Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
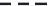
(a)
p
=
0.25
s
=
3
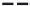
(b)
p
=
0.50
s
=
8
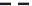
(c)
p
=
0.75
s
=
∞
Site percolation on a square lattice for three values of the fraction p of filled sites.
Figure 3.5
Then, the number of sites in clusters of size s is proportional to sn(s), and the site-
weighted average cluster size is
av
for each value of the parameter p is given by
∞
s
2
n
ð
s
Þ
s
¼
1
s
av
¼
:
ð
3
:
6
Þ
∞
sn
ð
s
Þ
s
¼
1
The sum in the denominator is equal to p. is
av
starts at 1 for p = 0 and increases as p
increases. In
Figure 3.5b
, where p = 0.50, there are fewer singlet sites and more clusters of
larger size than in
Figure 3.5a
.In
Figure 3.5c
, p = 0.75. Here there is a major difference
compared to the two previous frames: there is now a very large cluster which connects the
four edges of the frame. As the lattice grows in
.
Note that there are still independent clusters which do not belong to the in
nitely large, s
av
→
∞
nite cluster,
and also empty sites (at least when p < 1). The in
nite cluster is called the percolation

















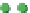






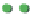




























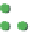





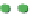

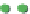
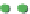














































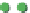

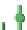











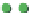










































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search