Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
microprocessors. As a consequence it represents a good test to evaluate the per-
formance of different logic solutions applied to NML logic. The microprocessor
is described using a RTL model of NML technology written using VHDL lan-
guage. The model is reported in Fig.
10
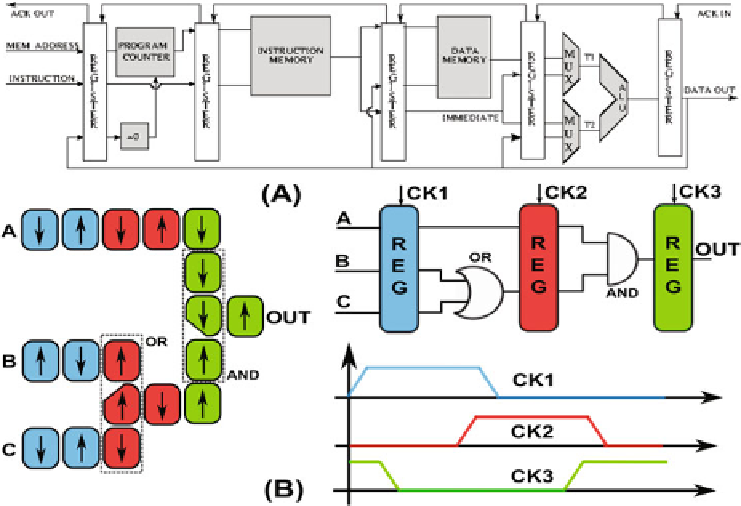
(B). The basic idea behind the high level
modeling of NML technology is to exploit its intrinsic pipelining. Figure
10
(B)
shows an example of NML circuit and its equivalent RTL model. Registers are
used to emulate the signals propagation delay while ideal logic gates without
delay are used to model the circuit logic behavior. The result is a circuit that
behaves exactly like its NML counterpart, but the advantage is that this circuit
can be described and simulated using powerful design tool already available for
CMOS technology, like Modelsim [
42
]. In this way complex NML circuits can
be easily described and simulated. More information on the model itself can be
found in [
29
].
Fig. 10.
NML microprocessor. (A) The microprocessor architecture is made by a pro-
gram counter, to execute programs, two memories, one for data and one for instructions
and an ALU to execute the instructions. The architecture is simple but it allows the
execution of all common microprocessors instructions. (B) NML equivalent RTL model
used to describe and simulate the microprocessor.
Detailed simulations of the microprocessor are not reported here, and can be
found together with a thorough description in [
32
,
41
]. The most important result
obtained from simulations is indeed the time needed to execute one instruction.
Using NCL logic one instruction takes 5.35
µ
s to be executed, while with the



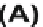










Search WWH ::

Custom Search