Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
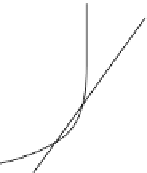
Quadratic
Linear
FIGURE 2.5
Discriminant analysis attempts to identify a boundary between groups in the data, which can
then be used to classify new observations. The boundary may be linear or nonlinear; in this
example both a linear and a quadratic line are fitted.
dimensions the separating line becomes a plane, or more generally a
hyperplane
.Dis-
criminant analysis also outputs an equation that can be used to classify new examples.
Discriminant analysis makes the assumptions that the variables are distributed
normally, and that the within-group covariance matrices are equal. However, dis-
criminant analysis is surprising robust to violation of these assumptions, and is usu-
ally a good first choice for classifier development.
Software Availability
R:
http://www.r-project.org/
.
R is a statistical programming language. It has a fairly steep
learning curve, but is extremely powerful. It has numerous libraries, including one for the
analysis of biological data:
Bioconductor:
http://www.bioconductor.org/
4.4
Principal components analysis
The aim of much data mining is to identify the variables, representing real-world
factors, which explain most of the variability in a dataset. Large datasets typically
contain many variables describing each record, and the effects of variables may
be nonlinear and interacting. To reduce the number of variables that must be consid-
ered, techniques for dimensionality reduction are often used.
Clustering is essentially a means of dimensionality reduction that involves retaining
all of thedata, but identifyingcommonalities that allowgroups of data items tobe treated
together. An alternative approach is to discard some of the data, retaining only those
features that contain the maximum information. Analysis of the data thus becomes less
computationally demanding, and the results may be easier to understand and interpret.
The most oldest and most widely used of these is a statistical method called Prin-
cipal Components Analysis (PCA). PCA takes an input matrix in which the rows are