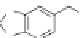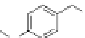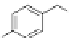Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
O
H
2
N
NH
2
NH
2
NH
2
NH
2
NH
2
O
S
O
R
2
O
Column 11 (controls)
NH
2
NH
2
R
1
O
NH
2
HO
NH
2
NH
2
O
Cl
Resynthesis of 16(1,1)
O
NH
2
O
NH
2
Resynthesis of 16(3,3)
O
16(parental)
NH
2
O
16(parental)-
without Eu (III)
H
2
N
NH
2
Empty beads treated
with Eu (III)
NH
2
NH
2
Empty beads without
Eu (III)
O
O
HO
NH
2
Water alone
(no beads)
NH
2
S
40
30
20
10
0
OH
O
O
O
O
O
N
O
O
HN
NH
H
H
N
N
N
NH
NH
N
N
N
O
Eu
3+
O
O
O
O
O
NN
S
O
NH
HN
O
O
HN
NH
N
N
O
O
NH
HN
R
1
:
ß
-alanine
O
O
O
O
OH
HO
R
2
:
-methoxyethylamine
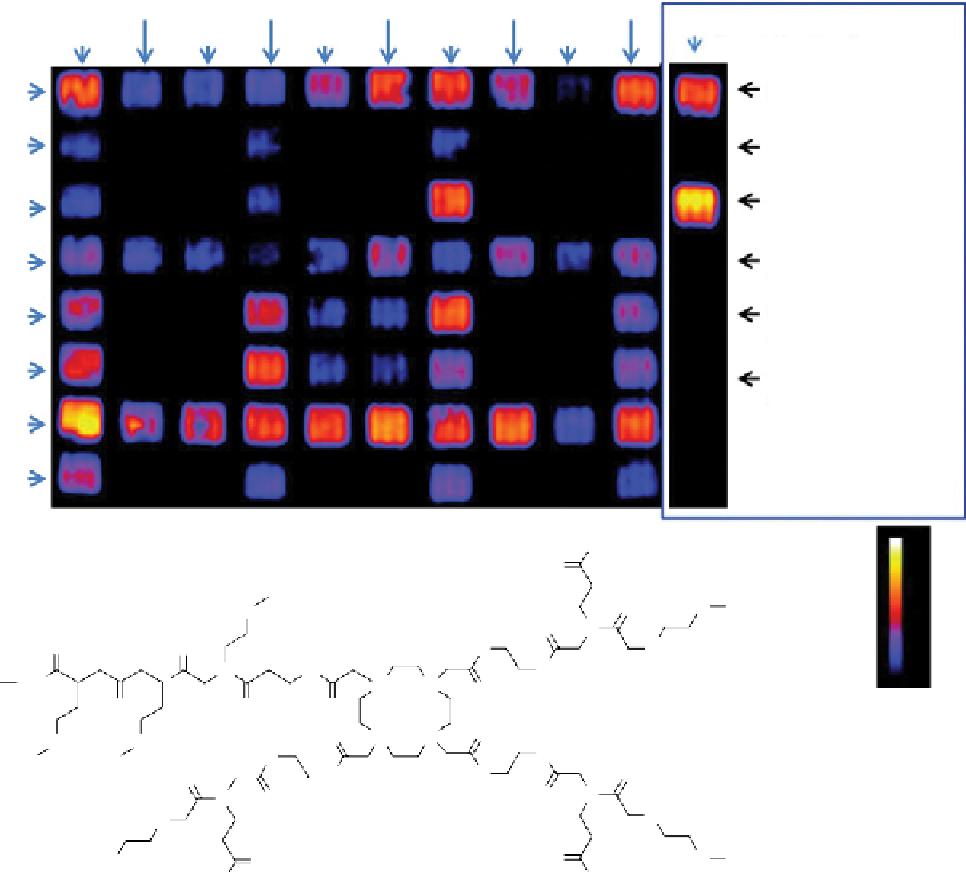
fIgurE 10.10
Top: CEST image of an 80-compound library of Eu(III)DOTA-tetraamide-peptoid derivatives attached to beads. The
chemical structures of each amine used to build the library are shown along each horizontal row (R
1
) and each vertical column (R
2
).
Bottom: Structure of Eu(III)DOTA-tetraamide-peptoid in well (7, 1) that showed the highest CEST intensity. Reproduced with permission
from Ref. [35]. (
See insert for colour representation of the figure.)
)
10.5
In VIVo
dEtEctIon of ParacESt agEntS
Although PARACEST agents show considerable promise as responsive MRI agents
in vitro
, translation of these sensors to
in vivo
measurements has so far been limited, especially for those PARACEST systems that operate through a water exchange
mechanism. One problem is that the water exchange rates and CEST spectra of most paramagnetic complexes designed as
CEST agents are typically measured on samples held at or near room temperature only. However, at body temperature typ-
ical of small animals (38-39 °C), water exchange in these systems is, not surprisingly, considerably faster, adding an addi-
tional complexity. Faster water exchange results in broader CEST peaks not only for the lanthanide-shifted bound water
exchange peak but also for the bulk water resonance. This added line broadening is not so noticeable in aqueous samples at
concentrations typically used in an
in vitro
CEST experiment (10-30 mM) even at 38 °C but can become quite evident once
one of these agents is injected into an animal and the agent concentrates in the kidneys as it is being filtered. This additional
T
2
exchange (T
2exch
) contribution to the water linewidth can result in as much as a 50% loss in water signal intensity in kidney