Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
(c)
0.8
(d)
16
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
-2
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0
3
Axial distance (µm)
6
9
12
15
0
2
Axial distance (µm)
4
6
8
10
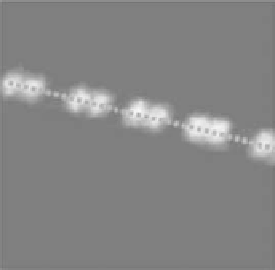
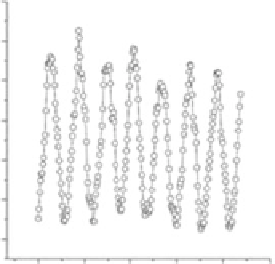
FIgurE 5.11
SHG spatial resolution. Endogenous SHG in single fiber from frog skeletal muscle (a) and in single
myofibril from rabbit skeletal muscle (b) in rigor solution at sarcomere length of 2.2 μm. Image dimensions are
15 × 15 μm
2
in fiber and 9 × 9 μm
2
in myofibril. (c) SHG intensity profile along the axis of the fiber and of the myo-
fibril (d). In the myofibril, the contours of the bands are better resolved and a dark zone is evident in the middle of
the bright band. (Modified from Vanzi, F. et al
.
2006.
J Muscle Res Cell Motil 27
, 469-479.)
An analogous effect of relative orientation of polarized polymers on detectable SHG was observed
for microtubules. Endogenous SHG was observed in microtubules of the mitotic spindle (Campagnola
et al., 2002; Dombeck et al., 2003) (see Figure 5.12a) and in neuronal axons (Dombeck et al., 2003; Kwan
et al., 2008) (see Figure 5.12b).
The polarity of microtubules forms the basis for SHG. In fact, due to the geometrical symmetry of
the microtubule itself, the HRS scatterers must be distributed with cylindrical symmetry and oriented
with respect to the microtubule axis. When microtubules align both in direction and sense (as in axons
and mitotic spindles), coherent summation takes place and SHG is detected. When, on the other hand,
microtubules are disposed with opposing polarities (as in dendrites) destructive interference among
HRS emitters cancels the signal out.
5.6 Source of the endogenous SHG
Characterization of SPA data from both muscle and collagen has indicated that the average polar angle ϑ
(see Equation 5.15) corresponds to the pitch angle of the helices in these samples (Bella et al., 1994; Isaac
Freund, 1986; Tiaho et al., 2007), suggesting the HRS emitters of these proteins are located within the
helical structure itself. In agreement with this observation, previous studies suggest that protein HRS lie
within the amide groups (HN-CO) of polypeptide chains (Conboy and Kriech, 2003; Mitchell et al., 2005).