.75 (the US dollar [US$] has also been legal tender since 1 Jan 2001; the colon is rarely in use).
Demography
Area: 8,124sq mi, 21,041 sq km. Population (2007): 6,857,000. Density(2007): persons persq mi 844.0, persons per sq km 325.9. Urban (2005): 59.8%. Sex distribution (2005): male 49.17%; female 50.83%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 34.0%; 15-29, 28.8%; 30-44, 19.1%; 45-59, 10.5%; 60-74, 5.6%; 75-84,1.6%; 85 and over, 0.4%. Ethnic composition (2000): mestizo 88.3%; Amerindian 9.1%, of which Pipil 4.0%; white 1.6%; other/unknown 1.0%. Religious affiliation (2005): Roman Catholic 71%; independent Christian 11%; Protestant 10%; Jehovah’s Witness 2%; other 6%. Major cities (2005): San Salvador 507,700 (urban agglomeration 2,232,300); Soyapango 294,600; Mejicanos 188,700; San Miguel 183,200; Santa Ana 178,600. Location: Central America, bordering Guatemala, Honduras, and the North Pacific Ocean.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 16.3 (world avg. 20.3); (1998) within marriage 27.2%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 4.5 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 3.12. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 67.9 years; female 75.3 years.
National economy
Budget. Revenue (2005): US$2,307,500,000 (VAT 47.8%; individual income taxes 29.0%; import duties 7.8%; nontax revenue 5.5%). Expenditures: $2,484,600,000 (education 18.6%; defense and public security 11.4%; public health and welfare 9.8%; public works 6.3%; other 53.9%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$4,760,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): sugarcane 4,405,000, corn (maize) 727,607, sorghum 141,400; livestock (number of live animals) 1,256,517 cattle, 355,991 pigs, 13,437 chickens; roundwood 4,855,000 cu m, of which fuel-wood 86%; fisheries production 43,317 (from aqua-culture 5%). Mining and quarrying (2004): limestone 1,161,000. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2004): food products 875; textiles and wearing apparel 262; chemicals and chemical products 262; refined petroleum 234. Energy production (consumption):electricity (kW-hr; 2006) 5,293,000,000 (5,204,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) none (7,100,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 989,000 (1,851,000). Households. Average household size (2004) 4.2; average income per household (2004) US$5,016; expenditure (2005): food, beverages, and tobacco 36.4%, housing and energy 16.8%, transportation and communications 10.2%, household furnishings 8.4%. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 31.9%, in permanent crops 12.1%, in pasture 38.3%; overall forest area (2005) 14.4%. Population economically active (2004): total 2,710,237; activity rate of total population 40.1% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 63.2%; female 39.6%; unemployed [2005] 7.2%). Gross national income (2006): US$15,553,000,000 (US$2,300 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 543; remittances (2006) 3,316; foreign direct invest-ment(2001-05 avg.) 357; official development assistance (2005) 234 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 347; remittances (2005) 24.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004; c.i.f.): US$6,268,754,000 (imports for reexport 22.0%; machinery and apparatus 12.3%; food 11.3%; petroleum [all forms] 10.2%; chemicals and chemical products 9.6%). Major import sources (2006): US 40.5%; Guatemala 8.0%; Costa Rica 2.9%; Honduras 2.3%; Japan 2.0%. Exports (2004; f.o.b.): US$3,295,258,000 (reexports [mostly clothing] 55.2%; yarn, fabrics, and made-up articles 6.8%; chemicals and chemical products 4.8%). Major export destinations (2006): US 57.1%; Guatemala 13.0%; Honduras 8.0%; Nicaragua 4.8%; Costa Rica 3.4%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2007): length 562 km. Roads (2002): total length 11,458 km (paved 23%). Vehicles (2000): passenger cars 148,000; trucks and buses 250,800. Air transport (2005; TACA International Airlines only): passenger-km 8,117,465,000; metric ton-km cargo 37,883,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 250,000 (37); televisions (2004): 1,560,000 (233); telephone landlines (2006): 1,037,000 (148); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 3,852,000 (551); personal computers(2005): 350,000(51); total Internet users (2005): 637,000(93); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 42,000 (6.2).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2004). Percentage of population ages 26 and over having: no formal schooling 22.0%; primary education 39.0%; secondary 28.5%; higher 10.5%. Literacy (2004): total population ages 10 and over literate 84.5%; males literate 87.0%; females literate 82.3%. Health (2003): physicians 4,100 (1 per 1,620 persons); hospital beds 4,625 (1 per 1,436 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2004) 10.5. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,680 (vegetable products 89%, animal products 11%); 149%of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 15,500 (army 89.4%, navy 4.5%, air force 6.1%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 0.6%; per capita expenditure US$16.
Background
The Spanish arrived in the area in 1524 and subjugated the Pipil Indian kingdom of Cuzcatlan by 1539. The country was divided into two districts, San Salvador and Sonsonate, both attached to Guatemala. When independence came in 1821, San Salvador was incorporated into the Mexican Empire; upon its collapse in 1823, Sonsonate and San Salvador combined to form the newstate of El Salvador within the United Provinces of Central America. From its founding, El Salvador experienced a high degree of political turmoil and was under military rule from 1931 to 1979, when the government was ousted in a coup. Elections held in 1982 setup a new government, and in 1983 a new constitution was adopted, but civil war continued through the 1980s. An accord in 1992 brought an uneasy truce.
Recent Developments
A close ally of the US, El Salvador continued to boycott Cuba in 2007 and was the only Latin American country to keep troops in Iraq, despite widespread opposition. The US rewarded Salvadoran support with leniency regarding the deportation of illegal immigrants back to El Salvador. Nearly one-third of native-born Salvadorans lived in the US, and their remittances of about US$2.5 billion annually aided El Salvador’s weak economy. El Salvador enjoyed a rise in exports to the US, including the reexport of Brazilian ethanol, which was made possible under the Central America-Dominican Republic Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA-DR) with the US, but American corn-produced ethanol drove up grain prices in El Salvador.
Equatorial Guinea
Official name: Republica de Guinea Ecuatorial (Spanish); Republique du Guinee Equatoriale (French) (Republic of Equatorial Guinea). Form of government: republic with one legislative house (House of Representatives of the People [100]). Chief of state: President Teodoro Obiang Nguema Mbasogo (from 1979). Head of government: Prime Minister Ricardo Mangue Obama Nfubea (from 2006). Capital: Malabo. Official languages: Spanish; French. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 CFA franc (CFAF) = 100 centimes; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = CFAF 414.60 (pegged since 1 Jan 2002 to the euro at €1 = CFAF 655.96).
Demography
Area: 10,831 sq mi, 28,051 sq km. Population (2007): 507,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 46.8, persons per sq km 18.1. Urban (2006): 50.9%. Sex distribution (2005): male 48.82%; female 51.18%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 42.4%; 15-29, 26.2%; 30-44,15.5%; 45-59, 9.5%; 60-74, 5.0%; 75-84, 1.2%; 85 and over 0.2%. Ethnic composition (2000): Fang 56.6%; migrant laborers from Nigeria 12.5%, of which Yoruba 8.0%, Igbo4.0%; Bubi 10.0%; Seke 2.9%; Spaniard 2.8%; other 15.2%. Religious affiliation (2000): Roman Catholic 79.9%; Sunni Muslim 4.1%; independent Christian 3.7%; Protestant 3.2%; traditional beliefs 2.1%; nonreli-gious/atheist 4.9%; other 2.1%. Major cities (2003): Malabo 92,900; Bata 66,800; Mbini 11,600; Ebe-biyin 9,100; Luba 6,800. Location: western Africa, the mainland portion bordering Cameroon, Gabon, and the Bight of Biafra (inlet of the Atlantic Ocean).
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 39.1 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 15.6 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2005): 23.5 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 5.50. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 49.2 years; female 51.7 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:CFAF 1,528,825,000,000 (oil revenue 94.3%, of which profit sharing 32.1%, royalties 30.1%; non-oil revenue 5.6%, of which tax revenue 3.8%, nontax revenue 1.8%; grants 0.1%). Expend/tures:CFAF 697,948,000,000 (capital expenditure 63.9%; current expenditure 22.8%; net lending 13.3%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$4,760,000,000. Gross national income (at 2006 market prices): US$3,023,000,000 (US$2,300 per capita). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agr culture, forestry, f sh ng (2005): cassava 45,000, sweet potatoes 36,000, oil palm fruit 35,000; livestock (number of live animals) 37,600 sheep, 9,000 goats, 6,100 pigs; roundwood 866,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 52%; fisheries production (2004) 3,500. M/n/ng and quarry/ng: gold (2005) 200 kg. Manufacturing (2004): methanol 1,027,300; processed timber 31,200 cu m. Energy product on (consumpt on): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 83,000,000 (51,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2005) 153,000,000 ([2004] negligible); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (47,000); natural gas (cu m; 2005) 2,300,000,000 ([2004] 480,000,000). Population economically active (1997): total 177,000; activity rate of total population 40.0% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 74.7%; female 35.4%; unemployed [1998] 30%). Households. Expenditure (2000): food and beverages 60.4%, clothing 14.7%, household furnishings 8.6%. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 4.6%, in permanent crops 3.6%, in pasture 3.7%; overall forest area (2005) 58.2%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,-000): tourism (2005) 5; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 1,245; official development assistance (2005) 39.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): CFAF 1,112,500,000,000 (for petroleum sector 55.8%; for public sector 33.0%; petroleum products 4.5%). Major import sources: US 26.8%; Cote d’Ivoire 21.4%; Spain 13.6%; France 8.8%; UK 7.8%. Exports (2005): CFAF 3,764,200,000,000 (crude petroleum 92.1%; methanol 6.9%; timber 0.7%). Major export destinations (2003): US 33.2%; Spain 25.4% China 14.2%; Canada 12.7%; Italy 6.3%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (1999): total length 2,880 km (paved 13%). Vehicles (2002): passenger cars 8,380; trucks and buses 6,618. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2002): 55,000 (116); telephone landlines (2005): 10,000 (20); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 97,000 (193); personal computers (2004): 7,000 (3.3); total Internet users (2006): 8,000 (16).
Education and health
Literacy (2006): percentage of total population ages 15 and over literate 87.0%; males literate 93.4%; females literate 80.5%. Health: physicians (2004) 101 (1 per 5,020 persons); hospital beds (1998) 907 (1 per 472 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 96.5.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 1,320 (army 83.3%, navy 9.1%, air force 7.6%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 0.1%; per capita expenditure US$14.
Background
The first inhabitants of the mainland region appear to have been Pygmies. The now-prominent Fang and Bubi reached the mainland region in the 17th-century Bantu migrations. Equatorial Guinea was ceded by the Portuguese to the Spanish in the late 18th century; it was frequented by slave traders, as well as by British, German, Dutch, and French merchants. Bioko was administered by British authorities (1827-58) before the official takeover by the Spanish. The mainland (Rio Muni) was not effectively occupied by the Spanish until 1926. Independence was declared in 1968, followed by a reign of terror and economic chaos under the dictatorial president Macfas Nguema, who was overthrown by a military coup in 1979 and later executed. A new constitution was adopted in 1982, but political unrest persisted.
Recent Developments
Equatorial Guinea continued in 2007 to have one of the highest GDP growth rates in the world, estimated at more than 20%. The country was one of the members that participated in the 2006 inaugural meeting of the Gulf of Guinea Commission, which aimed to ensure that the energy resources of the region led to development and that Malabo’s long-standing dispute with neighboring Gabon over the status of the islands in Corsico Bay would at last be settled. In May it was announced that there would be a delay in the awarding of further offshore exploration blocks because the bids were not satisfactory, but in September seven new oil blocks were granted to foreign companies. Relations with Zimbabwe, which had become close since 2004 when Zimbabwe intercepted mercenaries bound for Equatorial Guinea to stage a coup, remained warm. Zimbabwe extradited Simon Mann, the leader of the mercenaries, to Equatorial Guinea in February 2008 to face charges there.
Eritrea
Official name: State of Eritrea. Form of government: transitional regime with one interim legislative body (Transitional National Assembly [150]). Constitution adopted in May 1997 was still not implemented in early 2008. Head of state and government: President Isaias Afwerki (from 1993). Capital: Asmara. Official language: none. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 nakfa (Nfa) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = Nfa 15.00.
Demography
Area: 46,774 sq mi, 121,144 sq km. Population (2007): 4,907,000. Density(2007): persons persq mi 125.5, persons persq km 48.6. Urban (2006): 21.3%. Sex distribution (2006): male 49.84%; female 50.16%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 44.0%; 15-29, 27.9%; 30-44,14.3%; 45-59, 8.2%; 60-74, 4.5%; 75 and over, 1.1%. Ethnolinguistic composition (2004): Tigrinya (Tigray) 50.0%; Tigre 31.4%; Afar 5.0%; Saho 5.0%; Beja 2.5%; Bilen 2.1%; other 4.0%. Religious affiliation (2004): Muslim (virtually all Sunni)50%; Christian 48%, of which Eritrean Orthodox 40%, Roman Catholic 5%, Protestant 2%; traditional beliefs 2%. Major cities (2003): Asmara 435,000; Keren 57,000; Assab 28,000; Mendefera 25,000; Massawa 25,000. Location: the Horn of Africa, bor-deringThe Sudan, the Red Sea, Djibouti, and Ethiopia.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 34.3 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 9.6 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 24.7 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 5.08. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 57.4 years; female 60.7 years.
National economy
Budget (2002). Revenue:Nfa 3,409,800,000 (tax revenue 45.1%, of which import duties 18.1%, sales tax 10.8%, corporate tax 9.9%; grants 32.8%; nontax revenue 21.2%; extraordinary revenue 0.9%). Expend/-tures:Nfa 6,138,200,000 (defense 34.3%; health 9.6%; humanitarian assistance 7.9%; education 7.6%; transportation, construction, and communications 6.5%; debt service 5.7%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$723,000,000. Gross national income (2006): US$1,360,000,000 (US$290 per capita). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agr culture, forestry, f sh ng (2005): sorghum 114,300, roots and tubers 102,500, pulses 35,200; livestock (number of live animals) 2,100,000 sheep, 1,950,000 cattle, 75,000 camels; roundwood 2,449,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 99.9%; fisheries production 4,027. M/n/ng and quarry/ng (2005): granite 350,280; basalt 184,027; coral 91,348. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2004): beverages 31; tobacco products 8; furniture 7. Energy product on (consumpt on): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 283,000,000 (283,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (239,000). Households (1996-97). Average household size (2004) 5.0; average annual disposable income per household: Nfa 10,967 (US$1,707); sources of income (urban areas only): wages and salaries 34.0%, transfers 29.3%, rent 19.8%, self-employment 16.9%; expenditure (urban areas only): food 36.2%, housing 30.2%, clothing and footwear 9.3%, energy 6.8%, household furnishings 4.6%, transportation and communications 4.1%. Population economically active (2000): total 1,451,000; activity rate of total population 40.8% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 75.4%; female 41.5%). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 66; remittances (2003) 150; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 11; official development assistance (2005) 355. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): remittances (2000) 1. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 5.6%, in permanent crops 0.03%, in pasture 69.0%; overall forest area (2005) 15.4%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2003; c.i.f.): US$432,800,000 (food and live animals 40.5%, of which cereals 25.5%; machinery and apparatus 14.8%; road vehicles 7.3%; chemicals and chemical products 6.1%). Major /mport sources (2005): Italy 31.4%; US 11.9%; Belarus 5.9%; France 5.1%; Germany 4.6%. Exports (2003; f.o.b.): US$6,600,000 (food and live animals 36.4%, of which fresh fish 22.7%; leather 10.6%; corals and shells 9.1%). Major export dest/nat/ons (2005): Italy 15.1%; France 11.8%; US 9.5%; Germany 8.6%; Taiwan 7.4%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Ra/lroads (2005): route length 306 km. Roads (2004): total length 4,000 km (paved 20%). Ve-h/cles (1996): automobiles 5,940. A/r transport (2001; Asmara airport only): passenger arrivals 39,266, passenger departures 46,448; freight loaded 202 metric tons, freight unloaded 1,548 metric tons. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 49,000 (10); televisions (2004): 250,000 (58); telephone landlines (2006): 38,000 (8.2); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 62,000 (14); personal computers (2005): 35,000 (7.5); total Internet users (2006): 100,000 (22).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2002). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal education/unknown 67.6%; incomplete primary education 16.6%; complete primary 1.3%; incomplete secondary 5.8%; complete secondary 5.7%; higher 3.0%. Literacy (2006): total population ages 15 and over literate 61.4%; males literate 72.3%; females literate 50.7%. Health: physicians (2004) 215 (1 per 20,791 persons); hospital beds (2000) 3,126 (1 per 1,187 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 46.3. Food (2003): daily per capita caloric intake 1,519 (vegetable 94%, animal products 6%); 88% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 201,750 (army 99.1%, navy 0.7%, air force 0.2%); UN peacekeeping force along Eritrean-Ethiopian border (July 2007) 1,470 troops. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2003): 24.1%; per capita expenditure US$49.
Background
As the site of the main ports of the Aksumite empire, Eritrea was linked to the beginnings ofthe Ethiopian kingdom, but it retained much of its independence until it came under Ottoman rule in the 16th century. From the 17th to the 19th century, control of the territory was disputed among Ethiopia, the Ottomans, the kingdom ofTigray, Egypt, and Italy; it became an Italian colony in 1890. Eritrea was used as the main base for the Italian invasions of Ethiopia (1896 and 1935-36) and in 1936 became part of Italian East Africa. It was captured by the British in 1941, federated to Ethiopia in 1952, and made a province of Ethiopia in 1962. Thirty years of guerrilla warfare by Eritrean secessionist groups ensued. A provisional Eritrean government was established in 1991 after the overthrow of the Ethiopian government, and independence came in 1993. A new constitution was ratified in 1997.
Recent Developments
Eritrea’s enmity with neighboring Ethiopia continued to dominate the 2007 agenda ofthe country, sapping energy required for improving relations with the West and resolving the dire economic and social needs of its people. In January a proxy war exploded when both countries lent support to opposing sides in a conflict in Somalia, which reached a climax when Somalia’s Transitional Federal Government, backed by Ethiopian troops, routed the Islamic Courts Union, supported by Eritrea. As Eritrea’s relations with Western countries worsened, Asmara strengthened its ties with China, which in January cancelled a portion of Eritrea’s foreign debt. In July the countries signed economic pacts, and in October Eritrea granted mineral exploration rights to two Chinese firms.
Estonia
Official name: Eesti Vabariik (Republic of Estonia). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with a single legislative body (Riigikogu [101]). Chief of state: President Toomas Hendrik Ilves (from 2006). Head of government: Prime Minister Andrus Ansip (from 2005). Capital: Tallinn. Official language: Estonian. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 kroon(KR) = 100senti;valuation(1 Jul 2008)US$1 = KR9.90.
Demography
Area: 17,462 sq mi, 45,227 sq km. Population (2007): 1,338,000. Density (2006): persons per sq mi 81.8, persons per sq km 31.6. Urban (2005): 69.3%. Sex distribution (2005): male 46.06%; female 53.94%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 15.1%; 15-29, 22.7%; 30-44, 20.5%; 45-59, 20.2%; 60-74,14.7%; 75-84, 5.7%; 85 and over, 1.1%. Ethnic composition (2005): Estonian 68.6%; Russian 25.7%; Ukrainian 2.1%; Belarusian 1.2%; Finnish 0.8%; other 1.6%. Religious affiliation (2000): Christian 63.5%, of which unaffiliated Christian 25.6%, Protestant (mostly Lutheran) 17.2%, Orthodox 16.5%, independent Christian 3.3%; nonreligious 25.1%; atheist 10.9%; other 0.5%. Major cities (2006): Tallinn 396,852; Tartu 101,965; Narva 66,712; Ko-htla-Jarve 45,399; Parnu 44,074. Location: eastern Europe, bordering the Gulf of Finland, Russia, Latvia, the Gulf of Riga, and the Baltic Sea.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 11.0 (world avg. 20.3); (2005) within marriage 41.5%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 13.0 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): -2.0 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.50. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 67.3 years; female 78.1 years.
National economy
Budget (2004). Revenue:KR 54,836,300,000 (tax revenue 82.3%, of which social security contributions 28.3%, VAT 20.6%, personal income taxes 17.4%, excise taxes 9.6%; nontax revenue 11.8%; grants 5.9%). Expend/tures: KR 52,429,100,000 (current expenditure 90.9%, of which social benefits 29.6%; capital expenditure 7.8%; other 1.3%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, f/sh/ng (2005): barley 366,700, wheat 263,400, potatoes 209,800; livestock (number of live animals) 340,100 pigs, 249,800 cattle; roundwood 6,800,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 19%; fisheries production 100,136. M/n/ng and quarry/ng (2005): oil shale 11,500,000; peat 800,000. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2004): food products 163; fabricated metal products 150; wood products (excluding furniture) 138. Energy product/on (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 10,184,000,000 (7,494,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2004) none (58,000); lignite (metric tons; 2004) 13,993,000 (15,503,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (862,000); natural gas (cu m; 2005) none (997,000,000). Population economically active (2005): total 659,600; activity rate of total population 48.8% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 69.6%; female 50.1%; unemployed [2006] 5.9%). Households (2005). Average household size (2004) 2.5; average annual disposable income per household member KR 41,176 (US$3,272); sources of income: wages and salaries 66.1%, transfers 25.6%, self-employment 3.3%; expenditure: food and beverages 28.3%, transportation and communications 16.8%, housing 15.0%, recreation and culture 7.6%. Public debt (external, outstanding; January 2005): US$435,000,000. Gross national income (2006): US$15,183,000,000 (US$11,331 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 948; remittances (2006) 402; foreign direct investment (FDI; 2001-05 avg.) 1,129. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 448; remittances (2006) 75; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 272. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 12.9%, in permanent crops 0.4%, in pasture 6.3%; overall forest area (2005) 53.9%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; c.i.f.): KR 165,298,500,000 (mineral fuels 16.1%; electrical machinery and equipment 15.9%; vehicles and transport equipment 12.1%; chemicals and chemical products 6.5%; textiles and apparel 5.1%). Major mport sources: Finland 18.2%; Russia 13.1%; Germany 12.4%; Sweden 9.0%; Lithuania 6.5%. Exports (2006; f.o.b.): KR 119,519,700,000 (electrical machinery and equipment 19.4%; mineral fuels 15.9%; wood and paper products 11.6%; vehicles and transport equipment 6.7%; textiles and apparel 5.2%). Major export dest -nat ons: Finland 18.2%; Sweden 12.3%; Latvia 8.7%; Russia 7.9%; Germany 5.0%.
Transport and communications
56,856 km (paved 24%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 493,800; trucks and buses 91,400. Air transport (2006; Estonian Air only): passenger-km 1,132,997,000; metric ton-km cargo 2,796,200. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 257,000 (192); televisions (2003): 686,000 (507); telephone landlines (2006): 542,000 (409); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 1,659,000 (1,252); personal computers (2005): 650,000 (483); total Internet users (2006): 760,000 (574); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 228,000 (170).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2000). Percentage of population ages 10 and over having: no formal schooling/incomplete primary education 6.7%; complete primary/lower secondary 31.6%; complete secondary 29.2%; higher vocational 17.5%; undergraduate 12.3%; advanced degree 0.4%; unknown 2.3%. Literacy (2003): virtually 100%. Health: physicians (2003) 4,277 (1 per 316 persons); hospital beds (2004) 7,850 (1 per 172 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2005) 5.5. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,744 (vegetable products 72%, animal products 28%); 140% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 4,934 (army 89.4%, navy 6.7%, air force 3.9%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.7%; per capita expenditure US$152.
Background
The lands on the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea were invaded by Vikings in the 9th century ad and later by Danes, Swedes, and Russians, but the Estonians were able to withstand the assaults until the Danes took control in 1219. In 1346 the Danes sold their sovereignty to the Teutonic Order, which was then in possession of Livonia (southern Estonia and Latvia). In the mid-16th century Estonia was once again divided, with northern Estonia capitulating to Sweden and Poland gaining Livonia, which it surrendered to Sweden in 1629. Russia acquired Livonia and Estonia in 1721. Nearly a century later, serfdom was abolished, and from 1881 Estonia underwent intensive Russification. In 1918 Estonia obtained independence from Russia, which lasted until the Soviet Union occupied the country in 1940 and forcibly incorporated it into the USSR. Germany held the region (1941-44) during World War II, but the Soviet regime was restored in 1944, after which Estonia’s economy was collectivized and integrated into that of the Soviet Union. In 1991, along with other parts of the former USSR, it proclaimed its independence and subsequently held elections. Estonia continued negotiations with Russia to settle their common border.
Recent Developments
Controversy surrounded Estonia’s removal of a Soviet-era World War II monument—the Bronze Soldier— from central Tallinn to a remote military cemetery in 2007. In April two days of riots broke out, resulting in one death and scores of injuries, and a wave of cyber attacks against Estonian government, media, and banking Web sites, thought by many to be the work of Russian hackers, followed.
Ethiopia
Official name: Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia. Form of government: federal republic with two legislative houses (House of the Federation [112]; House of People’s Representatives [547]). Chief of state: President Girma Wolde-Giorgis (from 2001). Head of government: Prime Minister Meles Zenawi (from 1995). Capital: Addis Ababa. Official language: none. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 birr (Br) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = Br 9.66.
Demography
Area: 435,186 sq mi, 1,127,127 sq km. Population (2007): 76,512,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 175.8, persons per sq km 67.9. Urban (2006): 16.2%. Sex distribution (2006): male 49.88%; female 50.12%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 43.7%; 15-29, 28.1%; 30-44,15.3%; 45-59, 8.5%; 60-74, 3.7%; 75 and over, 0.7%. Ethnolinguistic composition (2000): Oromo 35.8%; Amharic 31.0%; Tigrinya 6.1%; Gurage 4.9%; Sidamo 3.8%; Welaita 2.1%; Somali 1.4%; other 14.9%. Religious affiliation (2005): Muslim 33.7%; Ethiopian Orthodox 33.4%; Protestant 16.3%; traditional beliefs 10.4%; other 6.2%. Major cities (2006): Addis Ababa 2,973,000; Dire Dawa 281,750; Nazret 228,623; Gonder 194,773; Dese 169,104. Location: the Horn of Africa, bordering Eritrea, Djibouti, Somalia, Kenya, and The Sudan.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 38.0 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 14.9 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 5.22. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 47.9 years; female 50.2 years.
National economy
Budget (2004-05). Revenue: Br 20,032,000,000 (tax revenue 61.2%, of which import duties 28.7%, income and profits tax 17.8%, sales tax 9.3%; grants 22.8%; nontax revenue 16.0%). Expend/tures: Br 24,551,000,000 (current expenditure 53.1%, of which defense 11.9%, education 11.8%; capital expenditure 46.9%, of which economic development 31.6%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$5,897,000,000. Gross national income (2006): US$13,278,000,000 (US$164 per capita). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, f/sh/ng (2005): corn (maize) 3,342,892, wheat 2,306,862, sorghum 2,200,241; leading producer of beeswax, honey, cut flowers, and khat; livestock (number of live animals) 38,500,000 cattle, 17,000,000 sheep, (2004) 468,390 camels, (1998) 3,037 civets; roundwood 97,409,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 97%; fisheries production 9,450. M n ng and quarry ng (2005): rock salt 200,000; tantalum 45,000 kg; niobium 7,100 kg. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2004): food products 157; beverages 118; bricks, cement, and ceramics 69. Energy product on (consumpt on): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 2,547,000,000 (2,547,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) none (5,600,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 3,000 (1,624,000). Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 11.1%, in permanent crops 0.7%, in pasture 20.0%; overall forest area (2005) 11.9%. Population economically active (2005): total 32,158,392; activity rate of total population 50.9% (participation rates: ages 10 and over 78.4%; female [1999] 45.5%; unemployed 5.0%). Households (1999-2000). Average household size (2004) 5.3; sources of income: self-employment 70.9% (of which agriculture-based 57.6%), wages and salaries 10.9%, salvaging 6.6%, rent 3.9%, other 7.7%; expenditure: food and beverages 52.8%, housing and energy 14.4%, household operations 13.9%, clothing and footwear 7.9%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 168; remittances (2006) 172; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 364; official development assistance (2005) I,937. Disbursements for (US$’000, 000): tourism (2005) 77; remittances (2006) 14.
Foreign trade
Imports (2003-04): US$2,587,400,000 ([2002] machinery and apparatus 20.2%; chemicals and chemical products 12.8%; road vehicles 12.0%; refined petroleum 11.7%; iron and steel 6.4%). Major /mport sources (2004-05): Saudi Arabia 17.0%; China II.2%; US 10.5%; India 6.1%; Italy 4.2%. Exports (2003-04): US$600,700,000 (coffee 37.2%; khat 14.7%; sesame seeds 13.8%; nonmonetary gold 8.1%; leather 7.5%). Major export dest nat ons (2004-05): Germany 15.1%; Djibouti 13.4%; Japan 7.8%; Saudi Arabia 5.9%; US 5.5%.
Transport and communications
length 36,469 km (paved 19%). Vehicles (2003): passenger cars 71,311; trucks and buses 65,557. A/r transport (2005; Ethiopian Airlines only): passenger-km 5,418,376; metric ton-km cargo 132,601,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 83,000 (1.1); televisions (2003): 547,000 (7.9); telephone landlines (2006): 725,000 (9.1); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 867,000 (11); personal computers (2004): 113,000 (1.7); total Internet users (2005): 164,000 (2.2).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2000). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: no formal schooling 63.8%; incomplete primaryeducation 21.6%; primary 2.6%; incomplete secondary 8.1%; secondary 2.5%; post-secondary 1.4%. Literacy (2006): total population ages 15 and over literate 46.3%; males literate 53.3%; females literate 39.3%. Health (2004-05): physicians 1,077 (1 per 66,236 persons); hospital beds 13,851 (1 per 5,150 persons); infant mortality rate (2006) 93.6. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 1,582 (vegetable products 94%, animal products 6%); 92% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 182,500 (army 98.6%, air force 1.4%); UN peacekeeping personnel along Ethiopian-Eritrean border (July 2007): 1,470 troops. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 3.9%; per capita expenditure US$5.
Background
Ethiopia, the Biblical land of Cush, was inhabited from earliest antiquity and was once under ancient Egyptian rule. Ge’ez-speaking agriculturalists established the kingdom of Da’amat in the 2nd millennium BC. After 300 bc they were superseded by the kingdom of Aksum, whose King Menilek I, according to legend, was the son of King Solomon and the Queen ofSheba. Christianity was introduced in the 4th century ad and became widespread. Ethiopia’s prosperous Mediterranean trade was cut off by the Muslim Arabs in the 7th and 8th centuries, and the area’s interests were directed eastward. Contact with Europe resumed in the late 15th century with the arrival of the Portuguese. Modern Ethiopia began with the reign of Tewodros II, who began the consolidation of the country. In the wake of European encroachment, the coastal region was made an Italian colony in 1890, but under Emperor Menilek II the Italians were defeated and ousted in 1896. Ethiopia prospered under his rule, and his modernization programs were continued by Emperor Haile Selassie in the 1930s. In 1936 Italy again gained control of the country, and it was held as part of Italian East Africa until 1941, when it was liberated by the British. Ethiopia incorporated Eritrea in 1952. In 1974 Haile Selassie was deposed, and a Marxist government, plagued by civil wars and famine, controlled the country until 1991. In 1993 Eritrea gained its independence, but border conflicts with Ethiopia and neighboring Somalia continued in the 1990s.
Recent Developments
Turn to normal politics, though thousands of others remained incarcerated throughout the country. Inflation and ballooning consumer prices put a strain on efforts to meet demands for economic development—price increases on basic consumer products were nearly 100% in some cases. The Ethiopian economy grew at a rate of 6.3% in 2007, up from 5.9% in 2006, but despite generally good harvests and improvements in markets and infrastructure, at least 7.3 million Ethiopians were considered in need of food assistance. Ethiopia and Eritrea supported opposing sides in the war in Somalia, feeding speculation that a regional war was possible.
Faroe Islands
Official name: F0royar (Faroese); F^r0erne (Danish) (Faroe Islands; alternative spelling is Faeroe Islands). Political status: self-governing region of the Danish realm with a single legislative body (Lagting [32]). Chief of state: Danish Queen Margrethe II (from 1972), represented by High Commissioner Dan M. Knudsen (from 2008). Head of home government: Prime Minister Joannes Eidesgaard (from 2004). Capital: Torshavn (Thorshavn). Official languages: Faroese; Danish. Official religion: Faroese Lutheran. Monetary unit: 1 Faroese krona (plural kronur); valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = Faroese kronur 4.72 (the Faroese krona is equivalent in value to the Danish krone [DKK]).
Demography
Area: 540.1 sq mi, 1,398.8 sq km. Population (2007): 48,400. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 89.6, persons per sq km 34.6. Urban (2003): 38.8%. Sex distribution (2006): male 51.99%; female 48.01%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 22.4%; 15-29, 19.3%; 30-44, 20.6%; 45-59, 18.9%; 60-74, 12.2%; 75-84, 4.9%; 85 and over, 1.7%. Ethnic composition (2000): Faroese 97.0%; Danish 2.5%; other Scandinavian 0.4%; other 0.1%. Religious affiliation (2005): Protestant 91%, of which Lutheran 79%, Plymouth Brethren 10%; other 9%. Major municipalities (2005): Torshavn 19,314; Klaksvfk 4,889; Runavfk 3,642; Tv0royri 1,814. Location: island group north of the British Isles between the Norwegian Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 14.7 (world avg. 20.3); (1998) within marriage 62.0%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 8.6 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 5.1 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2004): 1.80. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 75.9 years; female 82.8 years.
National economy
Budget (2003). Revenue: DKK 5,737,000,000 (tax revenue 78.6%, of which income taxes 47.6%, VAT 18.5%; transfers from the Danish government 14.8%; other 6.6%). Expenditures:DKK 5,329,000,000 (social welfare 34.7%, education 15.3%, health 14.5%, debt service 4.0%, agriculture, fishing, and hunting 2.8%). Gross national income (at current market prices; 2003): US$1,472,000,000 (US$30,680 per capita). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): potatoes 1,500, othervegetables, grass, hay, and silage are produced; livestock (number of live animals) 68,100 sheep, 2,000 cattle; fisheries production 588,715 (including blue whiting 267,447, pollock 75,971, cod 35,755, and capelin 19,752; from aquaculture 4%). Manufacturing (value added in DKK ’000,000; 1999): processed fish 393; all other manufacturing 351 (important products include handicrafts and woolen textiles and clothing). Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2006) 259,000,000 ([2004] 290,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (215,000). Population economically active (2006): total 29,400; activity rate of total population 61% (participation rates: ages 16-74, 85.8%; female 44.8%; unemployed 2.7%). Public debt (external, outstanding; including Danish debt; 2004): US$155,000,000. Households. Expenditure (1998): food and beverages 25.1%, transportation and communications 17.7%, housing 12.5%, recreation 11.9%, energy 7.7%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 25; remittances (2003) 44. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): remittances (2003) 5. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 2.1%, in pasture 93%; overall forest area (2005) 0.1%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006): DKK 4,649,488,600 (goods for household consumption 27.7%; fuels, lubricants, and electric current 18.5%; machinery and apparatus 10.8%; goods for the construction industry 9.7%; road vehicles 7.9%). Major import sources (2005): Denmark 26.7%; Sweden 17.4%; Spain 6.7%; Germany 6.6%; Finland 5.4%. Exports (2006): DKK 3,744,957,600 (chilled and frozen fish 64.9%; salted fish 12.8%; dried fish 12.7%; smoked, canned, and other conserved fish 3.5%). Major export destinations (2005): UK 28.6%; Denmark 14.4%; Spain 9.7%; France and Monaco 8.2%; Norway 5.9%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2006): total length 464 km. Vehicles (2006): passenger cars 19,110; trucks, vans, and buses 4,452. A/r transport (2005): passenger arrivals 89,190, passenger departures 89,101. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2003): 18,000 (375); televisions (2000): 47,000 (1,022); telephone land-lines (2006): 23,000 (478); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 50,000 (1,040); total Internet users (2005): 32,000 (645); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 10,000 (208).
Education and health
Health (2005): physicians 57 (1 per 849 persons); hospital beds 295 (1 per 164 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2004) 6.4.
Military
Defense responsibility lies with Denmark.
Background
First settled by Irish monks (c. 700), the islands were colonized by the Vikings (c. 800) and were ruled by Norway from the 11th century until 1380, when they passed to Denmark. They unsuccessfully sought independence in 1946 but received self-government in 1948.
Recent Developments
In 2007 the Faroe Islands and Iceland signed agreements that would increase trade and that defined the maritime boundary between the two countries, officially establishing the valuable fishing rights of both and the limits of each country’s continental shelf claim, which would prove extremely important in the event of the future discovery of offshore petroleum fields.
Fiji
Official name: Republic of the Fiji Islands; Kai Vakarairai ni Fiji (Fijian). Form of government: military regime. Chief of state: President Ratu Josefa Iloilo (from 2000). Head of government: Prime Minister Voreque Bainimarama (from 2007). Capital: Suva. Official languages: English, Fijian, and Hindustani have equal status per constitution. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 Fiji dollar (F$) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = F$1.49.
Demography
Area: 7,055 sq mi, 18,272 sq km. Population (2007): 839,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 118.9, persons per sq km 45.9. Urban (2007): 50.9%. Sex distribution (2006): male 50.17%; female 49.83%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 31.1%; 15-29, 28.6%; 30-44, 19.7%; 45-59, 13.6%; 60-74, 6.1%; 75 and over, 0.9%. Ethnic composition (2007): Fijian 57.3%; Indian 37.6%; other 5.1%. Religious affiliation (2005): Protestant (mostly Methodist) 35%; Hindu 33%; independent Christian 11%, Roman Catholic 8%; Muslim 7%; other 6%. Major urban areas (2007): Suva 86,178 (urban agglomeration, 219,759); Lautoka 52,742; Nausori 46,811; Nadi 42,712. Location: archipelago in the South Pacific Ocean, between Hawaii (US) and New Zealand.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 22.6 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 5.7 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 16.9 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 2.73. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 67.3 years; female 72.5 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: F$1,218,332,000 (customs duties and port dues 59.4%; income taxes 28.9%; fees and royalties 4.7%; other 7.0%). Expend/tures: F$1,231,556,000 (department expenditures 70.7%, charges on public debt 26.3%, other 3.0%). Public debt (external, outstanding; September 2005): US$96,200,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, f/sh/ng (2005): sugarcane 2,952,000, coconuts 140,000, taro 38,000; livestock (number of live animals) 310,000 cattle, 260,000 goats, 140,000 pigs; roundwood 509,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 7%; fisheries production 41,596. M/n/ng and quarry/ng (2005): gold 3,800 kg; silver 1,500 kg. Manufacturing (value added in F$’000,000; 2001): food products 94.6; textiles and clothing 92.4; beverages and tobacco 88.3. Energy product on (consumpt on): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 540,000,000 (540,000,000); coal (metric tons; 2004) none (13,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (321,000). Population economically active (2000): total 341,700; activity rate of total population 42.2% (participation rates: ages 15-64 [1996] 60.6%; female 32.2%; unemployed [2002] 14.1%). Gross national income (at 2006 market prices): US$2,929,000,000 (US$3,515 per capita). Households. Average household size (2007) 4.7; average annual income per household (2002) F$15,757 (US$12,784); sources of income (2002): wages and salaries 64.3%, transfers 8.4%, self-employment 7.2%; expenditure (2002): food, beverages, and tobacco 31.2%, housing and energy 18.5%, transportation and communications 17.9%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 431; remittances (2006) 216; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 36; official development assistance (2005) 43 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 106; remittances (2005) 40. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 10.9%, in permanent crops 4.7%, in pasture 9.6%; overall forest area (2005) 54.7%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; ci.f.): F$3,119,920,000 (mineral products 33.4%; machinery and apparatus 14.9%; transport equipment 7.1%; chemicals and chemical products 5.3%; textiles and clothing 5.0%). Major import sources (2005): Singapore 29.9%; Australia 24.5%; New Zealand 18.0%; Japan 4.2%; US 3.8%. Exports (2006; f.o.b.): F$1,175,206,000 (reexports [mostly petroleum products] 29.4%; sugar 18.3%; fish 8.3%; clothing 8.1%; mineral water 7.4%). Major export destinations (2005): Australia 20.4%; Singapore 20.3%; US 15.5%; UK 15.1%; New Zealand 5.1%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2003; owned by the Fiji Sugar Corporation): length 597 km. Roads (1999): total length 3,440 km (paved 49%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 76,273; trucks and buses 42,311. Air transport (2004-05; Air Pacific only): passenger-km 2,360,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 92,108,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2001): 49,000 (60); televisions (2003): 98,000 (118); telephone landlines (2005): 113,000 (133); cellular telephone subscribers (2005): 205,000 (242); personal computers (2004): 44,000 (52); total Internet users (2006): 80,000 (94).
Education and health
Educational attainment (1996). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling 4.4%; some education 22.3%; incomplete secondary 47.7%; completesecondary 17.0%; some higher 6.7%; university degree 1.9%. Literacy (2003): total population ages 15 and over literate 93.7%; males literate 95.5%; females literate 91.9%. Health (2005): physicians 361 (1 per 2,343 persons); hospital beds 1,810 (1 per 467 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 12.3. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,197 (vegetable products 82%, animal products 18%); 166% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 3,500 (army 91.4%, navy 8.6%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2004): 1.2%; per capita expenditure US$36.
Background
Archaeological evidence shows that the islands of Fiji were occupied in the late 2nd millennium bc and that the inhabitants had developed pottery by c. 1300 bc. The first European sighting was by the Dutch in the 17th century; in 1774 the islands were visited by Capt. James Cook, who found a mixed Melanesian-Polynesian population with a complex society. Traders and the first missionaries arrived in 1835. In 1857 a British consul was appointed, and in 1874 Fiji was proclaimed a crown colony. It became independent as a member of the Commonwealth in 1970 and was declared a republic in 1987 following a military coup. Elections in 1992 restored civilian rule. A new constitution was approved in 1997.
Recent Developments
In early 2007 Fiji military commander Voreque (“Frank”) Bainimarama declared himself interim prime minister. Within the country short-lived opposition to the coup reflected both the military’s efficiency and some public support for its determination to eliminate corruption. Opposition from international aid partners was more intense and sustained. Fiji was suspended from the Commonwealth of Nations, and aid was withheld until the country established a program for a return to civilian government. Donors also imposed “smart sanctions,” designed to limit the mobility of coup leaders (and their families) without imposing further hardship on Fiji’s poor.
Finland
Official names: Suomen Tasavalta (Finnish); Repub-liken Finland (Swedish) (Republic of Finland). Form of government: multiparty republic with one legislative house (Parliament [200]). Chief of state: President Tarja Halonen (from 2000). Head of government: Prime Minister Matti Vanhanen (from 2003). Capital: Helsinki. Official languages: none. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 euro (€) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = €0.63.
Demography
Area (includes inland water area of 13,001 sq mi [33,672 sq km]): 130,559 sq mi; 338,145 sq km. Population (2007): 5,286,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 45.0, persons per sq km 17.4. Urban (2004): 62.1%. Sex distribution (2006): male 48.96%; female 51.04%. Age breakdown (2006): under 15, 17.1%; 15-29, 18.7%; 30-44, 19.5%; 45-59, 22.3%; 60-74, 14.7%; 75-84, 5.9%; 85 and over, 1.8%. Linguistic composition (2006): Finnish 91.5%; Swedish 5.5%; Russian 0.8%; other 2.2%. Religious affiliation (2005): Evangelical Lutheran 83.1%; nonreligious 14.7%; Finnish (Greek) Orthodox 1.1%; Muslim 0.4%; other 0.7%. Major cities (2006): Helsinki 564,521 (urban agglomeration [2003] 1,075,000); Espoo 235,019; Tampere 206,368; Vantaa 189,711; Turku 175,354. Location: northern Europe, bordering Norway, Russia, the Gulf of Finland, the Baltic Sea, the Gulf of Bothnia, and Sweden.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 11.2 (world avg. 20.3); within marriage (2004) 59.2%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 9.1 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 2.0 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2004): 1.80. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 75.8 years; female 82.8 years.
National economy
Budget (2006). Revenue:€39,582,000,000 (VAT 33.3%; income and property taxes 32.4%; excise duties 11.7%). Expenditures: €39,582,000,000 (social security and health 28.6%; education 16.3%; agriculture and forestry 6.8%; defense 5.7%). Public debt (2006): US$73,898,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2006): barley 1,972,000, oats 1,029,000, sugar beets 952,000; livestock (number of live animals) 1,436,000 pigs, 949,000 cattle, 198,000 reindeer; roundwood 51,599,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 9%; fisheries production (2005) 146,096 (from aquacul-ture 10%). Mining and quarrying (2005): chromite 326,000; zinc (metal content) 72,474; gold 3,747 kg. Manufacturing (value added in €’000,000; 2005): electrical and optical equipment (largely telephone apparatus) 7,187; nonelectrical machinery and apparatus 3,744; chemicals and chemical products 3,615. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 67,862,000,000 (84,851,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2004) none (8,082,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) none (79,300,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 12,459,000 (10,242,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) none ([2005] 3,863,000,000). Population economically active (2006): total 2,648,000; activity rate of total population 50.3% (participation rates: ages 15-64 [2004] 73.8%; female [2004] 48.1%; unemployed 7.7%). Households (2004). Average household size 2.2; disposable income per household €31,706 (US$39,367); sources of gross income (2003): wages and salaries 74.4%, rent 18.0%, self-employment 7.1%; expenditure: housing 25.6%, food, beverages, and tobacco 17.7%, transportation and communications 16.0%, recreation, culture, and education 11.7%. Gross national income (2006): US$210,516,000,000 (US$40,013 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2006) 2,357; remittances (2006) 698; foreign direct investment (FDI; 2001-05 avg.) 4,614. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2006) 3,417; remittances (2006) 251; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 3,069. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 7.3%, in permanent crops 0.03%, in pasture 0.09%; overall forest area (2005) 73.9%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004; c.i.f.): €40,729,700,000 (electrical machinery and apparatus 15.0%; nonelectrical machinery and apparatus 12.4%; mineral fuels 12.2%; automobiles and bicycles 9.2%). Major import sources (2006): Russia 14.1%; Germany 13.9%; Sweden 9.8%; China 7.4%; UK 4.8%. Exports (2004; f.o.b.): €48,917,000,000 (electrical machinery and apparatus 21.5%, of which telecommunications equipment 15.3%; paper and paper products 16.8%; nonelectrical machinery and apparatus 12.0%; base metals 6.8%; wood and wood products [excluding furniture] 5.1%). Major export destinations (2006): Germany 11.3%; Sweden 10.5%; Russia 10.1%; UK 6.5%; US 6.5%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2006): route length 5,905 km; passenger-km 3,600,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 11,100,000,000. Roads (2004): total length 78,168 km (paved 65%). Vehicles (2005): passenger cars 2,430,345; trucks and buses 363,644. Airtransport (2005; Finnaironly): passenger-km 16,735,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 340,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 2,255,000 (431); televisions (2003): 3,540,000 (679); telephone landlines (2006): 1,920,000 (365); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 5,670,000 (1,078); personal computers (2004): 2,515,000 (482); total Internet users (2006): 2,925,000 (556); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 1,428,000 (271).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2003). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: incomplete upper-secondary education 35.6%; complete upper secondary or vocational 35.8%; higher 28.6%. Literacy: virtually 100%. Health (2004): physicians (2006) 18,507 (1 per 285 persons); hospital beds 36,082 (1 per 145 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 3.3. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,387 (vegetable products 68%, animal products 32%).
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 28,300 (army 72.4%, navy 17.7%, air force 9.9%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.4%; per capita expenditure US$515.
Background
Recent archaeological discoveries have led some to suggest that human habitation in Finland dates back at least 100,000 years. Ancestors of the Sami apparently were present in Finland by about 7000 bc. The ancestors of the present-day Finns came from the southern shore of the Gulf of Finland in the 1st millennium bc. The area was gradually Christianized from the 11th century. From the 12th century Sweden and Russia contested for supremacy in Finland, but by 1323 Sweden ruled most of the country. Russia was ceded part of Finnish territory in 1721; in 1808 Alexander I of Russia invaded Finland, which in 1809 was formally ceded to Russia. The subsequent period saw the growth of Finnish nationalism. Russia’s losses in World War I and the Russian Revolution of 1917 set the stage for Finland’s independence in 1917. It was defeated by the Soviet Union in the Russo-Finnish War (1939-40) but then sided with Nazi Germany against the Soviets during World War II and regained the territory it had lost. Facing defeat again by the advancing Soviets in 1944, it reached a peace agreement with the USSR, ceding territory and paying reparations. Finland’s economy recovered after World War II. It joined the EU in 1995.
Recent Developments
A leading theme of the opposition in elections to the Finnish parliament in March 2007 was the purportedly low wages of nurses. Agreement was reached with nurses’ unions in November to provide raises of 22-28% over four years and a 2007 year-end (Christmas) bonus of €270 (about US$400). Finnish cellular phone giant Nokia agreed in October to buy the American company Navteq, a maker of digital maps for mobile systems, for €5.7 billion (about US$8.1 billion). The move was seen as the cell phone behemoth’s effort to evolve with the times by providing content (and advertising space).
France
Official name: Republique Frangaise (French Republic). Form of government: republic with two legislative houses (Senate [331], National Assembly [577]). Chief of state: President Nicolas Sarkozy (from 2007). Head of government: Prime Minister Frangois Fillon (from 2007). Capital: Paris. Official language: French. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 euro (€) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = €0.63.
Demography
Area: 210,026 sq mi, 543,965 sq km. Population (2007): 61,709,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 293.8, persons per sq km 113.4. Urban (2003): 76.3%. Sex distribution (2006): male 48.60%; female 51.40%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 18.4%; 15-29, 19.1%; 30-44, 21.1%; 45-59, 20.4%; 60-74, 12.7%; 75-84, 6.3%; 85 and over, 2.0%. Ethnic composition (2000): French 76.9%; Algerian and Moroccan Berber 2.2%; Italian 1.9%; Portuguese 1.5%; Moroccan Arab 1.5%; Fleming 1.4%; Algerian Arab 1.3%; Basque 1.3%; Jewish 1.2%; German 1.2%; Vietnamese 1.0%; Catalan 0.5%; other 8.1%. Religious affiliation (2004): Roman Catholic 64.3%, of which practicing 8%; nonreligious/atheist 27%; Muslim 4.3%; Protestant 1.9%; Buddhist 1%; Jewish 0.6%; Jehovah’s Witness 0.4%; Orthodox 0.2%; other 0.3%. Major cities (urban agglomeration; 2005): Paris 2,153,600 (9,854,000); Marseille 820,900 (1,384,000); Lyon 466,400 (1,408,000); Toulouse 435,000 (839,000); Nice 347,900 (915,000); Nantes 281,800; Strasbourg 272,700; Montpellier 244,300; Bordeaux 230,600 (794,000); Lille 225,100 (1,031,000); Rennes 209,900; Reims 184,800; Le Havre 183,900; Saint-Etienne 175,700; Toulon 166,800. Location: western Europe, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Italy, the Mediterranean Sea, Spain, and Andorra. Dependent territories: French Guiana, French Polynesia, Guadeloupe, Martinique, Mayotte, New Caledonia, Reunion, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, and Wallis and Futuna. Households (2004). Average household size 2.4; 1 person 32.8%, 2 persons 32.5%, 3 persons 15.1%, 4 persons 12.8%, 5 persons or more 6.8%. Individual households 14,320,000 (56.0%); collective households 11,232,000 (44.0%). Immigration: total immigrant population (2004) 4,850,000; immigrants admitted (2002) 205,707, of which North African 30.7%, EU 20.8%, sub-Saharan African 15.2%, Asian 14.1%, other European 11.8%.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 13.1 (world avg. 20.3); (2005) within marriage 52.6%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 8.4 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 2.00. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 77.2 years; female 84.1 years.
Social indicators
Educational attainment (2002). Percentage of population ages 25-64 having: no formal schooling through lower-secondary education 35%; upper secondary/higher vocational 41%; university 24%. Quality of working life. Legally worked week for full-time employees (2005) 36.0 hours. Rate of fatal injuries per 100,000 insured workers (2004) 3.7. Average days lost to labor stoppages per 1,000 workers (2004) 13. Trade union membership (2003) 1,900,000 (8% of labor force). Access to services (2004). Proportion of principal residences having: electricity 97.4%; indoor toilet 94.6%; indoor kitchen with sink 94.2%; hot water 60.3%; air conditioner 15.4%. Social participation. Eligible voters participating in last (May 2007) national election 84.0%. Population over 15 years of age participating in voluntary associations (1997) 28.0%. Social deviance. Offense rate per 100,000 population (2006) for: murder 1.5, rape 16.0, other assault 269.2; theft (including burglary and housebreaking) 3,403.8. Incidence per 100,000 in general population (2001) of: homicide 0.8; suicide 16.1. Leisure. Members of sports federations (2004) 15,226,000, of which football (soccer) 2,147,000, tennis 1,066,000. Movie tickets sold (2005) 174,200,000. Average daily hours of television viewing for population age 4 and over (2005) 3.43. Material well-being (2004).
Households possessing: automobile 81%; color television 95%; personal computer 45%; washing machine 92%; microwave 74%; dishwasher (2001) 39%.
National economy
Gross national income (2006): US$2,256,465,-000,000 (US$35,725 per capita). Budget (2004). Revenue: €330,140,000,000 (VAT 47.1%; direct taxes 38.3%; other taxes 14.6%). Expenditures: €355,470,000,000 (current civil expenditure 86.0%; military expenditure 8.7%; development expenditure 5.3%). Public debt (2005): US$1,375,000,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): corn (maize) for forage and silage 43,600,000, wheat 36,840,806, sugar beets 31,242,506, corn (maize) 13,849,729, barley 10,317,062, grapes 6,793,249, potatoes 6,680,817, rapeseed 4,533,841, apples 2,246,351, triticale 1,793,974, sunflower seeds 1,502,106, dry peas 1,330,640, tomatoes 790,049, carrots 659,313, oats 505,652, lettuce 488,736, peaches and nectarines 430,619, green peas 428,000, cauliflower 377,056, string beans 359,608, leeks 182,910, chicory roots 181,198, mushrooms 165,000, flax fibre and tow 90,000; livestock (number of live animals) 19,383,000 cattle, 15,020,198 pigs, 9,185,475 sheep, 189,998,000 chickens, 30,820,000 turkeys, 22,406,000 ducks; roundwood 34,420,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 8%; fisheries production 832,805 (from aquaculture 31%); aquatic plants production 76,678. Mining and quarrying (2005): gypsum 3,500,000; crude talc 340,000; kaolin 316,000; gold (2004) 1,312 kg. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2003): food products 27,023; pharmaceuticals, soaps, and paints 22,675; motor vehicles, trailers, and motor vehicle parts 20,269; fabricated metal products 14,264; general purpose machinery 10,595; plastic products 8,754; medical, measuring, and testing appliances 7,551; aircraft and spacecraft 7,476; publishing 6,911; special purpose machinery 6,605; bricks, cement, and ceramics 5,922; basic chemicals 5,843; base metals 5,547, of which basic iron and steel 4,117; paper and paper products 5,532; beverages 5,509; furniture 4,218. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 572,241,000,000 (510,201,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2004) 872,000 (20,780,000); lignite (metric tons; 2004) none (40,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2005) 7,800,000 ([2004] 631,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 74,910,000 (74,274,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 1,374,000,000 (49,845,000,000). Retail trade (value of sales in €’000,000; 2004): large food stores 162,600; large nonfood stores 136,400; auto repair shops 120,400; pharmacies and stores selling orthopedic equipment 32,600; shops selling bread, pastries, or meat 31,800; small food stores and boutiques 15,300. Population economically active (2005): total 27,637,000; activity rate of total population 45.5% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 69.1%; female 46.4%; unemployed [April 2007] 8.2%). Households. Average household size (2004) 2.4; average disposable income per household (2004) €28,340 (US$35,187); sources of income (2004): wages and salaries 66%, transfers 23%, self-employment 7%, other 4%; expenditure (2005): housing and energy 24.7%, transportation 14.9%, food and nonalcoholic beverages 13.9%, recreation and culture 9.3%, restaurants and hotels 6.2%, household furnishings 5.8%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 42,283; remittances (2006) 12,554; foreign direct investment (FDI; 2001-05 avg.) 47,391. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 31,180; remittances (2006) 4,268; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 72,600. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 33.5%, in permanent crops 2.0%, in pasture 18.4%; overall forest area (2005) 28.3%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004; c.i.f.): US$431,005,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 24.0%, of which electrical machinery and electronic microcircuits 6.2%, industrial machinery 4.5%; chemicals and chemical products 13.9%; road vehicles 11.7%; crude petroleum and refined petroleum 8.5%; food products 7.2%). Major import sources/Germany 17.4%; Italy 9.0%; Spain 7.4%; Belgium 7.3%; UK 6.5%; US 6.4%; China 4.7%; The Netherlands 4.4%; Japan 3.1%; Switzerland 2.3%. Exports (2004; f.o.b.): US$410,700,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 22.1%, of which electrical machinery and electronic microcircuits 6.3%, industrial machinery 4.6%; transport equipment 20.6%, of which road vehicles and parts 14.7%, aircraft, spacecraft, and related parts 5.3%; chemicals and chemical products 16.9%, of which pharmaceuticals 5.0%; food 8.0%; iron and steel 3.4%; perfumes, cosmetics, and toiletries 3.0%; alcoholic beverages 2.4%). Major export destinations. Germany 15.0%; Spain 10.0%; UK 9.3%; Italy 9.3%; Belgium 7.7%; US 6.9%; The Netherlands 4.0%; Switzerland 3.1%; Japan 1.6%; China 1.6%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads. route length (in operation; 2004) 29,085 km; passenger-km (2003) 53,080,000,000; metric ton-km cargo (2003) 46,840,000,000. Roads (2004): total length 951,220 km (paved 100%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 29,900,000; trucks and buses 6,139,000. Airtransport (2005): passenger-km 115,116,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 5,526,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 7,934,000 (131); televisions (2004): 23,723,000 (391); telephone landlines (2006): 33,897,000 (558); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 51,662,000 (851); personal computers (2005): 35,000,000 (573); total Internet users (2006): 30,100,000 (496); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 12,699,000 (208).
Education and health
Health (2003): physicians 203,487 (1 per 296 persons); hospital beds 457,132 (1 per 132 persons); infant mortality rate (2006) 3.7. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,681 (vegetable products 67%, animal products 33%).
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 254,895 (army 52.4%, navy 17.3%, air force 24.9%, headquarters staff 2.0%, health services 3.4%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 2.5%; per capita expenditure US$871.
Also called the Maid of Orleans, Joan of Arc was a peasant girl who, believing that she was acting under divine guidance, led the French army in a momentous victory at Orleans that repulsed an English attempt to conquer France during the Hundred Years’War (1337-1453).
Background
Archaeological excavations in France indicate continuous settlement from Paleolithic times. About 1200 bc the Gauls migrated into the area, and in 600 bc Ionian Greeks established several settlements, including one at Marseille. Julius Caesar completed the Roman conquest of Gaul in 50 bc. During the 6th century ad, the Salian Franks ruled; by the 8th century power had passed to the Carolingians, the greatest of whom was Charlemagne. The Hundred Years’ War (1337-1453) resulted in the return to France of land that had been held by the British; by the end of the 15th century, France approximated its modern boundaries. The 16th century was marked by the Wars of Religion between Protestants (Huguenots) and Roman Catholics. Henry IV’s Edict of Nantes (1598) granted substantial religious toleration, but this was revoked in 1685 by Louis XIV, who helped to raise monarchical absolutism to new heights. In 1789 the French Revolution proclaimed the rights of the individual and destroyed the ancient regime. Napoleon ruled from 1799 to 1814, after which a limited monarchy was restored until 1871, when the Third Republic was created. World War I (1914-18) ravaged the northern part of France. After Nazi Germany’s invasion during World War II, the collaborationist Vichy regime governed. Liberated by Allied and Free French forces in 1944, France restored parliamentary democracy under the Fourth Republic. A costly war in Indochina and rising nationalism in French colonies during the 1950s overwhelmed the Fourth Republic. The Fifth Republic was established in 1958 under Charles de Gaulle, who presided over the dissolution of most of France’s overseas colonies. In 1981 Frangois Mitterrand became France’s first elected Socialist president. During the 1990s the French government, balancing right- and left-wing forces, moved toward solidifying European unity.
Recent Developments
In the 6 May 2007 runoff presidential election, French voters chose Nicolas Sarkozy of the center-right Union for a Popular Movement over the Socialist candidate, Segolene Royal, to succeed Pres. Jacques Chirac. While maintaining Europe as the prime focus of his foreign policy, Sarkozy was relatively pro-American compared with his predecessors. He created a coalition government, which influenced his decision not to scrap the famous law that placed a 35-hour maximum on the standard workweek (a landmark Socialist law) but rather to use tax relief on overtime pay to moderate the law’s rigidity. To the relief of many European Union partners, Sarkozy agreed to put forward a revamped EU treaty for ratification by the French parliament and not by referendum (as Chirac had tried and failed to do in 2005). Sarkozy also took a pragmatic approach to the issue of Turkey’s application for EU membership, which he opposed. He gave a green light to negotiations compatible with Turkey’s becoming an associate, but not a member, of the EU. Meanwhile, he promoted the idea of a union of Mediterranean rim countries and went to Libya in July and Algeria in December. Visiting Beijing on the eve of a European Union-China summit, Sarkozy bluntly complained about China’s surplus with the EU and the undervaluation of the Chinese currency, which was effectively pegged to the dollar. He also warned that the EU might penalize imports from carbon-emitting countries such as China that did not do enough on climate change. Sarkozy made his first official visit as president to the US in early November. He stressed that France would continue to support the fight against terrorism, including keeping French troops in Afghanistan, and endorsed a strong joint stand against Iran’s nuclear program. In April 2008 at the NATO summit in Bucharest, Romania, France pledged an additional 700-800 troops to its 1,500-strong contingent in Afghanistan.
French Guiana
Official name: Departement de la Guyane frangaise (Department of French Guiana). Political status: overseas department of France with two legislative houses (General Council [19]; Regional Council [31]). Chief of state: French President Nicolas Sarkozy (from 2007). Heads of government: Prefect Jean-Pierre Laflaquiere (from 2006), President Pierre Desert of the General Council (from 2004), and President Antoine Karam of the Regional Council (from 1992). Capital: Cayenne. Official language: French. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 euro (€) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = €0.63.
Demography
Area: 32,253 sq mi, 83,534 sq km. Population (2007): 211,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 6.5, persons per sq km 2.5. Urban (2003): 75.4%. Sex distribution (2005): male 50.58%; female 49.42%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 29.3%; 15-29, 22.8%; 30-44, 21.1%; 45-59, 17.4%; 60-74, 7.2%; 75 and over, 2.2%. Ethnic composition (2000): Guianese Mulatto 37.9%; French 8.0%; Haitian 8.0%; Surinamese 6.0%; Antillean 5.0%; Chinese 5.0%; Brazilian 4.9%; East Indian 4.0%; other (other West Indian, Hmong, other South American) 21.2%. Religious affiliation (2000): Christian 84.6%, of which Roman Catholic 80.0%, Protestant 3.9%; Chinese folk-religionist 3.6%; Spiritist 3.5%; nonreli-gious/atheist 3.0%; traditional beliefs 1.9%; Hindu 1.6%; Muslim 0.9%; other 0.9%. Major cities (1999; commune population): Cayenne (2003) 60,500 (urban agglomeration 84,181); Saint-Laurent-du-Ma-roni 19,211; Kourou 19,107; Matoury 18,032; Remire-Montjoly 15,555. Location: northern South America, bordering the Atlantic Ocean, Brazil, and Suriname.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 30.9 (world avg. 20.3); (2005) within marriage 10%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 4.0 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 4.10. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 74.0 years; female 80.8 years.
National economy
Budget (2002). Revenue:€145,000,000 (direct taxes 33.1%; indirect taxes 31.7%; revenue from French central government 20.7%). Expenditures: €145,000,000 (current expenditures 83.4%; capital expenditures 16.6%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): rice 17,774, cassava 10,400, cabbages 6,350; livestock (number of live animals) 10,500 pigs, 9,200 cattle; roundwood 160,373 cu m, of which fuelwood 63%; fisheries production 5,302. Mining and quarrying (2004): stone, sand, and gravel 3,000; gold 2,564 kg; tantalum 1,500 kg. Manufacturing (2001): pork 1,245; chicken meat 560; rum (2004) 3,786 hectolitres; other products include leather goods, clothing, rosewood essence, yogurt, and beer. Number of satellites launched from the Kourou Space Centre (2005) 5 (in 2004 the European Space Agency, which uses Kourou, accounted for 26% of GDP and employed 8,300). Energy production (consumption).electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 430,000,000 (430,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (317,000). Households. Average household size (1999) 3.3; income per household (2000) €30,542 (US$28,139); sources of income (2000): wages and salaries 55.4%, self-employment 17.6%, transfer payments 14.4%; expenditure (2005): food and beverages 21.7%, housing and energy 20.8%, transportation and communications 15.4%, restaurants and hotels 7.9%, household furnishings 7.3%. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 0.14%, in permanent crops 0.05%, in pasture 0.08%; overall forest area (2005) 91.8%. Gross national income (at 2003 market prices): US$1,610,000,000 (US$9,040 per capita). Population economically active (2005): total 60,012; activity rate of total population 30.3% (participation rates: ages 15 and over 65.0%; female 44.7%; unemployed [2006] 29.1%). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 45.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004): €672,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 18.3%; transportation equipment 16.7%; food products, beverages, and tobacco 13.1%; mineral fuels [mostly refined petroleum] 10.7%; chemicals and chemical products 9.7%). Major import sources: France 47.2%; Trinidad and Tobago 9.4%; Japan 2.3%; Martinique 1.8%; US 1.5%. Exports (2004): €91,000,000 (nonferrous metals [nearly all gold] 49.7%; live animals and food products [mostly fish, shrimp, and rice] 13.3%; transportation equipment [mostly parts for air and space vehicles] 9.9%; machinery and apparatus 9.9%). Major export destinations: France 62.0%; Switzerland 17.1%; Martinique 5.9%; Guadeloupe 3.3%; Italy 2.7%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (1996): total length 1,245 km. Vehicles (1999): passenger cars 32,900; trucks and buses 11,900. Air transport (2005): passengers carried 375,844; cargo carried (2004) 4,400 metric tons. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 9,000 (46); televisions (1998): 37,000 (202); telephone landlines (2001): 51,000 (301); cellular telephone subscribers (2004): 98,000 (536); personal computers (2004): 33,000 (180); total Internet users (2005): 42,000 (216).
Education and health
Educational attainment (1999). Percentage of population ages 20 and over having: no formal education/unknown through lower secondary education 60.9%; vocational 17.5%; upper secondary 9.3%; incomplete higher 5.6%; completed higher 6.7%. Health (2005): physicians 342 (1 per 580 persons); hospital beds 697 (1 per 284 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 12.1.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): French troops 1,470 (army 88.4%, navy 11.6%).
Background
Originally settled by the Spanish, French, and Dutch, the territory of French Guiana was awarded to France in 1667, and the inhabitants were made French citizens after 1877. By 1852 the French began using the territory as a penal colony with one locale, on Devils Island, being especially notorious. It became an overseas territory of France in 1946; the penal colonies were closed by 1939.
Recent Developments
Authorities cracked down on environmentally harmful gold mining in 2008 in French Guiana. Neighboring Suriname expected an influx of gold miners entering the country after French authorities announced new restrictions. Additionally, the establishment of a gold mine by a Canadian company, which environmentalists feared would wreak havoc on the ecosystem, was blocked.
Official name: Polynesie frangaise (French); Polynesia Farani (Tahitian) (French Polynesia). Political status: overseas country of France with one legislative house (Assembly [57]). Chief of state: French President Nicolas Sarkozy (from 2007), represented by High Commissioner Anne Boquet (from 2005). Head of government: President Gaston Flosse (from 2008). Capital: Papeete. Official languages: French; Tahit-ian. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 franc de la Comptoirs frangaise du pacifique (CFPF) = 100 centimes; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = CFPF 75.59 (pegged to the euro [€] at €1 = CFPF 119.25).
Demography
Area: 1,544 sq mi, 4,000 sq km. Population (2007): 261,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 192.1, persons persq km 74.1. Urban (2005): 51.9%. Sexdis-tribution (2005): male 51.64%; female 48.36%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 26.8%; 15-29, 27.5%; 30-44, 22.9%; 45-59, 14.0%; 60-74, 6.9%; 75 and over, 1.9%. Ethnic composition (2000): Polynesian 58.4%, of which Tahitian 41.0%, Tuamotuan 8.5%; mixed European-Polynesian 17.0%; Han Chinese 11.3%; French 11.0%; other 2.3%. Religious affiliation (2005): Protestant 36%, of which Maohi Protestant Church (Presbyterian) 33%; Roman Catholic 31%; other Christian 11%, of which Mormon 6%; Chinese folk-religionist, nonreligious, and other 22%. Major communes (2007): Faaa 29,851; Papeete 26,017 (urban agglomeration 131,695); Punaauia 25,441; Moorea-Maiao 14,550; Pirae 14,475. Location: Oceania, archipelago in the South Pacific Ocean, about midway between South America and Australia.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 17.8 (world avg. 20.3); (2004) within marriage 26%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 4.4 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 2.20. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 73.0 years; female 76.9 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:CFPF 100,343,000,000 (indirect taxes 70.7%; direct taxes and nontax revenue 29.3%). Expenditures: CFPF 148,618,000,000 (current expenditure 68.7%; capital expenditure 31.3%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): coconuts 87,000, copra 8,000, cassava 4,300; livestock (number of live animals) 27,000 pigs, 16,500 goats, 12,000 cattle; fisheries production 15,105 (from aquaculture 20%); export production of black pearls (2004) 9,015 kg. Manufacturing (2004): copra (metric tons sold) 4,143; coconut oil (2001) 5,000; other manufactures include monoi oil (primarily refined coconut and sandalwood oils), beer, printed cloth, and sandals. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 607,100,000 ([2004] 485,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (218,000). Population economically active (2002): total 99,498; activity rate of total population 40.6% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 61.7%; female 40.0%; unemployed 11.7%). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 550; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 20. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 303. Gross national income (2006): US$5,643,000,000 (US$21,766 per capita). Public debt (external, outstanding; 1999): US$542,000,000. Households. Average household size (2007) 3.8; sources of income (1993): salaries 61.9%, self-employment 21.5%, transfer payments 16.6%; expenditure (2000-01): food and beverages 21.9%, housing 19.2%, transportation 16.7%, hotel and cafe expenditures 7.7%, culture and recreation 6.9%, household furnishings 5.8%. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 0.8%, in permanent crops 6.0%, in pasture 5.5%; overall forest area (2005) 28.7%.
French Polynesia
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; c.i.f.): CFPF 157,489,000,000 (machinery and apparatus 16.9%; mineral fuels 12.7%; motor vehicles and parts 10.0%; pharmaceutical products 4.1%). Major import sources: France 30.6%; Singapore 12.4%; US 10.3%; China 6.6%; New Zealand 6.5%. Exports (2006; f.o.b.): CFPF 22,380,000,000 (pearl products [mostly black cultured pearls] 56.2%; transportation [including aerospace] equipment 8.3%; noni fruit 5.2%; fish 1.9%; coconut oil 1.1%; vanilla 0.9%; monoi oil 0.9%). Major export destinations: Hong Kong 26.8%; Japan 23.1%; France 11.0%; US 10.1%; New Caledonia 1.7%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (1999): total length 2,590 km (paved 67%). Motor vehicles: passenger cars (1996) 47,300; trucks and buses (1993) 15,300. Air transport (Air Tahiti and Air Tahiti Nui only): passenger-km (2005) 4,023,700,000; metric ton-km cargo (2004) 96,492,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 27,000 (106); televisions (2004): 56,000 (223); telephone landlines (2004): 53,000 (216); cellular telephone subscribers (2004): 73,000 (289); personal computers (2005): 28,000 (109); total Internet users (2005): 55,000 (216); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 11,000 (43).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2002). Percentage of population ages 25 and over having: no formal schooling 4.9%; less than lower-secondary education 46.2%; lower secondary 10.9%; upper secondary 11.7%; vocational 15.8%; higher 10.5%. Literacy (2000): total population ages 15 and over literate, virtually 100%. Health: physicians (2004) 447 (1 per 561 persons); hospital beds (2003) 971 (1 per 256 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 6.8. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 3,202 (vegetable products 70%, animal products 30%); 166% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 1,510 French military personnel (army 53.0%, navy 47.0%).
Background
European contact with the islands of French Polynesia was gradual. Portuguese navigator Ferdinand Magellan sighted Pukapuka in the Tuamotu group in 1521. The southern Marquesas Islands were discovered in 1595. Dutch explorer Jacob Roggeveen in 1722 discovered Makatea, Bora-Bora, and Maupiti. Captain Samuel Wallis in 1767 discovered Tahiti, Moorea, and Maiao Iti. The Society Islands were named after the Royal Society, which had sponsored the expedition under Capt. James Cook that observed from Tahiti the 1769 transit of the planet Venus. Tubuai was discovered on Cook’s last voyage, in 1777. The islands became French protectorates in the 1840s, and in the 1880s the French colony of Oceania was established. French Polynesia became an overseas territory of France after World War II and was granted partial autonomy in 1977.
Recent Developments
French Polynesia had another tumultuous year in 2007 after the pro-independence government of Pres. Oscar Temaru was deposed in December 2006. Pres. Gaston Tong Sang, whose coalition advocated autonomy, announced that the territory would secede from France. Tong Sang was soon deposed by members of his own party, however, and Temaru returned in September to win election as president for the third time in three years. France, seeking a solution to the ongoing instability, proposed to shorten the local assembly’s term and to change the electoral system.
Gabon
Official name: Republique Gabonaise (Gabonese Republic). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with two legislative houses (Senate [91]; National Assembly [120]). Chief of state: President Omar Bongo Ondimba (from 1967). Head of government: Prime Minister Jean Eyeghe Ndong (from 2006). Capital: Libreville. Official language: French. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 CFA franc (CFAF) = 100 centimes; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = CFAF 414.60.
Demography
Area: 103,347 sq mi, 267,667 sq km. Population (2007): 1,331,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 12.9, persons per sq km 5.0. Urban (2006): 85.7%. Sex distribution (2006): male 49.67%; female 50.33%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 40.0%; 15-29, 28.3%; 30-44,16.1%; 45-59, 9.3%; 60-74, 4.6%; 75-84, 1.4%; 85 and over, 0.3%. Ethnic composition (2000): Fang 28.6%; Punu 10.2%; Nzebi 8.9%; French 6.7%; Mpongwe 4.1%; Teke 4.0%; other 37.5%. Religious affiliation (2005): Christian 73%, of which Roman Catholic 45%, Protestant/independent Christian 28%; Muslim 12%; traditional beliefs 10%; nonreligious 5%. Major urban areas (2003): Libreville 661,600; Port-Gentil 116,200; Franceville 41,300; Lambarene 9,000. Location: western Africa, bordering Cameroon, the Republic of the Congo, the South Atlantic Ocean, and Equatorial Guinea.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 36.2 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 12.3 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 23.9 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 4.74. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 53.2 years; female 55.8 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue:CFAF 1,432,200,000,000 (oil revenues 63.3%; taxes on international trade 15.0%, of which VAT 5.6%; direct taxes 9.7%; indirect taxes 7.9%; other revenues 4.1%). Expenditures: CFAF 872,400,000,000 (current expenditure 82.2%, of which wages and salaries 26.1%, transfers 23.8%, debt service 14.8%; capital expenditure 17.8%). Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$3,582,-000,000. Gross national income (2006): US$6,828,-000,000 (US$5,209 per capita). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): plantains 270,000, sugarcane 235,000, cassava 230,000; livestock (number of live animals) 300,000 rabbits, 212,000 pigs, 195,000 sheep; roundwood 3,728,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 14%; fisheries production 43,941. Mining and quarrying (2005): manganese ore 2,859,000; gold 300 kg. Manufacturing (value added in CFAF ’000,000,000; 2004): agricultural products 48.0; wood products (excluding furniture) 31.3; refined petroleum products 18.1. Energy production (consumption):electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 1,537,000,000 (1,537,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) 78,000,000 (5,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 713,000 (412,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 126,000,000 (126,000,000). Population economically active (2003): total 570,000; activity rate of total population 42.5% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 74.1%; female 43.0%; unemployed 21%). Households (2004). Average household size 5.0; average annual income per household CFAF 1,730,000 (US$3,275); expenditure: food 85.3%, transportation and communications 3.6%, clothing 1.8%. Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 15; remittances (2005) 6; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 154; official development assistance (2005) 65 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000, 000): tourism (2004) 214; remittances (2005) 110. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 1.3%, in permanent crops 0.7%, in pasture 18.1%; overall forest area (2005) 84.5%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2005): CFAF 722,600,000,000 (for petroleum sector 27.3%; unspecified 72.7%). Major import sources (2003): France 50%; US 5%; UK 5%; The Netherlands 4%; Cameroon 4%. Exports (2005): CFAF 2,882,000,000,000 (crude petroleum and petroleum products 83.2%; manganese ore and concentrate 6.4%). Major export destinations (2003): US 52%; France 9%; China 8%; Japan 4%; Trinidad and Tobago 3%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2002): route length (2005) 814 km; passenger-km 97,500,000; metric ton-km cargo 1,553,000,000. Roads (2004): total length 9,170 km (paved 10%). Vehicles (1997): passenger cars 24,750; trucks and buses 16,490. Air transport (2002): passenger-km 643,000,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2005): 48,000 (35); televisions (2004): 220,000 (173); telephone landlines (2006): 37,000 (26); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 765,000 (544); personal computers (2005): 45,000 (33); total Internet users (2006): 81,000 (58); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 1,200 (0.9).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2000): no formal schooling 6.2%; incomplete primary and complete primary education 32.7%; lower secondary 41.3%; upper secondary 14.2%; higher 5.6%. Literacy (2000): total population ages 15 and over literate 71%; males literate 80%; females literate 62%. Health (2003-04): physicians 270 (1 per 5,006 persons); hospital beds 4,460 (1 per 303 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 54.5. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,705 (vegetable products 87%, animal products 13%); 146%of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 4,700 (army 68.1%, navy 10.6%, air force 21.3%); French troops (2006) 2,260. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.5%; per capita expenditure US$79.
Background
Artifacts dating from late Paleolithic and early Neolithic times have been found in Gabon, but it is not known when the Bantu speakers who established Gabon’s ethnic composition arrived. Pygmies were probably the original inhabitants. The Fang arrived in the late 18th century and were followed by the Portuguese and by French, Dutch, and English traders. The slave trade dominated commerce in the 18th and much of the 19th century. The French then took control, and Gabon was administered (1843-86) with French West Africa. In 1886 the colony of French Congo was established to include both Gabon and the Congo; in 1910 Gabon became a separate colony within French Equatorial Africa. An overseas territory of France from 1946, it became an autonomous republic within the French Community in 1958 and declared its independence in 1960. Rule by a sole political party was established in the 1960s, but discontent with it led to riots in Libreville in 1990. Legalization of opposition parties led to new elections in 1990. Peace negotiations with Chadian rebels and with the Republic of the Congo were ongoing in the 1990s.
Recent Developments
China in January 2007 agreed to send 44 agricultural experts to assist small farmers in Gabon. The government promised in March to supply free electricity and water to the country’s poorest households to offset the impact of a 25% increase in the price of foodstuffs and fuel, and in an attempt to control surging inflation, price ceilings on basic commodities were put in place in September for a six-month period.
The Gambia
Official name: The Republic of The Gambia. Form of government: multiparty republic with one legislative house (National Assembly [53]). Head of state and government: President Col. Yahya Jammeh (from 1994). Capital: Banjul. Official language: English. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 dalasi (D) = 100 butut; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = D 20.90.
Demography
Area (including inland water area of 802 sq mi [2,077 sq km]): 4,127 sq mi, 10,689 sq km. Population (2007): 1,709,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 514.0, persons per sq km 198.4. Urban (2006): 26.2%. Sex distribution (2003): male 49.59%; female 50.41%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 40.1%; 15-29, 26.4%; 30-44, 17.3%; 45-59, 10.2%; 60-74, 5.0%; 75-84, 0.9%; 85 and over, 0.1%. Ethnic composition (2003): Malinke 42%; Fulani 18%; Wolof 16%; Diola 10%; Soninke 9%; other 5%. Religious affiliation (2005): Muslim 90%; Christian (mostly Roman Catholic) 9%; traditional beliefs/other 1%. Major cities (2004): Serekunda 225,500; Brikama 81,400; Bakau 74,700; Banjul 36,100 (Greater Banjul [2003] 523,589); Farafenni 31,600. Location: western Africa, bordering Senegal and the North Atlantic Ocean.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 39.4 (world avg. 20.3). Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 12.3 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): 27.1 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2003): 5.13. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 52.3 years; female 56.0 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: D 2,823,500,000 (tax revenue 80.2%, of which taxes on international trade 42.7%, corporate taxes 14.4%; nontax revenue 12.0%; grants 7.8%). Expenditures: D 3,961,100,000 (current expenditure 61.1%, of which interest payments 28.6%; capital expenditure 38.9%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): millet 127,600, peanuts (groundnuts) 100,000, oil palm fruit 35,000; livestock (number of live animals) 330,000 cattle, 270,000 goats, 148,000 sheep; roundwood 760,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 85%; fisheries production 32,000. Mining and quarrying: sand, clay ([2005] 13,700), and gravel are excavated for local use. Manufacturing (value added in US$; 1995): food products and beverages 6,000,000; textiles, clothing, and footwear 750,000; wood products 550,000. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2005) 156,000,000 (156,000,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) none (93,000). Population economically active (2003): total 730,000; activity rate of total population 52.2% (participation rates: female 44.2%; unemployed [2004] extremely high). Households. Average household size (2003) 8.6; expenditure (1991; low-income population in Banjul and Kanifing only): food and beverages 58.0%, clothing and footwear 17.5%, energy and water 5.4%, housing 5.1%. Public debt (external, outstanding; 2005): US$626,000,000. Gross national income (at 2006 market prices): US$485,000,000 (US$292 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 56; remittances (2005) 58; foreign direct investment (FDI; 2001-05 avg.) 21; official development assistance (2005) 58. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 5; remittances (2005) 1; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 8. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 31.5%, in permanent crops 0.5%, in pasture 45.9%; overall forest area (2005) 41.7%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2004; c.i.f.): US$236,600,000 (food and live animals 27.3%; machinery and transport equipment 18.1%; mineral fuels 10.1%; chemicals and chemical products 7.4%). Major import sources: China 24.6%; Brazil 16.8%; Senegal 10.4%; UK 5.8%; The Netherlands 4.5%. Exports (2004; f.o.b.): US$127,000,000 (reexports 79.7%; peanuts [groundnuts] 13.3%; fruits and vegetables 4.1%). Major export destinations: Thailand 16.5%; UK 15.4%; France 14.0%; India 12.8%; Germany 9.1%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Roads (2004): total length 3,742 km (paved 19%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 8,109; trucks and buses 2,961. Air transport (2001; Yum-dum International Airport at Banjul only): passenger arrivals 300,000, passenger departures 300,000; cargo loaded and unloaded 2,700 metric tons. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Televisions (2003): 20,000 (13); telephone landlines (2006): 53,000 (32); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 404,000 (243); personal computers (2004): 23,000 (16); total Internet users (2005): 58,000 (36); broadband Internet subscribers (2005): 100 (0.06).
Education and health
Literacy (2006): total population ages 15 and over literate 43.7%; males literate 51.1%; females literate 36.6%. Health (2003): physicians 156 (1 per 9,769 persons); hospital beds (2000) 1,140 (1 per 1,199 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births (2006) 71.6. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 2,537 (vegetable products 93%, animal products 7%); 137% of FAO recommended minimum.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 800 (army 100%). Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 0.5%; per capita expenditure US$2.
Background
Beginning about the 13th century AD, the Wolof, Ma-linke, and Fulani peoples settled in different parts of what is now The Gambia and established villages and then kingdoms in the region. European exploration began when the Portuguese sighted the Gambia River in 1455. Britain and France both settled in the area in the 17th century. The British Fort James, on an island about 20 mi (32 km) from the river’s mouth, was an important collection point for the slave trade. In 1783 the Treaty of Versailles reserved the Gambia River for Britain. After the British abolished slavery in 1807, they built a fort at the mouth of the river to block the continuing slave trade. In 1889 The Gambia’s boundaries were agreed upon by Britain and France; the
British declared a protectorate over the area in 1894. Independence was proclaimed in 1965, and The Gambia became a republic within the Commonwealth in 1970. It formed a limited confederation with Senegal in 1982 that was dissolved in 1989. During the 1990s the government was in turmoil.
Recent Developments
Pres. Yahya Jammeh of The Gambia made international news in January 2007 when he announced that on particular days of the week, he could cure HIV, using herbs and bananas and spiritual methods. He also resisted pressure from China to drop his country’s support for Taiwan. In early 2008 Jammeh announced that significant amounts of uranium had been discovered in the country and would be exploited.
Georgia
Official name: Sak’art’velo (Georgia). Form of government: unitary multiparty republic with a single legislative body (Parliament [235]). Head of state and government: President Mikheil Saakashvili (from 2008), assisted by Prime Minister Lado Gurgenidze (from 2007). Capital: Tbilisi. Official language: Georgian (locally Abkhazian, in Abkhazia). Official religion: none (special recognition is given to the Georgian Orthodox Church). Monetary unit: 1 Georgian lari (GEL) = 100 tetri; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = 1.42 lari.
Demography
Area: 27,086 sq mi, 70,152 sq km. Population (2007): 4,613,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 170.3, persons per sq km 65.8. Urban (2004): 52.3%. Sex distribution (2005): male 47.50%; female 52.50%. Age breakdown (2005): under 15, 17.9%; 15-29, 24.2%; 30-44, 21.5%; 45-59, 18.9%; 60 and over, 17.5%. Ethnic composition (2002): Georgian 83.8%; Azerbaijani 6.5%; Armenian 5.7%; Russian 1.5%; Ossetian 0.9%; other 1.6%. Religious affiliation (2005): Georgian Orthodox 54.8%; Sunni Muslim 14.5%; Shi’i Muslim 5.0%; Armenian Apostolic (Orthodox) 3.9%; Catholic 0.8%; Yazidi 0.4%; Protestant 0.4%; nonreligious 13.0%; other 7.2%. Major cities (2006): Tbilisi 1,103,300; K’ut’aisi 190,100; Bat’umi 122,100; Rust’avi 118,200; Sokhumi (2002) 45,000. Location: Caucasus region of southwestern Asia, bordering Russia, Azerbaijan, Armenia, Turkey, and the Black Sea.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2005): 10.7 (world avg. 20.3); within marriage 50.3%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2005): 9.9 (world avg. 8.6). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2005): 1.35. Life expectancy at birth (2005): male 69.3 years; female 76.7 years.
National economy
Budget (2005). Revenue: GEL 3,257,200,000 (tax revenue 74.0%, of which VAT 30.3%, income tax 8.9%, excise tax 8.8%, taxes on corporate profits 6.5%; nontax revenue 23.0%; grants 3.0%). Expenditures: GEL 3,280,800,000 (social security and welfare 19.1%; defense 12.1%; general public service 10.8%; education 8.8%; public order 8.7%). Public debt (external, outstanding; March 2006): US$1,642,850,000. Population economically active (2005): total 2,023,900; activity rate of total population 44.1% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 68.4%; female 46.9%; unemployed 13.8%). Production (metric tons except as noted). Agriculture, forestry, fishing (2005): potatoes 432,202, corn (maize) 421,347, grapes 250,294; livestock (number of live animals) 1,250,672 cattle, 804,900 sheep and goats; round-wood 615,900, ofwhich fuelwood 74%; fisheries production 3,072 (from aquaculture 2%). Mining and quarrying (2004): manganese ore 218,700. Manufacturing (value of production in GEL ’000,000; 2005): food products and beverages 799.6, basic metals 205.7, nonmetallic mineral products 131.2. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 6,920,000,000 ([2005] 9,800,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) 718,000 (271,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 16,000 (508,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 11,000,000 ([2005] 1,500,000,000). Households (2005). Average household size (2004) 3.7; average annual income per household GEL 3,642 (US$2,009); sources of income: wages and salaries 28.8%, self-employment 13.0%, remittances 12.0%, agricultural income 10.6%, non-cash income 26.1%, other 9.5%; expenditure: food, beverages, and tobacco 38.9%, transportation 7.8%, energy 7.6%, health 5.7%, clothing and footwear 4.3%. Gross national income (2006): US$8,296,000,000 (US$1,871 per capita). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 242; remittances (2006) 545; foreign direct investment (2001-05 avg.) 318; official development assistance (2005) 258 (commitments). Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 169; remittances (2006) 131. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 11.5%, in permanent crops 3.8%, in pasture 27.9%; overall forest area (2005) 39.7%.
Foreign trade
Imports (2006; c.i.f.): US$3,681,230,000 (mineral fuels 17.8%; food products and beverages 15.4%; motor vehicles 9.1%; nonelectrical machinery 9.1%; chemicals and chemical products 8.2%). Major import sources (2005): Russia 15.4%; Turkey 11.4%; Azerbaijan 9.4%; Ukraine 8.8%; Germany 8.3%. Exports (2006; f.o.b.): US$993,054,000 (food and beverages [including wine] 23.3%; iron and steel 16.6%; transportation equipment 14.1%; chemicals and chemical products 7.8%). Major export destinations (2005): Russia 17.8%; Turkey 14.1%; Azerbaijan 9.6%; Turkmenistan 8.7%; Bulgaria 4.9%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2005): 1,559 km; passenger-km 719,500,000; metric ton-km cargo 6,127,100,000. Roads (2005): 20,329 km (paved (2004) 40%). Vehicles (2004): passenger cars 255,200; trucks and buses 68,600. Air transport (2005): passenger-km 510,800,000; metric ton-km cargo 3,600,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2001): 23,000 (5); televisions (2003): 1,627,000 (357); telephone landlines (2006): 553,000 (119); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 1,704,000 (368); personal computers (2004): 192,000 (42); total Internet users (2006): 332,000 (72); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 27,000 (5.8).
Education and health
Educational attainment (2004). Percentage of population ages 15 and over having: no formal education/unknown 1.6%; primary education 4.1%; incomplete secondary 10.5%; secondary 48.2%; incomplete higher 12.3%; higher 23.3%. Literacy (2004): virtually 100%. Health (2005): physicians 20,311 (1 per 226 persons); hospital beds 17,100 (1 per 268 persons); infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births 19.7. Food (2005): daily per capita caloric intake 1,797 (vegetable products 72%, animal products 28%); 92% of FAO recommended minimum.
Azerbaijan to Circassia, forming a pan-Caucasian empire. Invasions by Mongols and Turks in the 13th and 14th centuries disintegrated the kingdom, and the fall of Constantinople (now Istanbul) to the Ottoman Turks in 1453 isolated it from western Christendom. The next three centuries saw repeated invasions by the Armenians, Turks, and Persians. Georgia sought Russian protection in 1783, and in 1801 it was annexed to Russia. After the Russian Revolution of 1917, the area was briefly independent; in 1921 a Soviet regime was installed, and in 1936 Georgia became the Georgian SSR, a full member of the Soviet Union. In 1990 a noncommunist coalition came to power in the first free elections ever held in Soviet Georgia, and in 1991 Georgia declared independence. In the 1990s, while Pres. Eduard Shevardnadze tried to steer a middle course, internal dissension resulted in conflicts with the northwestern republic of Abkhazia, and external distrust of Russian motives in the area grew. In 1992 Abkhazia reinstated its 1925 constitution and declared independence, which Georgia refused to recognize.
Recent Developments
The Georgian parliament in May 2007 endorsed a proposal to create a temporary administration for the breakaway republic of South Ossetia. Dmitry Sanakoyev, who was elected alternative South Osset-ian “president” in November 2006, was named to head that administration. Two unidentified aircraft entered Georgian airspace in August 2007 and dropped a missile that failed to explode. International experts tentatively concluded that the aircraft were Russian. Georgian special forces killed two Russian military instructors in Abkhazia in September and took seven Abkhaz border guards prisoner. In August 2008, Georgian troops entered South Ossetia, and Russia responded by invading. Several weeks of fighting and Russian occupation ensued, leaving hundreds dead. Russia withdrew most of its forces to the two separatist regions by the end of the month, but on 26 August Moscow recognized the independence of both.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 11,320 (army 62.2%, national guard 14.0%, navy 11.9%, air force 11.9%); UN peacekeeping troops (September 2007): 120 observers and 17 police; the final withdrawal of Russian troops (in Georgia since the collapse of the USSR in 1991) occurred in November 2007. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 3.5%; per capita expenditure US$51.
Background
Ancient Georgia was the site of the kingdoms of Iberia and Colchis, whose fabled wealth was known to the ancient Greeks. The area was part of the Roman empire by 65 bc and became Christian in ad 337. For the next three centuries it was involved in the conflicts between the Byzantine and Persian empires; after 654 it was controlled by Arab caliphs, who established an emirate in Tbilisi.
Germany
Official name: Bundesrepublik Deutschland (Federal Republic of Germany). Form of government: federal multiparty republic with two legislative houses (Federal Council [69]; Federal Diet [614]). Chief of state: President Horst Kohler (from 2004). Head of government: Chancellor Angela Merkel (from 2005). Capital: Berlin; some ministries remain in West Germany’s previous capital, Bonn. Official language: German. Official religion: none. Monetary unit: 1 euro (€) = 100 cents; valuation (1 Jul 2008) US$1 = €0.63.
Demography
Area: 137,856 sq mi, 357,046 sq km. Population (2007): 82,249,000. Density (2007): persons per sq mi 596.6, persons per sq km 230.4. Urban (2003): 88.1%. Major cities (urban agglomerations) (2005): Berlin 3,395,189 (4,200,072); Hamburg 1,743,627 (2,549,339); Munich 1,259,677 (7,940,477); Cologne 983,347 (1,846,241); Frankfurt am Main 651,899 (1,915,002); Stuttgart 592,569 (2,625,690); Dortmund 588,168 (5,746,018); Essen 585,430 (5,746,018); Dusseldorf 574,514 (1,318,512); Bremen 546,852 (858,488); Hannover 515,729 (1,001,580); Leipzig 502,651 (580,050); Duisburg 501,564 (5,746,018); Nuremberg (Nurn-berg)499,237 (1,030,168). Location: central Europe, bordering Denmark, the Baltic Sea, Poland, the Czech Republic, Austria, Switzerland, France, Luxembourg, Belgium, The Netherlands, and the North Sea. Sex distribution (2006): male 48.96%; female 51.04%. Ethnic composition (by nationality; 2000): German 88.2%; Turkish 3.4% (including Kurdish 0.7%); Italian 1.0%; Greek 0.7%; Serb 0.6%; Russian 0.6%; Polish 0.4%; other 5.1%. Households (2005). Number of households 39,178,000; average household size 2.1; 1 person 37.5%, 2 persons 33.9%, 3 persons 14.0%, 4 persons 10.7%, 5 or more persons 3.9%. Age breakdown (2003): under 15, 14.7%; 15-29, 17.4%; 30-44, 23.9%; 45-59, 19.3%; 60-74, 16.9%; 75-84, 6.1%; 85 and over, 1.7%. Religious affiliation (2005): Protestant 35.0%, of which Lutheran/Reformed churches 34%; Roman Catholic 32.5%; Sunni Muslim 4.3%; Orthodox 1.7%; New Apostolic (an independent Christian group) 0.5%; Buddhist 0.3%; Jewish 0.2%; nonreli-gious 18.0%; atheist 2.0%; other 5.5%. Immigration (2003): immigrant arrivals 601,759, from Poland 14.6%,Turkey 8.0%, Russia 5.2%, Romania 3.9%.
Vital statistics
Birth rate per 1,000 population (2006): 8.2 (world avg. 20.3); (2004) within marriage 72.0%. Death rate per 1,000 population (2006): 10.0 (world avg. 8.6). Natural increase rate per 1,000 population (2006): -1.8 (world avg. 11.7). Total fertility rate (avg. births per childbearing woman; 2006): 1.39. Life expectancy at birth (2006): male 75.8years; female 82.0 years.
Social indicators
Educational attainment (2002). Percentage of population ages 25-64 having: no formal schooling through lower secondary 17%; upper secondary/higher vocational 60%; university 23%. Quality of working life. Average workweek (2005) 38.2 hours. Annual rate per 100,000 workers (2002) for: injuries or accidents at work 3,554; deaths 2.9. Proportion of labor force insured for damages of income loss resulting from: injury, virtually 100%; permanent disability, virtually 100%; death, virtually 100%. Average days lost to labor stoppages per 1,000 workers (2005) 0.5. Access to services. Proportion of dwellings (2002) having: electricity, virtually 100%; piped water supply, virtually 100%; flush sewage disposal (1993) 98.4%; public fire protection, virtually 100%. Social participation. Eligible voters participating in last (September 2005) national election 77.7%. Trade union membership in total workforce (2003) 18%. Social deviance (2000). Offense rate per 100,000 population for: murder and manslaughter 3.8; sexual abuse 37.0, of which rape and forcible sexual assault 11.7, child molestation 10.2; assault and battery 153.2; theft 754.2. Material well-being (2005). Households possessing: automobile 76.8%; telephone (2006) 95.2%; mobile telephone (2006) 80.6%; refrigerator 99.1%; television (2004) 95.0%; DVD player 50.1%; washing machine (2004) 95.5%; clothes dryer 39.3%; personal computer (2006) 71.6%; dishwasher 59.1%; microwave oven 67.0%; Internet access (2006) 57.9%; MP3 player 14.7%.
National economy
Budget (2004). Revenue: €639,220,000,000 (social security contributions 58.3%; tax revenue 37.6%, of which individual income taxes 13.7%, taxes on goods and services 10.2%, excise taxes 10.2%; nontax revenue 2.2%; other 1.9%). Expenditures: €691,480,-000,000 (social benefits 71.4%; grants 7.9%; interest 5.7%; compensation of employees 5.5%). Total public debt (2004): US$1,732,000,000,000. Production (metric tons except as noted; 2005). Agriculture, forestry, fishing: sugar beets 25,284,700, wheat 23,692,700, potatoes 11,624,000, barley 11,613,800, rapeseed 5,051,700, grapes 1,014,700, apples 852,600, cabbages 721,500, currants 148,000, gooseberries 38,000, hops 34,500; livestock (number of live animals) 26,857,800 pigs, 13,034,500 cattle, 2,642,400 sheep, 107,267,000 chickens; roundwood 56,946,000 cu m, of which fuelwood 11%; fisheries production 330,353 (from aquaculture 14%). Mining and quarrying: potash (potassium oxide content) 3,664,000; feldspar 500,000. Manufacturing (value added in US$’000,000; 2003): transportation equipment 80,003, of which motor vehicles 46,854, motor vehicle parts 20,655; nonelectrical machinery and apparatus 64,943; electrical machinery and electronics 47,403, of which electricity distribution and control apparatus 18,799; fabricated metal products 41,855; food and food products 31,727; paints, soaps, and pharmaceuticals 26,172; industrial chemicals 20,211; printing and publishing 19,829; professional and scientific equipment 19,045, of which medical, measuring, and testing appliances 16,737; plastic products 17,333; cement, bricks, and ceramics 10,736. Energy production (consumption): electricity (kW-hr; 2004) 533,268,000,000 (616,785,000,000); hard coal (metric tons; 2004) 29,200,000 (57,900,000); lignite (metric tons; 2004) 181,900,000 (182,000,000); crude petroleum (barrels; 2004) 25,100,000 (810,600,000); petroleum products (metric tons; 2004) 103,600,000 (99,900,000); natural gas (cu m; 2004) 29,100,000,000 (120,600,000,000). Gross national income (2006): US$2,901,482,000,000 (US$35,110 per capita). Households. Average annual disposable income per household (2003) >33,840 (US$38,194); sources of take-home income (1997): wages 77.6%, self-employment 12.0%, transfer payments 10.4%; expenditure (2003): housing and energy 32.5%, transportation 14.4%, food, beverages, and tobacco 14.0%, recreation and culture 11.8%, household furnishings 5.7%, clothing and footwear 5.0%, restaurants and hotels 4.3%. Population economically active (2005): total 41,150,000; activity rate of total population 49.9% (participation rates: ages 15-64, 73.7%; female 44.8%; unemployed [2006] 8.1%). Selected balance of payments data. Receipts from (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 29,151; remittances (2006) 6,667; foreign direct investment (FDI) (2001-05 avg.) 25,337. Disbursements for (US$’000,000): tourism (2005) 72,488; remittances (2006) 12,344; FDI (2001-05 avg.) 22,464. Land use as % of total land area (2003): in temporary crops 33.9%, in permanent crops 0.6%, in pasture 14.2%; overall forest area (2005) 31.7%.
Military
Total active duty personnel (2006): 284,500 (army 67.3%, navy 9.0%, air force 23.7%); German peacekeeping troops abroad (April 2006) more than 7,500; US troops in Germany (2005) 66,000; British troops (2005) 22,000; French troops (2005) 2,800; Dutch troops (2005) 2,300. Military expenditure as percentage of GDP (2005): 1.4%; per capita expenditure US$462.
The Berlin Wall surrounded West Berlin and prevented access to it from East Berlin and adjacent areas of East Germany during the period from 1961 to 1989 (28 years).
Foreign trade
Imports (2005; c.i.f.): €625,632,000,000 (machinery and equipment 21.7%, of which televisions, telecommunications equipment, and electronic components 6.4%, office machinery and computers 4.6%; transport equipment 14.2%, of which road vehicles 10.2%; chemicals and chemical products 11.3%; crude petroleum and natural gas 8.3%; base metals 6.0%; food products and beverages 4.5%; wearing apparel 2.6%). Major import sources (2006): France 8.7%; The Netherlands 8.3%; China 6.7%; US 6.6%; UK5.9%; Italy 5.5%; Belgium 4.9%; Russia 4.1%; Austria 4.1%; Switzerland 3.4%. Exports (2005; f.o.b.): €786,186,000,000 (machinery and equipment 26.5%, of which televisions, telecommunications equipment, and electronic components 4.7%; transport equipment 22.6%, of which road vehicles 19.2%; chemicals and chemical products 13.1%; base metals 5.2%; medical and precision instruments and watches and clocks 4.2%). Major export destinations (2006): France 9.6%; US 8.7%; UK 7.3%; Italy 6.7%; The Netherlands 6.2%; Belgium 5.5%; Austria 5.5%; Spain 4.7%; Switzerland 3.9%; Poland 3.2%.
Transport and communications
Transport. Railroads (2001): length 85,653 km; pas-senger-km (2003) 71,292,000,000; metric ton-km cargo (2004) 86,400,000,000. Roads (2004): total length 231,420 km (paved 100%). Vehicles (2006): passenger cars 46,090,300; trucks and buses 2,573,100. Air transport (2005): passenger-km 137,364,000,000; metric ton-km cargo 7,680,396,000. Communications, in total units (units per 1,000 persons). Daily newspaper circulation (2004): 22,095,000 (268); televisions (2003): 55,758,000 (675); telephone landlines (2006): 54,200,000 (658); cellular telephone subscribers (2006): 84,300,000 (1,023); personal computers (2004): 46,300,000 (561); total Internet users (2006): 38,600,000 (469); broadband Internet subscribers (2006): 14,085,000 (171).
Background
Germanic tribes entered the region about the 2nd century bc, displacing the Celts. The Romans failed to conquer the region, which became a political entity only with the division of the Carolingian Empire in the 9th century ad. The monarchy’s control was weak, and power increasingly devolved upon the nobility, organized in feudal states. The monarchy was restored under Saxon rule in the 10th century, and the Holy Roman Empire, centering on Germany and northern Italy, was revived. Continuing conflict between the Holy Roman emperors and the Roman Catholic popes undermined the empire, and its dissolution was accelerated by Martin Luther’s revolt in 1517, which divided Germany, and ultimately Europe, into Protestant and Roman Catholic camps, culminating in the Thirty Years’ War (1618-48). Germany’s population and borders were greatly reduced, and its numerous feudal princes gained virtually full sovereignty. In 1862 Otto von Bismarck came to power in Prussia and over the next decade reunited Germany in the German Empire. It was dissolved in 1918 after the German defeat in World War I. Germany was stripped of much of its territory and all of its colonies. In 1933 Adolf Hitler became chancellor and established a totalitarian state, the Third Reich, dominated by the Nazi Party. Hitler’s invasion of Poland in 1939 plunged the world into World War II. Following its defeat in 1945, Germany was divided by the Allied Powers into four zones of occupation. Disagreement with the USSR over the reunification of the zones led to the creation in 1949 of the Federal Republic of Germany (West Germany) and the German Democratic Republic (East Germany). Berlin, the former capital, remained divided. West Germany became a prosperous parliamentary democracy, East Germany a one-party state under Soviet control. The East German Communist government was brought down peacefully in 1989, and Germany was reunited in 1990. After the initial euphoria over unity, the former West Germany sought to incorporate the former East Germany both politically and economically, resulting in heavy financial burdens for the wealthier western Germans. The country continued to move toward deeper political and economic integration with Western Europe through its membership in the European Union.
Recent Developments
Energy security in Germany in 2007 was very much bound up with the topic of nuclear energy. The idea of potentially having to increase the use of nuclear energy, or even build a new nuclear energy reactor, seemed inconceivable to many Germans—even though this might be the only way to reach the country’s ambitious emission goals (a reduction of 40% by 2020, relative to 1990). The renewable-energysector showed a large upswing in the economy. The overall economy posted a positive trend. Unemployment decreased to some 3.5 million (with a slight cyclical increase of unemployment in the summer), and in the year ending March 2008 the unemployment rate had dropped almost a full percent, to 8.0%. Germany’s GDP grew by 4.4%. The population growth rate in 2007 was estimated at -0.033%. As Germans had fewer children, the resulting decrease in the number of taxpayers—along with an increasing number of retirees—was likely to cause economic problems. In June 2008 Germany agreed to send an additional 1,000 troops to its force in Afghanistan.