Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Set A
a1
A1
A2
A3
D1
a2
a3
D2
D3
a
CS1
b1
b2
b3
E1
Set D
A
B1
B2
B3
CS2
CS3
E2
b
E3
B
D
Set E
Set B
E
CC1
C1
CC2
CC3
C2
C
C3
Set C
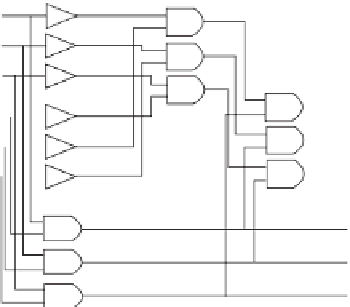
Figure
10.3.
Nonredundant and TIR implementation of half adder.
in 1952 and developed a technique called multiplexing. He introduced multi-
plexing as a technique for constructing a system whose malfunction cannot be
caused by the failure of a single device or a small set of devices. It has been
identified as one of the most effective techniques for transient fault mitigation.
Von Neumann proposed multiplexing architectures based on two universal logic
functions—NAND and MAJ—which will be discussed in detail
later in the
chapter.
10.2.2. Information Redundancy
Information redundancy, i.e., providing more information, is used in applications
for error detection and correction to make systems more reliable. Below, some
basic information redundancy techniques are discussed.
10.2.2.1. Parity.
A parity bit is a binary digit that indicates whether the
number of bits with value of 1 in a given set of bits is even or odd. There are two
types of parity bits: even and odd. An even parity bit is set to 1 if the number of
ones in a given set of bits is odd (thus making the total number of ones even). An
odd parity bit is set to 1 if the number of ones in a given set of bits is even (thus
making the total number of ones odd). If an odd number of bits (including the
parity bit) are changed in transmission of a set of bits then parity bit will be
incorrect and will thus indicate that an error during transmission has occurred.
Therefore, parity bit is used as an error-detecting code. Note that it is not an error-
correcting code as there is no way to determine which particular bit is corrupted. If
an error occurred during transmission, then the entire data must be discarded, and
retransmitted from scratch.










































Search WWH ::

Custom Search