Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
many herbicides that interfere with AHAS. They are classified as group 2
(WSSA) or group B (HRAC).
NH
3
+
NH
3
+
NH
3
+
CO
2
−
CO
2
−
CO
2
−
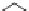
Valine
Leucine
Isoleucine
Certain types of organic compounds inhibit AHAS, resulting in plant death.
One reason for the success of AHAS inhibitors is that they are effective at
extremely low application rates [51]. The first type discovered was based
upon the sulfonylurea moiety. Chlorsulfuron (Glean
®
, Dupont), a first gener-
ation sulfonyl urea was introduced in 1982 [52] for broadleaf control. Second
generation sulfonyl ureas replaced the chlorobenzene ring with a substituted
pyridine and increased the spectrum of activity. Azimsulfuran is a newer rice
herbicide and was first introduced in 1996. About 60% of the global pop-
ulation rely on rice as a major food source [53]. Altogether, more than 30
sulfonylurea herbicides have been commercialized.
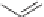
CH
3
N
OCH
3
N
N
OCH
3
N
O
N
N
O
O
Cl
O
N
N
O
O
S
H
H
N
OCH
3
S
H
H
N
CH
3
N
N
CH
3
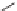
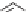
Chlorsulfuran
Azimsulfuran
Imidazolinone herbicides are another type of AHAS inhibitors. Imazapic
is an example. Other variants either have different substituents on the pyridine
ring or substitute a substituted phenyl ring for the pyridine.
H
3
C
CO
2
H
N
N
HN
O
Imazapic
Flumetsulam is one of several in the triazolopyrimidine sulfonamide class
of herbicide. This class of AHAS inhibitors is effective for broadleaf weed


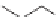


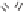













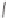

























Search WWH ::

Custom Search