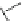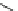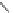Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
O
Ar
Ar
O
Ar
O
Ar
O
O
COOR
COR
O
O
Me
Me
N
H
N
H
R
1
N
H
R
1
Me
N
H
N
H
Me
Me
Me
O
O
Ar
COOR
Ar
R = OMe, OEt, N(Et)
2
R
1
= Me, Et
X = O, S, NH
COOMe
HN
R
1
O
N
H
X
Me
NH
COOR
O
O
N
H
Me
Me
Fig. 5 Derivatives containing dihydropyridine core into condensed ring systems
Fig. 6 Hexahydroquinolines,
fluroquinolines,
indenopyridines and lactones
O
Ar
O
Ar
A
CON(C
2
H
5
)
2
COOR
A
A
A
N
H
Me
N
H
Me
A = 6,6 and 7,7 dimethyl
Ar = difluorophenyl
R = CH
3
, C
2
H
5
Fig. 7 Nitroimidazoles
NO
2
N
N
CH
3
R
1
alkyl groups
R
2
= Me, Ph
R
1
OOC
COOC
2
H
5
R
2
N
H
Ph
Other studies indicate that dual-acting derivatives can be obtained by the
introduction of the dihydropyridine core into condensed ring systems (Fig.
5
)[
46
].
Racemic hexahydroquinolines, fluroquinolines, indenopyridines, and lactones
(Fig.
6
) exhibit calcium-antagonistic effects on smooth muscle and positive inotro-
pic activity [
46
,
47
].
A series of compounds resulting from the replacement of nitrophenyl in
Nifedipine analogs with its bioisoster 1-methyl-5-nitroimidazole (Fig.
7
), presented
[
48
-
52
] calcium channels antagonistic activities. A valuable QSAR model was
obtained by using constitutional and topological indices from which it is obvious
that nonrotable groups resulted in increasing calcium channel blocker activity [
53
].
Antagonists of the nifedipine type are flexible molecules, in which the C-4-aryl
moiety and the C-3 and C-5 ester substituents can rotate and the conformation of
the 1, 4-dihydropyridine ring can change [
54
]. The exact stereochemical and/or