Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
5.
Specify the certificate to use for IP-HTTPS connections. It can be a self-signed
certificate that is automatically created by DirectAccess, or you can use a public
certificate that matches the public DNS name or IP address you specified on the
Network Topology page. Click Next.
On the Prefix Configuration page, the IPv6 prefix settings that have been detected are
displayed, along with the IPv6 prefix that will be assigned to DirectAccess clients. You
can edit these settings if they don't look right, but the wizard is usually correct. Click
Next.
6.
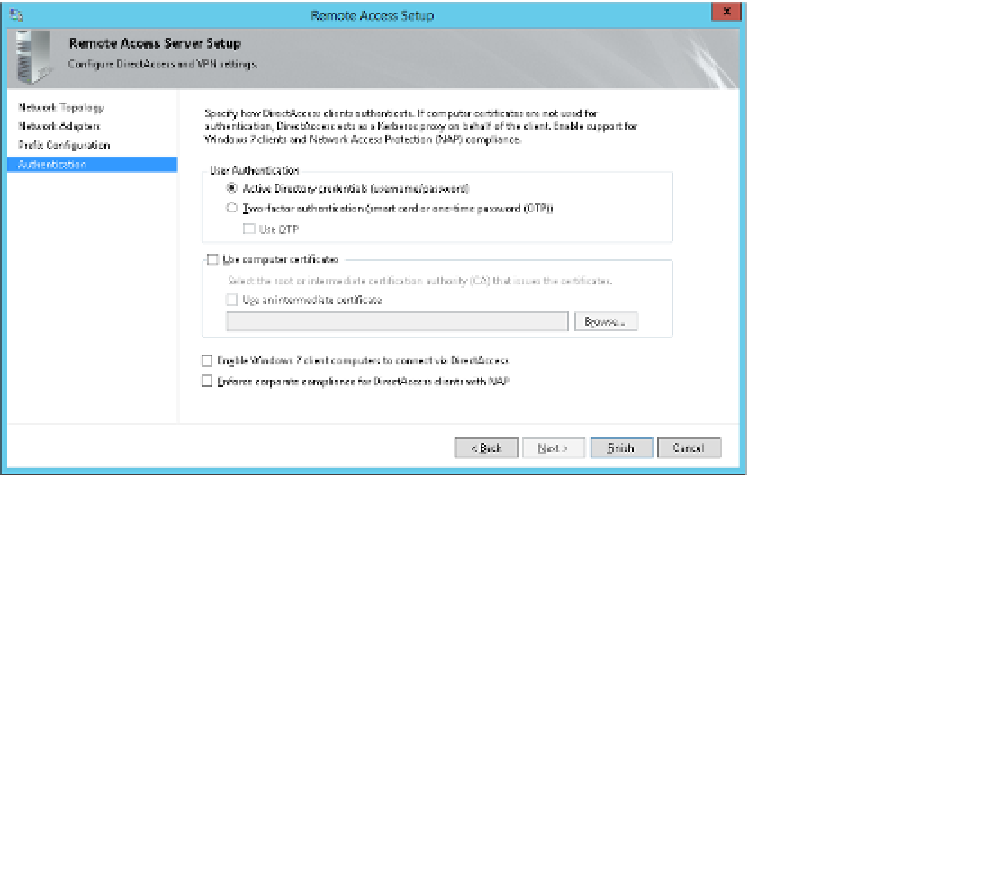
On the Authentication page, shown in Figure 3-59, specify the authentication used.
The choices on the page are these:
■
User Authentication
Active Directory credentials is the default choice. You can,
however, specify Two-Factor Authentication, which uses a smart card or one-time
password (OTP). Beginning with Windows Server 2012, the client computer's Trusted
Platform Module (TPM) can be used as a virtual smart card. OTP requires configur-
ing RADIUS and other configuration steps that are beyond the scope of this portion
of the exam, although you should know that it is an option.
7.
FIGURE 3-59
The Authentication page of the Remote Access Server Setup Wizard
■
Computer Certificates
The default is to use Kerberos for client authentication,
which doesn't require a certificate. However, certificate authentication is required
for two-factor authentication, for a multisite deployment, and for Windows 7
DirectAccess clients.
■
Windows 7 Clients
Windows 7 clients can't connect to a Windows Server 2012
DirectAccess deployment unless you configure computer certificates. If you select
this box, it automatically selects the Use Computer Certificates box.