Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
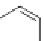
CO
2
H
O
Cl
Cl
2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
Chirality can be important in pharmaceuticals and also in other compounds
that have biological activity. It can be a factor in herbicides. Dimethenamid
(Frontier
®
, BASF) is an herbicide in group 15, inhibitors of synthesis of very
long-chain fatty acids. It can control a variety of annual grasses and several
broadleaf weeds and is used for corn crops.
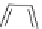
H
H
3
C
CH
2
OCH
3
Chiral carbon
H
3
C
N
Cl
O
CH
3
S
Dimethenamid
The molecule has two chiral elements. There is a chiral axis along the
bond from the carbon at the 3-position of the thiophene to the nitrogen. This
is because there is not free rotation around this single bond. There is also
an asymmetric carbon at the methine carbon attached to nitrogen. Because
of two chiral elements, there can be 2
2
or four possible stereoisomers.
Dimethenamid with S-configuration at the chiral carbon can be prepared
from S-methoxyisopropylamine. This single enantiomer amine is isolated
from a racemic mixture of amines by enantioselective enzymatic acyla-
tion [58]. The enzyme selectively acylates only one enantiomer and the
resultant amide can be readily separated from the unreacted free amine. The
undesired enantiomer can then be racemized to provide a source of (after
further separation) more of the desired enantiomer.
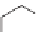
H
3
C
H
3
C
H
3
C
OCH
3
OCH
3
OCH
3
+
NH
2
NH
2
NHCOR
Amide
Racemic mixture
S-enantiomer
Dimethenamid with S configuration at the chiral carbon, (1S,aRS) would
be expected to be twice as effective as the previous version with a racemic
mixture at the chiral carbon (1RS,aRS) if this were the active diastereomer
and the 1R,aRS diastereomer was inactive. However, greenhouse and field



















Search WWH ::

Custom Search