Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
PEG
O
H
O
N
O
N
O
3+
In
H
N
PEG-phosphatid
yl-
ethanolamine
O
O
O
111
In
3+
-distearic acid
Antibody
figure 1.13
Immunoliposomes labeled with
111
In-eDTa-Sa complex incorporated into
the lipidic bilayer were modified with a Peg5000 derivative of phosphatidylethanolamine in
combination with a monoclonal antibody to target myosin heavy chain. (Based on ref. [79].)
1.8.2
Pegylation of nanoparticles
Besides targeting, another important development in nanoparticle design was the
introduction of polyethylene glycol (Peg). This inert hydrophilic polymer was intro-
duced around 1970 by f. Davis, at rutgers University, to modify bioactive proteins
for medical applications to extend blood life and control immunogenicity of the pro-
teins [77]. In 1988, a. gabizon and D. Papahadjopoulos published a seminal paper
describing a concept of Pegylated liposomes with increased retention time [78]. In
this publication, a shell of Peg of up to 5-10 kDa around liposomes largely pre-
vented the uptake by reS rendering liposomes more accessible to other organs
including implanted tumors. The potential of the Pegylated nanoparticles in imaging
was further revealed in 1991 by a publication from Torchillin's group [79]. In this
report, liposomes labeled with
111
In complex were modified with a Peg5000
derivative of phosphatidylethanolamine (fig. 1.13). Because of the presence of Peg,
the liposomes cleared slowly from the blood after intravenous injection and showed
up to 6-18-fold at the specific localization of the target.
1.9
concluding remarks
By the beginning of the twenty-first century, many diagnostic modalities, including
PeT, SPecT, cT, MrI, optical angiography, and ultrasound, became routine clinical
tools. emerging modalities such as optical tomography, photoacoustics, and raman
and fluorescence imaging have also begun their way into clinics. Hardware
development, novel and faster algorithms, sophisticated image acquisition, and better
processing software to further improve the resolution and accelerate the diagnostic
procedures also emerged. after several decades of research, facing problems such as
batch-to-batch variation, low
in vivo
stability, liver clogging, and legal issues that
required testing of each nanoparticle component, large clinical trials with nanoparti-
cles have finally been completed. Many imaging agents were approved by the fDa
and other regulatory agencies abroad. The advances in chemistry, material science,














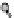




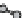

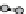






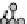







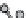



























Search WWH ::

Custom Search