Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
Memory
Column processor
ADC
Column amplifier
Pixel array
Column amplifier
ADC
Column processor
Memory
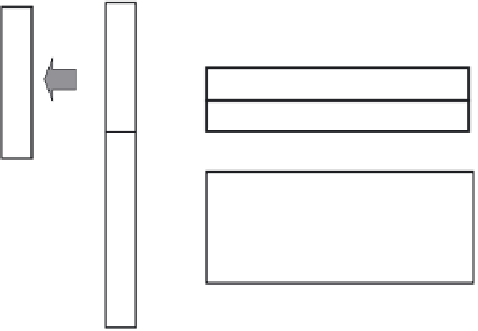
FIGURE 5.58
Block diagram of a 14-bit successive-approximation-type ADC sensor. (Reprinted with permission from
Matsuo, S., Bales, T.J., Shoda, M., Osawa, S., Kawamura, K., Andersson, A., Haque, M., et al.,
Transactions on
Electron Devices
, 56(11), 2380-2389, 2009.)
is equipped to reconvert once-converted digital code to analog signal to compare with ana-
log signal input by the comparator to judge the digital code of the second most significant
bit. By repeating this comparison, the precision of digital code is raised one bit at a time.
Although SA-ADC is operated
N
times if the bit number is
N
, A/D conversion is completed
by
N
-times repetition using only one comparator. While repletion time is necessary, it can
be designed in a compact circuit size.
Figure 5.58 is a block diagram of a 14-bit SA-ADC sensor.
46
Around the pixel array, the
control part and output are arranged on the left side, the driver and DAC are arranged on
the right side, and the column ADCs are arranged on the top and bottom.
Figure 5.59 is a circuit diagram of an SA-ADC. Pixel output is amplified by a variable
gain amplifier for noise reduction. An ADC consists of a dual comparator and DAC. In
DACs, capacitors are arranged with the necessary numbers and volumes to deal with mul-
tiple bits. Three different reference voltages, consisting of standard voltage and 1/4 and
1/16 of the standard voltage, are used to suppress increase of the circuit size by decreasing
the number of capacitance volumes. While SA-ADC generally excels in high-speed perfor-
mance and low consumption, the ratio of area size that capacitances occupy increases for
higher digital resolution.
This sensor has a pixel pitch of 4.2 μm, and a higher frame frequency of 60 fps for the
large pixel number of 8.9 M. The number of column FPN electrons is suppressed to 0.36
owing to digital CDS.
5.3.3.2.2.3 Cyclic-Type ADC
In cyclic ADC, digits are counted starting from the most
significant bit by one-bit-at-a-time comparison as well as successive-approximation type.
Since resolution is determined by cyclic number differently from in SA-ADC sensors, it
has the advantage of compatibility between high-speed performance and high resolution.