The animal kingdom is divided into approximately 15 phyla.These phyla represent large groupings of species descended ! from a single, ancient ancestor. Humans, as well as marine mammals, belong to the phylum Chordata and its largest subdivision, the Vertebrata. Vertebrates are animals with a segmented backbone consisting of a large series of similar bony elements, the vertebrae. Vertebrates are further divided into a number of classes, and mammals (Mammalia in Latin) is one of these (die others are amphibians, reptiles, birds, and several classes of fishes).
I. Mammalian Characteristics
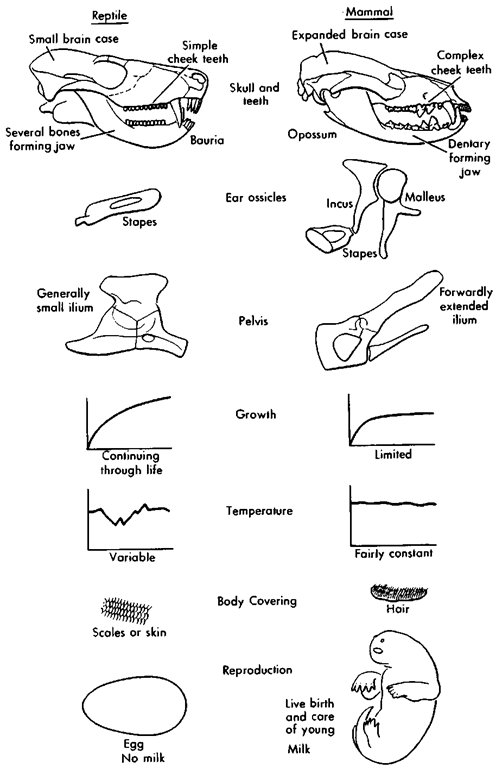
All mammals are derived from a single ancestor that lived in die Late Triassic, approximately 220 million years ago. Scientists distinguish Mammalia from Mammaliformes (Rowe, 1988), but that distinction is not important for marine mammals and we can treat those terms as synonyms here. The first mammal was different from contemporary reptiles by having a lower jaw (half of the mandible) that consisted of a single bone holding both the teeth and the joint with the skull. In all nonmammals (e.g., birds and reptiles), the dentary does not take part in die mandibular joint, and instead a bone called the articular forms die joint with a skullbone called the quadrate. The articular and quadrate did not disappear when mammals evolved, instead they became part of the sound transmission mechanism of the ear and are called malleus (hammer) and incus (anvil) in mammals.
II. Marine Mammals
Many other features characterize modern mammals (Fig. 1), but for most of these there are exceptions, and marine mammals are commonly among the exceptions. Most modern mammals, for instance, can be characterized as air-breathing, endotherm (warm-blooded) vertebrates with hair that chew their food with complex teeth and that feed their young milk produced by mammary glands of the female.
Figure 1 Some of the characters that distinguish mammals from other vertebrates.
Most modern mammals have a battery of strongly varied teeth that occlude well and are used for chewing. Mysticete whales have no teeth and many modern odontocete whales and pinnipeds lack the complex morphology of the molars. Odontocetes do not chew their food and there is no fine occlusion. Most mammals have hair that covers the entire body, but not whales and sirenians. There are commonly two generations of teeth (deciduous and adult) in an individual mammal, but modern toothed whales only have a single generation. The skull articulates with the vertebral column by means of two convex joints called occipital condyles, which are present in all marine mammals. Nearly all mammals have seven neck vertebrae, but the manatees only have six. Mammals commonly have two pairs of limbs, each with five digits; modern whales and sirenians lack external hindlimbs and digits are commonly not visible externally.