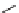Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
R
NC
CN
Ar
20 mol%
phosphin
e
benzene
NC
NC
CN
Ar
R
R
CO
2
Et + Ar
or
CN
CO
2
Et
CO
2
Et
7
42
reflux to rt
44
46
SCHEME 4.15
Synthesis of highly functionalized cyclohexenes.
4.2.4 Phosphine Organocatalysis of Allenes with Aldehydes
Relative to the extensive studies of annulation reactions between allenoates and
various imines or electron-deficient olefins described above, examples of phosphine-
catalyzed reactions between allenes and aldehydes are rather limited. To expand the
synthetic scope of phosphine-catalyzed annulations to construct heterocycles beyond
azacycles, we explored the reactivity of allenoates with aldehydes (Scheme 4.16)
[51-54].
Following the logic demonstrated for the [3
2] annulations between the allenoate
1
and
N
-sulfonylimines to form dihydropyrroles, we expected to harvest dihydrofuran
adducts. Instead, the phosphine-catalyzed reactions between allenoates and aldehydes
yielded dioxanes, pyrones, and dihydropyrones, with selectivity depending on the
nature of the phosphine catalyst and the reaction conditions. When the phosphine
was small (e.g., trimethylphosphine), the intermediate dienolate
48
having s-trans
geometry was favored, due to electrostatic association between the dienolate oxygen
anion and the phosphonium cation, leading to formation of the dioxane
2
. When
a sterically demanding phosphine was used or when a hydrogen-bond donor was
present, the s-cis-phosphonium dienolate intermediate was dominant and the reaction
provided pyrones
55
(bulky phosphine) or dihydropyrones
56
(in the presence of
protic solvents).
After investigating the steric and electronic effects of the allenoate and phosphine
on the reaction efficiency, we selected isopropyl 2,3-butadienoate
47a
as the starting
material and trimethylphosphine as the catalyst for the preparation of various diox-
anylidenes. Both pyridyl aldehydes and benzaldehydes bearing electron-withdrawing
+
TABLE 4.5 Highly Functionalized Cyclohexenes
Entry
R
Ar
Phosphine
Product
Yield (%)
cis : trans
1
H
Ph
HMPT
44
98
2
H
4-OMe-Ph
HMPT
44
94
3
H
4-Br-Ph
P(4-F-Ph)
3
46
86
4
H
2-Furyl
P(4-F-Ph)
3
46
88
5
H
N
-Me-2-indolyl
P(4-F-Ph)
3
46
91
6
Ph
Ph
HMPT
44
93
82 : 18
7
CO
2
Et
Ph
HMPT
44
96
66 : 33
8
Et
Ph
HMPT
44
98
92 : 8
9
CH
=
CH
2
Ph
HMPT
44
94
91 : 9