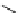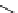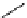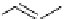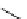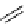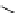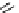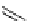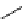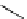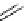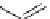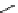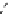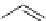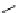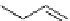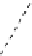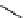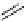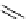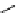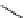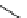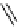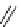Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
advantage, besides its high nucleofugacity, of giving an electrical charge to the precursor molecule that facilitates its sepa-
ration from the electrically neutral product. On the other hand, it may suffer from a side-reaction producing [
18
F]methyl
fluoride by [
18
F]fluoride attack on one of the methyls of the trimethylammonium group [128]. In order to be formed at a rea-
sonable rate, the Meisenheimer complex needs (resonance) stabilisation by the presence of auxiliary electron-withdrawing
groups on the ring, preferably at an
ortho
or
para
position relative to the leaving group, such as the carbonyl groups in
32
(Scheme 3.6) and
34
(Scheme 3.7). Electron withdrawing groups can be nitro, cyano, aldehyde, ketone, ester, and carboxylic
acid functions. More recently, a benzothiazol-2-yl moiety [129, 130], a 1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl [131] as well as a triphe-
nylphosphonium group [132]
para
to a nitro group were found to have sufficient activating power to allow radiofluorination.
The activating group is either an integrated part of the desired radiolabelled structure or is changed or removed afterwards
[26]. In the first case, the radiosynthesis can sometimes be performed in one step such as with [
18
F]setoperone (
33
) [133, 134]
or
p
-[
18
F]MPPF (
40
) [135] (Figure 3.4). With the latter, the activating group is an amide function, which usually gives
relatively low yields. The presence of activating groups at an
ortho
or
para
position is mostly but not always a guarantee of
good yields. The efflux protein inhibitor 1-[
18
F]fluoroelacridar (
41
) was obtained in < 2% yield despite the presence of both
an
ortho
carbonyl and a
para
amide function [136].
The formyl group in
p
-[
18
F]fluorobenzaldehyde (
36
) (Scheme 3.7) is a representative example of an activating group that
can be transformed after having served in the labelling reaction.
p
-[
18
F]Fluorobenzaldehyde (
36
) is a common starting
building block for more complex molecules in which the carbonyl group serves as a handle for further derivation [25], for
example, the transformation of
p
-[
18
F]fluorobenzaldehyde (
36
) into
p
-[
18
F]fluorobenzyl azide for further use in Huisgen
1,3-cycloaddition (see below) for peptide labelling [137]. A similar strategy, with the fluorination
ortho
to the formyl group,
is regularly applied in various syntheses of 6-[
18
F]fluoro-L-DOPA (
4
) [138]. A formyl group can be removed from an aro-
matic position, using Wilkinson's catalyst, after having served as an activating group in radiofluorination. This was the initial
strategy in the radiosynthesis of certain 4-(4-[
18
F]fluorobenzyl)piperidinyl compounds such as
46
via
43
[139] (Scheme 3.8),
O
H
3
CO
O
N
N
18
F
N
N
N
N
S
N
H
3
C
O
33
, [
18
F]setoperone
40
, p-[
18
F]MPPF
18
F
18
F
O
OCH
3
N
H
OCH
3
H
3
CO
O
N
41
, 1-[
18
1-[18F]fluoroelacridar
H
fIgure 3.4
Examples of [
18
F]molecules featuring an activating group so that direct radiofluorination was possible.
O
O
H
H
X
18
F
O
2
N
42
43
OCH
3
HN
N
18
F
N
O
O
46
18
F
O
2
N
45
44
scheme 3.8
Synthesis of certain ([
18
([18F]fluorobenzyl)piperidinyl compounds such as
46
with a
para
or
meta
carbonyl function as a
temporary activating group that is reduced after radiofluorination.