Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
magnetic tracker, and then to store
M
0
. Robot manipulation is shown
by controlling the camera motion using a micro-coil as human
interface. The robotic camera was then brought to initial state and
the controller
M
0
was activated in the software of the computer. After
initializing the magnetic tracker, the catheter was inserted manually
inside the silicon model to trigger the motions of the robot described
in
M
0
to generate automatically the images of catheter insertion
procedure.
+
Robotic
Camera
Rule Based
Controller
Sparse
LUT
Video of Catheter
Insertion
Magnetic
Tracker
Catheter
Motion
Operator
Figure 7.7
Controller for manipulation of the robotic camera.
7.3.4
Robot Manipulation
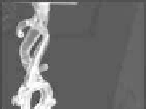
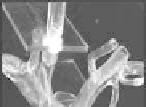
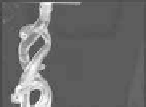
The seven reference points were detected inside predeined range
of 10 mm, allowing a controlled motion on the robotic camera
and capturing images of the catheter inside the silicone model
automatically (Figs. 7.8 and 7.9. The registered motion of the
motors and setting time of each reference point, experimental
detection ranges are shown in Table 7.3. The robotic system reacted
successfully to keep the catheter inside the vision range of the
camera. For almost all reference points the system reacted just after
entering the detection range. For point
P
0
, the system reacted at a
range of 4.56 mm from the reference point.
Initial
State
P
0
P
1
P
2
P
3
P
4
P
5
P
6
Figure 7.8
Image captured by the robotic camera at initial state and at
every reference point.















































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search