Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
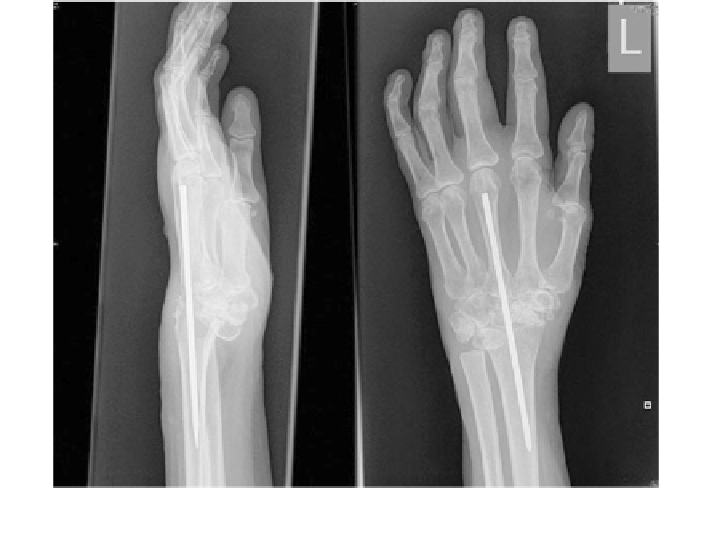
Fig. 3.4 Arthrodesis of the wrist affected by rheumatoid arthritis. Stanley pin is used for fusion,
together with excision of the distal ulna (Darrach's procedure) [
21
]
the functionality and stability of the wrist joint. Hand scoliosis could also be
observed in the rheumatic wrist. This was occurred as a result of ruptured tendon,
which has led to a changed axis of the wrist to the ulnar, and the rotation of
metacarpal in the radial direction.
3.3 Treatment
Treatments are given according to levels of severity of the diseased wrist. Syn-
thetic narcotics, opiods, Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and
cortisone are examples of medication given to the patients who are considered
under less severe level of pain. To prevent bacterial infections, antibiotics are used.
Joint inflammation could be inhibited with Biologic Response Modifiers (BRMs)
which targets the immune system preventing activation of tumor necrosis factor
(TNF). Similarly, Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) has also
given encouraging effects in reducing the pain. For severe cases, surgical proce-
dures are usually employed, which were categorised into two main objectives:
motion eliminating and motion preserving procedures.
Arthrodesis or wrist fusion as depicted in Fig.
3.4
is performed to relief pain by
fusing affected bones, partially or completely, established through plates and
screws fixations. This procedure obtained patients' satisfaction as it promotes
Search WWH ::

Custom Search