Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
s
a
D
1
V
1
Fsin
a
s
b
A
6 m
48 m
g
vk
= 78.1 kN/m
-4195.1
375 kN
375 kN
q
vk
= 43.8 kN/m
1.2 m
+
1.281
1.153
1.127
Figure 4.64 Determination of the force in diagonal member D
1
using the influence line
method.
the force in the vertical truss member V
1
is equal to that of D
1
multiplied
by sin
a
but with a negative sign (a compression force of 6711.5
sin
51.34
¼
5240.8 kN).
4.3.3.12 Calculation of the Reactions at Supports
The reactions at supports can be also calculated using the influence line
method, as shown in
Figure 4.65
, as follows:
A
+ve
ðÞ¼A
net
D
ðÞ¼
0
:
5
60
1
:
0
¼
30
:
0
F
D
:
L
:
ðÞ¼
30
:
0
78
:
1
¼
2343 kN
F
L
:
L
:
ðÞ
positive
ð
Þ
375
1
ð
:
0+0
:
98
Þ
+30
:
0
43
:
8
¼
2056
:
5kN
F
Ed
ðÞ¼F
D
:
L
:
g
g
+
F
L
:
L
:
g
q
F
Ed
ð
maximum
¼
2343
1
2kN
Figure 4.66
summarizes the calculated forces in the truss members and
presents the commonly known distribution of forces in the N-shaped main
truss under the dead and live cases of loading.
:
3 + 2056
:
5
1
:
35
¼
5822
:
4.3.3.13 Design of the Maximum Compression Upper Chord Member U
5
After the calculation of the design forces in the main truss members, we can
now design different members of the main truss. Let us start by designing the









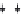

























































Search WWH ::

Custom Search