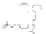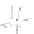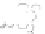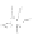Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
Bulk
water
Intraliposomal
water
10
86420
ppm
-2
-4
-6
-8
-10
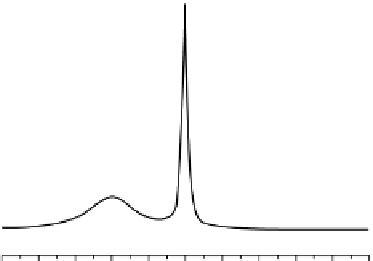
fIgurE 10.14
1
H NMR spectrum (14.1 T and 39°C) of a suspension of a lipoCEST agent entrapping Tm-DOTMA (inset). The signal
at 3.1 ppm downfield from the bulk water corresponds to the water protons entrapped within the liposomes that contain 0.1M of SR.
(g)
Δ
intralipo
=Δ
pseudo
+
Δ
BMS
(f)
O
O
OH
2
O
(e)
NN
O
Tm
3+
O
N
N
O
HO
CH
3
(d)
Hyperosmotic
stress
O
O
OH
2
O
NN
O
Tm
3+
O
(c)
N
N
O
HO
N
(b)
Δ
intralipo
=Δ
pseudo
(Δ
BMS
=0)
(a)
40
30
20
10
0
-10 -20 -30 -40
ppm
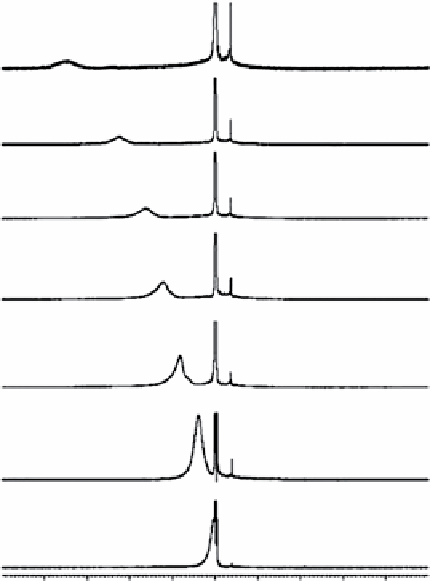
fIgurE 10.15
1
H-NMR spectra (14 T, 25°C) of a suspension of liposomes made of DPPC/Tm-1/DSPE-PEG2000 (65/30/5 mol%)
encapsulating 40 mM Tm-HPDO3A (shown on the top left) and suspended in a buffered medium (pH 7.4) with increasing osmolarity:
(a) 40 mOsm. (b) 80 mOsm. (c) 110 mOsm. (d) 160 mOsm. (e) 230 mOsm. (f) 300 mOsm (isotonic). (g) 600 mOsm. The structure of the
Tm-1 complex is shown on the bottom left. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [71].
and this concentration is influenced by osmotic effects for both spherical and non-spherical lipoCEST probes. In essence,
the amount of encapsulated SR will depend on the concentration of the paramagnetic agent in the solution that is used for
hydrating the thin lipid film. Successively, the intraliposomal SR concentration can then increase or decrease according to
the relative osmolarity of this solution with respect to the isotonic buffer used in the dialysis purification procedure.
On the other hand, non-spherical liposomes can be prepared by shrinking spherical ones through osmotic stress, and
the orientation of the resulting liposomes in the magnetic field (which determines the sign of Δ
int
ralipo
) can be modulated by