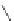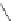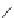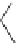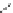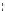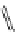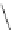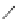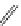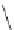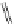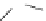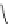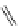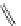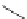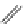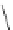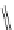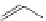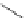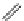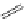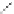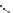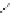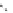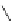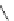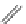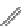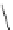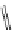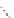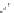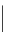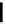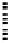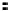Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
3+
CO
2
Me
O
Ph
HN
S
O
N
N
N
N
O
E
u
H
2
O
N
N
H
2
O
H
O
NH
Ph
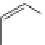
FigUre 12.22
An example of a mitochondrial localising probe.
O
+
O
O
O
N
N
N
O
Ln
N
N
N
O
O
O
FigUre 12.23
A 1,7-chromophorically substituted Ln(III) complex for staining chromosomal dNA.
Me
3+
Ph
HN
OH
2
O
O
N
N
N
Ph
O
L
n
N
N
O
O
Me
X
O
NH
Ph
Me
X=H;
t
Bu; CO
2
Me; CO
-
; CONHMe;
CONHC
6
H
13
; CONHC
12
H
25
;
CO-LysArg
7
; CO-Arg
8
;
CO-HSA; CO-guan.
4
FigUre 12.24
Functionalising the periphery of the
N
-coordinated azaxanthone chomophore: hydrophilic (X = carboxylate and
carboxamide), lipophilic (X = tertiary butyl, alkyl) and bio-inspired (X = LysArg, HSA, guan) variants.
cytotoxicity (IC
50
> 400 μM), single-photon illumination induces phototoxicity; it may be that for certain chromophores,
two-photon absorption, to which these compounds are amenable, will reduce such phototoxic effects.
The importance of the appended chromophore in determining behaviour
in cellulo
was further demonstrated by a
series of complex variants, wherein substituents added to the
N
-coordinated azaxanthone sensitiser dramatically
influence the trafficking behaviour of the Ln
III
probe. Relatively simple structural changes (Figure 12.24), that allow
tuning of hydrophilic (carboxylate and carboxamide) through to lipophilic (tertiary butyl) character, demonstrate an
element of control over cellular uptake, trafficking, localisation, and toxicity. More complex targeting vectors can also
be conjugated to the azaxanthone antenna: Peptide conjugates promote rapid internalisation, cytosolic localisation, and
lower toxicity; lipophilic oligo-guanidinium vectors induced apoptotic cell death (IC
50
12 μM) following localisation
within mitochondria [64].