Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
XES 02
XES 05
3.2
3.5
7.49)
0.5
s = (0.14t
+
0.91)
0.5
s = (0.13t
−
3.1
Sediment
storage
3.3
Sediment
storage
3
Sediment
release
3.1
Sediment
release
(a)
(b)
0.1
0.01
0
0
−
0.01
−
0.1
Topographic scan
0.5
1
Channelized flow
Channelized flow
0.4
0.8
0.3
0.6
0.2
0.4
Sheet flow
Sheet flow
1
2
3
4
0.1
0
0.2
0
Sheet flow
(c)
(d)
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
80
82
84
86
88 90
Run time [hr]
92
94
96
98
100
Run time [hr]
(e)
1
2
3
4
Avulsion and
lateral migration
RT = 13.0 hr
Sheet flow
deposition
RT = 15.0 hr
Channel cutting
Backfilling
RT = 12.2 hr
RT = 14.3 hr
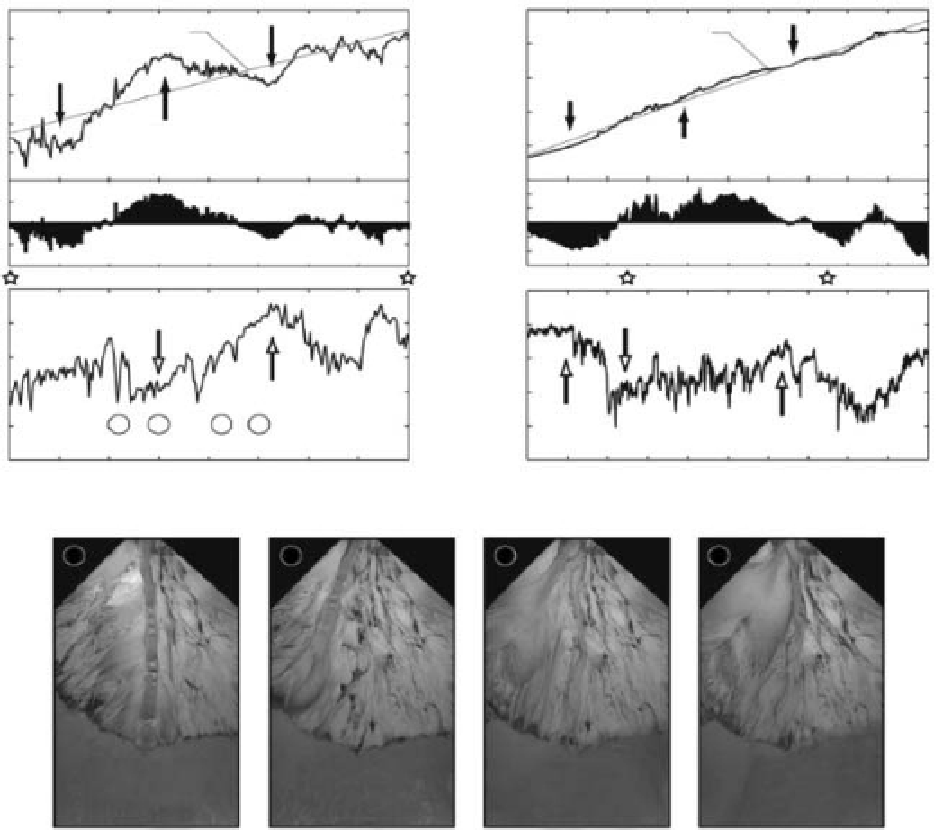
Figure 13.8
Shoreline and wet-fraction data from the XES experiment (Kim and Jerolmack, 2008). (a and b) Mean shoreline position
averaged normal to the mean sediment transport direction and best fit curves. Graphs show shoreline position fluctuation after
removal of long-term shoreline regression trend, (c and d) time series of wet fraction showing cyclic changes in fluvial pattern
between sheet and channelised flow, (e) representative overhead images showing a cycle of changes in the wet-fraction. Reproduced
from Kim & Jerolmack, Journal of Geology ''The Pulse of Calm Fan Deltas'' 116:4 (2008) Fig. 3, p. 319.
that became wet and the decay (decrease) in the area that
remained dry over a set time interval (Figure 13.9). A
faster decay represents stronger channel activity and vice-
versa. Kim and Paola (2007) used this analysis to compare
channel activity during various stages of the experiment
that were subject to different external forcing.
the dynamic interactions between flow and vegetation.
The experiments were designed to investigate whether
riparian vegetation could cause a braided channel to
evolve to a single-thread channel and were motivated by
many field cases in which the encroachment of ripar-
ian vegetation was driving a change in planform. The
experiments were conducted in a flume 16 m long by 2 m
wide with steel walls. Alfalfa sprouts (
Medicago sativa
)
were used as the experimental vegetation in the flume.
The initial condition for the experiments was steady-state
braiding in noncohesive sand under uniform discharge.
From here, an experiment consisted of repeated cycles
13.3.2 Experimental river channelswithriparian
vegetation
In a separate set of experiments at the St. Anthony
Falls Laboratory, Tal and Paola (2007, 2010) studied
Search WWH ::

Custom Search