Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
control. The structure - activity relationship (SAR) has been studied and
several variants are commercial. The ideal herbicide is effective at giving
a broad spectrum of weed control and not being harmful to the particular
crop being grown. Flumetsulam is used for broadleaf weed control in maize
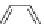
and soybeans; metosulam is used for maize and cereals. Diclosulam and
cloransulam-methyl are used in soybeans; florasulam is used in cereals [54].
Penoxsulam has a reversed sulfonamide linkage and is used in rice fields to
control grass, broadleaf, and sedge weeds [55].
CH
3
O
CH
2
CH
3
O
F
H
3
C
Cl
Cl
H
H
H
N
N
N
N
N
N
N
N
S
N
S
N
S
CH
3
O
F
N
N
N
N
N
O
O
CH
3
O
O
O
O
F
Flumetsulam
Cl
Cl
Diclosulam
Metosulam
CH
3
O
CH
2
CH
3
CH
3
O
O
CO
2
CH
3
N
F
CF
3
H
N
N
H
H
N
N
N
N
N
N
N
N
S
N
S
S
N
F
O
OCH
3
N
N
O
O
O
O
O
Cl
F
F
O
CHF
2
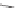
Cloransulam-methyl
Florasulam
Penoxsulam
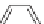
One relatively new herbicide is a pyrimidine-based chemical, salflufenacil
(Kixor
®
, BASF) [56]. This herbicide inhibits chlorophyll biosynthesis. In
particular it inhibits protoporphyrinogen IX oxidase (PPO) in the tetrapyrrole
biosynthetic pathway. Protoporphyrin IX is the heterocylic ring system sur-
rounding the magnesium cation in chlorophyll. There are several herbicides
that operate by this mechanism. They are in group 14 (WSSA).
CH
3
F
3
C
N
O
O
CH
3
O
O
N
S
N
CH
3
O
CH
3
F
Cl
Salflufenacil
One herbicide that has been used since the 1940s is 2,4-dichlorophen-
oxyacetic acid (2,4-D). It is currently found in about 600 products registered
for agricultural, residential, industrial, and aquatic uses [57].















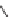


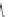



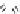










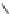
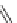

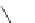































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search