Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
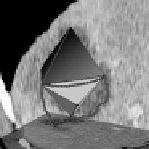
(a)
(b)
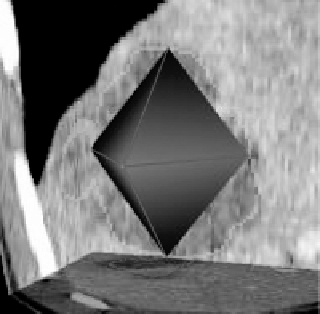
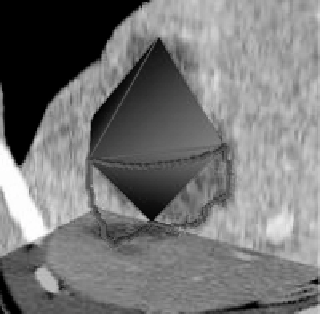
Figure 7.3:
(a) Octahedral approximation of a shape. (b) Edge contours delim-
iting a triangular patch.
Subdivision of a triangle is achieved as follows. If distances of voxels in an
edge contour to the associating edge are all within the required tolerance, that
edge is not subdivided. Otherwise, the farthest voxel in the contour to the edge
is used to segment the contour, producing two smaller contours. The farthest
contour point is then connected to the end points of the contour to produce two
new edges. In this manner, a triangular face is subdivided into 2, 3, or 4 smaller
triangles depending on whether 1, 2, or 3 edges of the triangle are replaced with
smaller edges. This is depicted in Figs. 7.4a-7.4c. If distances of voxels in all edge
contours to corresponding edges in a triangle are below the required tolerance,
a test is performed to determine whether or not distances of voxels associated
with the triangle are within a required tolerance to that triangle. If all distances
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Figure 7.4:
(a)-(c) Subdividing one, two, or three of the triangular edges, re-
spectively. (d) When no more triangular edges can be subdivided, error between
the triangular patch and the associating triangle is determined and, if that error
is above the given tolerance, the farthest voxel in the patch to the triangle is
determined and used to subdivide the triangle.