20.5
On front- end operations, telephone interfaces are monitored using GR-909 diagnostic methods. VQmon is mainly used for monitoring the voice quality
from signal and packet transmissions. VQmon, which was popularized by Telchemy, is voice quality monitoring based on the E-model algorithm discussed in previous sections. VQmon and the RTCP-XR framework provide a set of metrics for VoIP performance monitoring and diagnosis. They are used in addition to GR-909 and other proprietary diagnostic methods. It supports both real-time monitoring and postanalysis.
VQmon mainly derives parameters from packet transmission characteristics that include packet impediments on the network and end-to-end delays jitter buffer dynamics as well as signal transmission characteristics that include signal level, noise level, gain, echo rejections, R-factor, and MOS derived from the R-model. The VQmon parameter’s role in the RTCP-XR [Friedman et al. (2003)] packet is shown in Fig. 20.6. These parameters are typically updated once every 256 packets. Use of these parameters and applying feedback for improving the voice quality helps the VoIP system to deliver the highest quality under severe conditions.
RTCP-XR sends about 20 parameters categorized as packet loss, discarded metrics, delay metrics, signal-related metrics, call quality or transmission quality metrics, configuration metrics, and jitter buffer parameters. Complete details on these parameters are in RFC3611 [Friedman et al. (2003)]. A short description of parameters is provided here in Fig. 20.6.
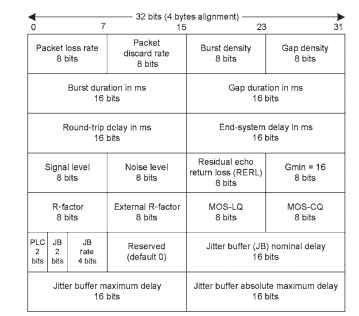
Figure 20.6. RTCP-XR packet with 22 parameters in 28-byte payload.
Packet Loss and Discard Metrics
Loss rate : The fraction of RTP data packets from the source lost since the beginning of reception.
Discard rate : The fraction of RTP data packets from the source that have been discarded since the beginning of reception, because of late or early arrival, under-run, or overflow at the receiving jitter buffer.
Burst Metrics
Burst density: The fraction of RTP data packets within burst periods since the beginning of reception that were either lost or discarded.
Gap density: The fraction of RTP data packets within inter-burst gaps from the beginning of reception that were either lost or discarded.
Burst duration: The mean duration expressed in milliseconds of the burst periods that have occurred since the beginning of reception.
Gap duration: The mean duration expressed in milliseconds of the gap periods that have occurred since the beginning of reception.
Delay Metrics
Round-trip delay: The most recently calculated round-trip time between RTP interfaces, which is expressed in milliseconds. If RTCP is used, then the reported delay value is the time of receipt of the most recent RTCP packet from the source SSRC, minus the last sender report (LSR) time reported in its SR, minus the delay since last SR (DLSR) reported in its SR. A nonzero LSR value is required to calculate round-trip delay.
End-system delay: Sum of the total sample accumulation and encoding delay associated with the sending direction, decoding, and jitter buffer playout buffer delay associated with the receiving direction. It is expressed in milliseconds.
Signal Metrics
Signal level: This level is measured only for packets containing speech energy. It is represented as a signed integer in a two’s complement format. A value of 127 indicates that this parameter is unavailable.
Signal level = 10Log10 (RMS talk-spurt power in mW).
Noise level: The noise level is defined for the silent period. A value of 127 indicates that this parameter is unavailable. Noise level = 10 Log10 (RMS silence power in mW).
Residual echo return loss: The residual echo return loss value may be measured directly by the VoIP end systenfs echo canceller or may be
estimated by adding the echo return loss (ERL) and echo return loss enhancement (ERLE) provided by the echo canceller. A value of 127 represents that it is undefined.
Call Quality Metrics
R-Factor: The R-factor is a voice quality metric that considers only equipment impairments. A value of 127 indicates that this parameter is unavailable.
Ext R-factor: This metric is defined as including the effects of delay and other parameters. A value of 127 indicates that this parameter is unavailable.
MOS-LQ: This mean opinion score is defined by not including the effects of delay. It is expressed in the range 10 to 50, which corresponds to 10 times scaled MOS. A value of 127 indicates that this parameter is unavailable.
MOS-CQ: This mean opinion score is defined by including the effects of delay. It is expressed in the range of 10 to 50, which corresponds to 10 times MOS. A value of 127 indicates that this parameter is unavailable.
Jitter Buffer Parameters
Nominal delay: Current nominal jitter buffer delay in milliseconds.
Maximum delay : Current maximum jitter buffer delay in milliseconds (in this case, the adaptive jitter buffer is used).
Absolute maximum delay: This delay is the absolute maximum in milliseconds that the adaptive jitter buffer can reach under worst-case conditions. Its value must be set to JB maximum for fixed jitter buffer implementations.
Configuration Parameters
Gmin: The recommended value of 16, which corresponds to a burst/gap decision threshold count of number of consecutive received packets.
Receiver configuration byte: This byte consists of the following information:
Packet loss concealment (PLC). This parameter represents the type of PLC
algorithm used. It is represented by 2 bits; Standard (11) / enhanced (10)
/ disabled (01) / unspecified (00). Jitter buffer adaptive (JBA). This parameter represents the jitter buffer
type represented by 2 bits; 11—Adaptive, 10—Nonadaptive, 01—reserved,
00—Unknown.
Jitter buffer rate (JB rate). This parameter represents the implementation-specific adjustment rate of a jitter buffer in adaptive mode.
RTCP-XR messages containing key call-quality-related metrics are exchanged periodically between IP phones and gateways. This exchange lets a probe or analyzer monitor these metrics midstream to support problem resolution, or be retrieved from a gateway using a simple network management protocol (SNMP). RTCP-XR in a deployment is also marked in Fig. 20.1.
VOICE QUALITY MONITORING AND RTCP-XR (VoIP)
Next post: VoIP VOICE FAQS
Previous post: SUMMARY AND DISCUSSIONS (VoIP)
