Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
(b)
y
(a)
(c)
x
S
(
x
i
,
y
j
): Light intensity information at (
x
i
,
y
j
)
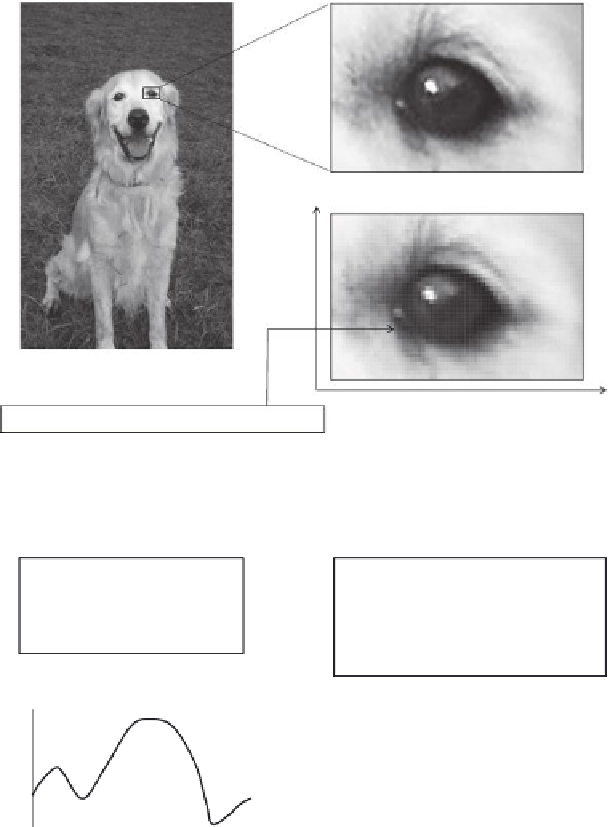
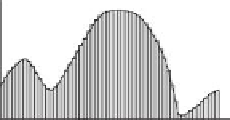
FIGURE 1.5 (See color insert)
Optical image and the image signal obtained by image sensors: (a) optical image; (b) enlarged optical image;
(c) image signal obtained by sensors.
Coordinate:
Coordinate:
Continuous analog value
Signal:
Cyclic sampling coordinate point
(discrete digital value)
Continuous analog value
Signal:
Continuous analog value
Digitization
of coordinate
(a)
Coordinate
(b)
Coordinate
FIGURE 1.6
Digitization of coordinate: (a) space coordinate of an optical image; (b) space coordinate in an image sensor.
number of coordinate points is a pixel count of the image sensors, a larger number of pix-
els can achieve a higher space frequency, that is, a higher space resolution.
Image sensors also have a scanning function, transmitting the light intensity informa-
tion of each pixel to the output part, which reads out the intensity information as an elec-
tric signal, as shown in Figure 1.4.
1.2.2 Color Still Images
The image information of color still images is formed by light intensity, space, and wave-
length, as discussed in Section 1.1. Therefore, it is necessary to take the wavelength infor-
mation in addition to the monochrome still image information. Although there are several
ways to gather wavelength information, the most common method, the single-sensor color