Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
Most ethylene glycol is used to make polyethylene terephthalate, the
largest volume polyester. Diethylene glycol contaminating the ethylene
glycol will also polymerize and result in a polyester with lower melting point
and poorer physical properties. The other major use of ethylene glycol is
antifreeze. When mixed with water, ethylene glycol lowers the melting point
of water. This is because of the freezing point depression which occurs when
a solute is dissolved in a solvent. This is the same phenomenon that explains
why salt water has a lower freezing point than pure water. The sodium
and chloride ions are the solute and lower the freezing point of water, the
solvent. In the case of ethylene glycol, it is soluble in water and lowers the
freezing point of water. When temperatures are cold, it prevents the water
in automobile radiators from freezing. When water freezes, it expands and
can crack and break parts of the engine. Other solutes lower the freezing
point, but have disadvantages. Methanol or ethanol is too volatile; sodium
chloride is too corrosive. Ethylene glycol is good for this purpose. A little
diethylene glycol contaminating the ethylene glycol does not prevent it from
being useful for antifreeze, but large amounts of diethylene glycol lower the
effectiveness. This is because the amount of the freezing point depression is
based on the number of moles of solute. Pure ethylene glycol has a greater
number of moles in a gallon than a gallon of an 80:20 molar ratio mixture of
ethylene glycol:diethylene glycol.
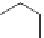
Ethylbenzene is also made from ethylene. This is a Friedel - Crafts
alkylation reaction, a type of electrophilic aromatic substitution.
H
+
H
H
CC
CH
2
CH
3
Et
H
H
H
Ethylene
H
H
+
H
+
−
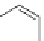
Ethylbenzene can also be isolated from the C8 stream of the BTX
petroleum fraction. Ethylbenzene is dehydrogenated to make styrene, which
in turn is used to make polystyrene. High temperatures, about 600
∘
C, and a
catalyst, often an iron oxide, are used to do the dehydrogenation.
CH
2
CH
3
−
H
2
Styrene






























Search WWH ::

Custom Search