Digital Signal Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
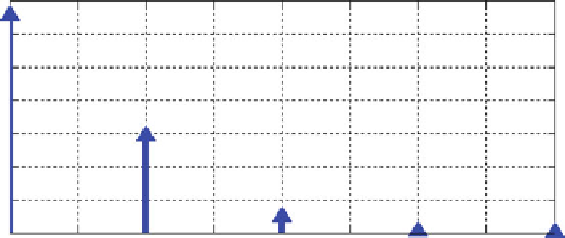
The corresponding probabilities are:
P
X
ð
0
;
4
Þ¼
0
:
6567
P
X
ð
1
;
4
Þ¼
0
:
2916
P
X
ð
2
;
4
Þ¼
0
:
0486
:
(5.128)
P
X
ð
3
4
Þ¼
0
:
;
0036
P
X
ð
4
4
Þ¼
0
:
;
001
The density function is given in Fig.
5.16
.
5.6.5 Approximation of Binomial Variable
For high values of
n
, the calculation of the probabilities
P
X
(
k
;
n
) is time consuming.
Instead, it is helpful to use the asymptotic approximations for the binomial random
variable.
We will consider two cases:
Case 1
The probability
p
is finite and
n
is very high.
Case 2
The probability
p
is very small, while
n
is very high, resulting in a finite
value of
np
.
In this case, the approximation is the Poisson random variable, which will be
considered in Sect.
5.7
.
Let us now consider
Case 1
.
It follows that
np
1
(5.129)
and
npq
1
:
(5.130)
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
X
2.5
3
3.5
4
Fig. 5.16
Binomial density function
Search WWH ::

Custom Search