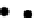Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
MS-325
40
MS-325+HSA
Δr
1
= 24.6
30
20
1.5T
10
0
0.001
0.01 0.1
Field (T)
1
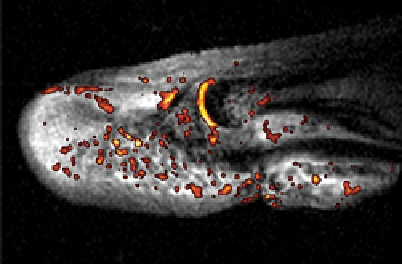
dreMR albumin in false colour
Overlaid on 1.5 T anatomical
image. 0.2×0.2 ×2 mm
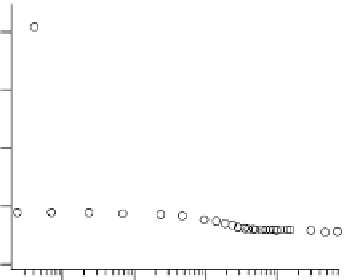
fIgure 8.7
(a) The variation in r
1
for MS-325 in albumin free and albumin bound forms with magnetic field. (b) dreMR albumin false
colour image overlaid on 1.5 T anatomical image of a finger fracture
.
Figure drawn from data kindly provided by Prof. Peter Caravan.
(
See insert for colour representation of the figure.)
)
giving rise to a much greater enhancement of r
1
as a consequence of greater affinity of MS-325 for the cyclodextrin host.
This approach has been extended further by Aime and co-workers, who used poly-β-cyclodextrin and an adamantly appended
gadolinium complex with high affinity for cyclodextrin: Combining these with functionalised dextran derivatives yields high
values of r
1
[80]. This has been elaborated to a system that can be used to assess pH through combined
1
H/
19
F MRI [81]. In
this system, a gadolinium component contributes to the proton relaxivity, while a fluorine-appended adamantyl derivative
contributes toward the fluorine MRI signal. The pH responsive behaviour in this case derives from pH dependent changes in
q, which will be discussed in greater detail in the next section.
8.6
responsIve mrI
In an effort to produce ever more clinically useful MRI agents, considerable research has been directed to developing 'smart'
contrast agents capable of sensing their biological surroundings. Upon administration of such a compound, the relaxivity of water
protons should be dependent on some biochemical variable - for example, pH - ion concentrations, oxygen concentration, or tem-
perature. One attractive concept is that of targeting biological entities that are specific to a given disease, for example, a receptor
or enzyme. The challenge encountered in this strategy is usually that the target molecule is present in insufficient concentration
to be able to deliver enough gadolinium to provide sufficient contrast for imaging, given the relatively low sensitivity and resolu-
tion of the MR technique. Either the relaxivity of the agent must be increased or multi-gd agents must be employed (see above).
A recent example of receptor targeting includes the activation of immunologically important macrophage cells using the
tetrapeptide, tuftsin (TKPR), and closely related pentapeptide (TKPPR) as targeting units, conjugated with gd.dOTA-
monoamide complexes to provide MR contrast. The terbium(III) analogues were also investigated by virtue of their optical
properties. Fortunately, N-terminal substituents do not affect the biological activity of tuftsin, and the peptide conjugate is inter-
nalised by the macrophage, a process that is mediated by the tuftsin receptor. The gd-tuftsin conjugate was found to have similar
relaxivity in comparison with other gd.dOTA-monoamide complexes. Both T
1
measurements of macrophage cells incubated
with gd-tuftsin and luminescence of Tb-tuftsin incubated cells confirmed the desired targeting ability of these compounds. The
analogous pentapeptide conjugates were found to have a stronger affinity for the macrophage cells than tuftsin [82, 83].
Considerable effort has been directed toward the targeted imaging of integrins [84]. Integrins are transmembrane proteins
that mediate interactions between cells, and the α
v
β
3
integrin has been shown to regulate angiogenesis, the formation of new
blood vessels key to the development of malignant tumours. The overexpression of the α
v
β
3
integrin in diseased tissue can
be targeted by exploiting its recognition of short amino acid sequences, such as Rgd. Shukla et al. conjugated a g-5
PAMAM (polyamidoamine) dendrimer with a doubly cyclised Rgd peptide and an Alexa Fluor 488 fluorescent probe. The
conjugate was shown to accumulate in cells expressing α
v
β
3
integrin [85]. Later, Boswell and co-workers extended this
strategy to include MR contrast by using a g-3 PAMAM dendrimer as a platform for conjugation of approximately two
Rgd-cyclopeptides and one Alexa Fluor 594 dye, along with 27 modified gd.dTPA chelates using orthogonal coupling
methodologies [86]. The Rgd-conjugated dendrimer prior to gd(III) complexation was selectively taken up by M21 cells,
known to express α
v
β
3
integrin, compared with the control RAd-conjugated assembly. However,
in vivo
studies employing
111
In in empty dTPA sites on the dendrimer revealed little accumulation in tumour cells (1.25 ± 0.51% after 2 h).