Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Carrier phase is defined as
a difference
between the phase of the incoming carrier signal
and the phase of the reference signal generated
by the receiver. At the initial epoch of the signal
acquisition, the receiver can measure only the
fractional phase, so the carrier phase observable
contains the initial unknown integer ambiguity,
N
.
Integer ambiguity is a number of full phase cycles
between the receiver and the satellite at the starting
epoch, which remains constant as long as the sig-
nal tracking is continuous. After the initial epoch,
the receiver can count the number of integer cycles
being tracked. Thus, the carrier phase observable
can be expressed as a sum of the fractional part, φ
(in cycles), measured with millimeter-level preci-
sion, and the integer number of cycles counted since
the starting epoch, t
0
. The integer ambiguity can be
determined using special techniques referred to as
ambiguity resolution algorithms. Once the integer
ambiguity is resolved, the ambiguous carrier phase
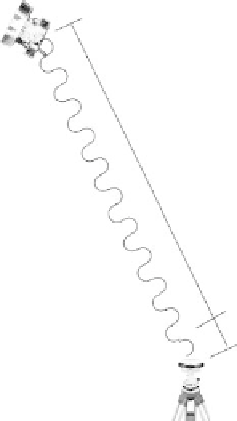
observable can be converted to unambiguous range measurement R = (N + φ)λ by multiplying the
sum of the measured phase (in cycles) and the initial integer ambiguity (in cycles) by the corre-
sponding wavelength, λ (see Figure 9.9). It should be noted that starting from epoch t
0
, the carrier
phase measurement φ will include not only the fractional part of a cycle, but also the number of full
cycles since the initial epoch t
0
. The phase-range observable, Φ (in meters; Equation (9.3)), equals
the sum of R and all the error sources affecting the measurement. This observable is used in the
applications where the highest accuracy is required.
Nλ
R = (N + φ)λ
φλ
fIGURe 9.9
Carrier phase range measurement.
I
f
s
r
Φ
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
=−++ +−+
ρ
T
λ
Ncdt
(
t
)
m
+
ε
1
,
1
r
,
1
,
1
r
,
1
r
r
r
r
2
1
(9.3)
s
I
f
s
s
r
s
s
s
s
s
Φ
=−++ +
ρ
T
λ
Nc
(
dt
−++
dt
)
m
ε
2
r
,
2
r
r
r
,
2
r
r
,
2
r
,
2
2
2
where
s
s
2
Phase-ranges (in meters) measured between station
r
and satellite
s
on L1 and L2
ΦΦ
r
,
:
,
1
r
,
1 2
Initial integer ambiguities on L1 and L2, corresponding to receiver
r
and satellite
s
λ
1
≈ 19 cm and λ
2
≈ 24 cm are wavelengths of L1 and L2
mm
r
s
s
NN
r
,
:
,
r
,
s
s
2
Multipath error on carrier phase observables on L1 and L2
,
:
,
1
r
,
s
s
εε
r
12
,
:
Measurement noise for carrier phase observables on L1 and L2
,
r
,
Another observation sometimes provided by GPS receivers, and primarily used in kinematic
applications for velocity estimation, is instantaneous Doppler frequency. It is defined as a time change
of the phase-range, and thus, if available, it is measured on the code phase (Lachapelle, 1990).
Equation (9.2), which is a nonlinear part of Equation (9.1) and Equation (9.3), requires Taylor
series expansion to enable the estimation of the three unknown user coordinates (X, Y, Z)
r
. Sec-
ondary (nuisance) parameters in the above equations are satellite and user receiver clock errors,