Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
+
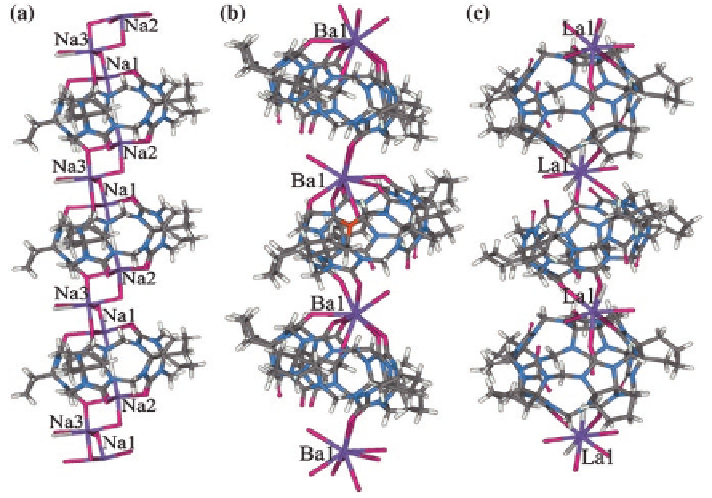
Fig. 3.6
X-ray crystal structures of 1D coordination polymers consisting of
a
CyH
5
Q[5]/Na
;
b
CyH
5
Q[5]/Ba
2
+
; and
c
CyH
5
Q[5]/La
3
+
coordination polymer [
15
]. In contrast, Ba
2
+
fully covers a portal of CyH
5
Q[5] in
the CyH
5
Q[5]/Ba
2
+
-based 1D coordination polymer, and coordinates to two por-
tal carbonyl oxygens of the neighboring CyH
5
Q[5] molecule. This coordination
results in the formation of an 1D polymer constructed from alternating CyH
5
Q[5]
molecules and Ba
2
+
cations (Fig.
3.6
b) [
16
]. Although the atomic radii of lantha-
nides are generally shorter than those of the alkali or alkaline earth cations, 1D
coordination polymers from alternating CyH
5
Q[5] molecules, and La
3
+
cations
(Fig.
3.6
c) may be observed. No portal of the CyH
5
Q[5] molecule is fully covered
with La
3
+
, but it offers two portal carbonyl oxygens to coordinate with La
3
+
[
17
].
Why do the alkyl-substituted SQ[5]s show such different coordination and
supramolecular assemblies from the unsubstituted Q[5]? A comparison of electro-
static potential surface calculations based on density functional theory (B3LYP/3-
21G* basis set) for three typical Q[5]s—Q[5], Me
10
Q[5], and CyP
5
Q[5] (Fig.
3.7
)
shows that the mapped on electron density isosurfaces (0.001 e/au
3
) for the por-
tal carbonyl oxygens on the three Q[5]s are different, the alkyl-substituted SQ[5]s
are generally more negatively charged as a consequence of the electron donating
effect of the alkyl substituents, we call them as self-structure directing agents,
resulting in more affinity for metal ions, and form novel coordination polymers
and supramolecular assemblies [
18
-
20
]. The alkyl-substituted SQ[5]s can not
only form 1D coordination polymers and supramolecular assemblies as shown in
Fig.
3.6
, but can also be linked directly by metal ions to create supramolecular
Search WWH ::

Custom Search