Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
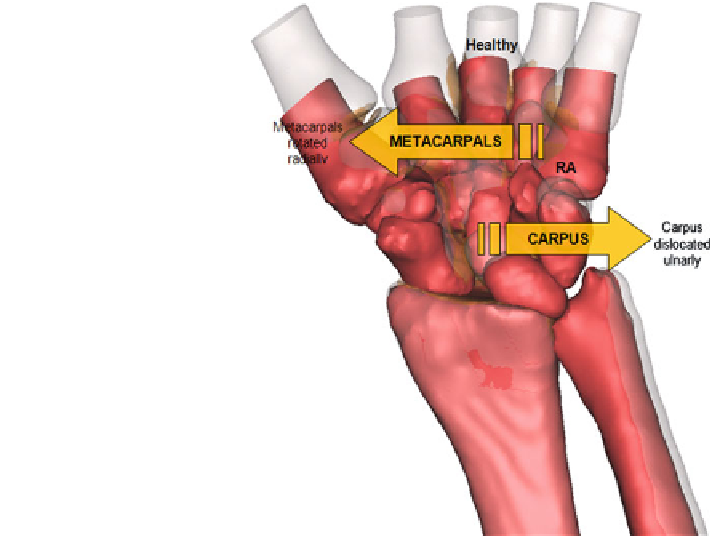
Fig. 5.7 The dislocation of
carpus towards ulnar and
rotation of metacarpals
radially due to tendon rupture
resulted in hand scoliosis.
The RA bones were in red
while transparent bones
depicting the normal healthy
wrist
5.1.8 Simulation of Reduction of Contact Between the Lunate
and the Radius
As revealed by Trieb et al., the contact between the lunate and the radius was
decreased in rheumatic wrist [
2
]. It was due to the dislocation of the proximal row
or the carpal bones towards ulnar. This condition was simulated through transla-
tion of 7 mm of the lunate towards ulnar direction (reference was positioned at the
center of the distal ulna) resulting in decreasing of the contact between the radius
and the lunate (Fig.
5.8
).
5.1.9 Simulation of Bone Erosion
Bone erosion was simulated by using Boolean operation (subtraction) after assuring
accuracy of the bone's position (Fig.
5.9
). Sharp edges due to eroded bone were
manually simulated by utilising local smoothing algorithm tool. Bone erosion was
regularly occurred in the rheumatic wrist attributed to the inflammation of the
synovial fluid and deterioration of the joint constraint [
1
-
3
,
6
-
8
]. The differences of
volumes between the healthy and the RA bones were summarised in Table
5.2
.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search