Graphics Programs Reference
In-Depth Information
7.
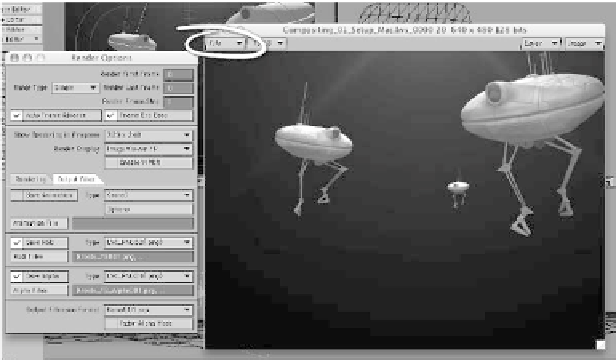
As shown in Figure 17-42, set the
ShadowCatch surface Color to
0, 0, 0
(black) and its Transparency to
0%
.On
the Advanced tab, set the Alpha Chan-
nel to
Shadow Density
(which is what
will let us composite the black of the
object's surface color onto our plate).
As final preparation for generating an
image that can be composited onto the
plate, we need a completely
black
back-
ground. (“Premultiplying” our
fore-
ground image
with black helps the
computer deal with the rather touchy
process of seamlessly blending the
edges of our foreground image into that
of our background.) Replace your
Effects | Compositing | Back-
ground Image
with
Images\Black-
Square.iff
.
both the image channel (24 bits) and its
alpha channel (another 8 bits), making
a total of 32 bits per channel in a
single
file
. If you wanted to save a
series of
frames
, perhaps if you were doing this
for a movie, you would set Save RGB
to a 32-bit file format under Rendering
Options (and possibly even save out
the alpha separately, just in case your
compositing application needs the alpha
as a separate file).
8.
Figure 17-43 shows our completed
foreground plate, ready for compositing
onto our background plate. To work
with a single frame, as we are here,
once you have hit <
F9
>, under the
Render Display's File menu, choose
Save RGBA | LW_PNG32 (.png)
.
Portable Network Graphics files are
the most compact file type that holds
Figure 17-44: The alpha channel for our plate.
Looking at Figure 17-43, you may be won-
dering where the shadows are. They're
there, but they're 0, 0, 0 (black), the same
Figure 17-43: The completed foreground plate, ready for compositing onto our
background plate.