Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
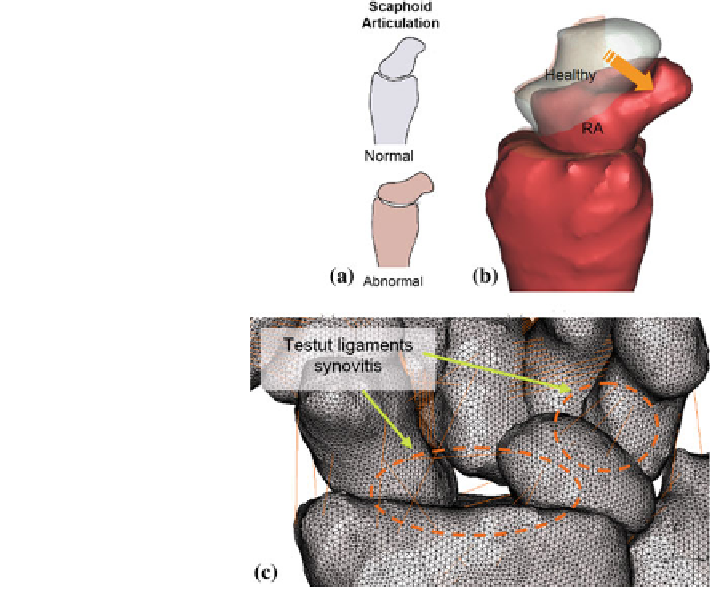
Fig. 5.6 Information from
literature on the rotatory
subluxation of the scaphoid,
producing incongruent
loading at the radioscaphoid
facet [
5
] was used to perform
the simulation (a).The
simulated scaphoid
dislocation in the palmar
direction from sagittal view
(b) and palmar view (c). The
RA bones were in red and the
transparent bones represent
the healthy bones
5.1.6 Simulation of Dislocation of the Scaphoid in the Palmar
Direction
Dislocation of the scaphoid in the palmar direction was due to the radial insertion
of the Testut ligament synovialitis has caused bone loss and the possibility of
so-called Mannerfelt crypt [
2
]. This is also one of the criteria of the SLAC [
5
]. The
simulation (Fig.
5.6
) was performed by rotating radially the scaphoid (center of
scaphoid as COR) and palmarly (the proximal end ulnar direction as COR) for
16.8 and 22.3, respectively.
5.1.7 Simulation of Hand Scoliosis
Hand scoliosis occurs due to tendon rupture. This mechanism ends in a changed axis
of the wrist to the ulna with a consecutive rotation of the metacarpal bones in the
radial direction [
2
]. Hand scoliosis was simulated by dislocating 7.23 mm all carpus
excluding the scaphoid towards ulnar and rotating radially 10 of all metacarpals
with the center of the radius as the COR. This mechanism resulted in a changed axis
of the wrist to the ulnar [
2
] (Fig.
5.7
).
Search WWH ::

Custom Search