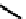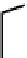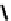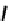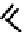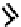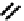Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
O
OH
N
O
N
O
Ga
O
O
O
N
HO
OH
NN
O
N
HO
N
OH
O
N
O
O
OH
12
13
fIGure 7.6
DOTA ligand (
12)
and the structure of its Ga complex (
13
).
7.2.5 n
4
o
4
donor ligands and related species
Gallium and indium radioisotopes have also been used extensively with bifunctional chelators incorporating N
4
macrocycles
with pendant carboxylic acid groups [37] such as DOTA (1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid)
(Figure 7.6) DOTA has been shown by an X-ray structure determination to be bound to Ga(III) via the four macrocyclic nitro-
gens and two
cis
carboxylate oxygens (Figure 7.6) [38]. One of the two pendant carboxylates is protonated, and the negative
charge on the other gives the complex an overall neutral charge. For the larger In(III) ion, the coordination in a complex of an
amine derivatised DOTA ligand was shown to be square anti-prismatic with four nitrogens and four carboxylate oxygens
bound to the metal [39].
DOTA has been very widely used for the targeting of
67
Ga and
111
In by conjugation to biomolecules via a pendant carbox-
ylate group. much interest has been focused on the radiolabelling of DOTA conjugates with both imaging (e.g.,
67
Ga,
111
In)
and therapeutic (e.g.,
90
y) radionuclides to provide the opportunity of using SPECT imaging for assessment both before and
after targeted radiotherapy. The most widely used peptides in clinical imaging have been those that the target somatostatin
receptor sites, which are overexpressed by a range of human tumour types. There are five subtypes of receptor sites (ssts
1-5); however, the sst2 is the most prevalent [40]. The majority of these are variants of the cyclic peptide octreotide: for
example, NOC, TOC, and TATE. Conjugation to the radionuclide chelator is achieved via the phenylalanine amino group.
111
In has now largely been replaced by PET-emitting
68
Ga, and
68
GaDOTA TOC [41, 42] and
68
Ga DOTA NOC [43-45]
have been widely investigated in clinical trials and been shown to be highly effective in imaging neuroendocrine tumours.
These three PET imaging agents all show subtle differences in receptor binding and specificity with
68
Ga DOTA TOC having
been the most widely used. A recent review discusses these and other examples of sst imaging using octreatide receptors with
DOTA derivatives and also other peptidic targeting agents [46] including some recent examples which showed enhanced
melanoma uptake and reduced renal uptake [46b].
These DOTA conjugates with octreotide analogues also bind the therapeutic radionuclides
90
y and
177
lu, which have been
explored clinically for therapy with good responses to neuroendocrine tumours reported [46]. The proto-oncogene C-kit is
overexpressed in gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST) and small cell lung cancer (SClC) and is a target molecule for
cancer diagnostics and therapeutics.
Recently, an
111
In labelled C-kit (incorporating the ligands DTPA and DOTA for radiometal chelation) was synthesised
and tested by
in vitro
binding and cellular internalisation assays. The analogous
64
Cu system was evaluated
in vivo
by PET
and enabled clear tumour visualisation in a mouse model, indicating its possible use as a tool to enable an informed decision
to be made prior to targeted therapy [47].
Human serum albumin (HSA) was recently modified by DOTA mono-N-hydroxysuccinimide ester (DOTA-NHS ester) as
well as with the bifunctional cross-linker sulfosuccinimidyl 4-[N-maleimidomethyl]cyclohexane-1-carboxylate (Sulfo-SmCC).
Subsequently, a HER2 affibody analogue, Ac-Cys-Z(HER2:342), was covalently conjugated with HSA, and the resulting bio-
conjugate DOTA-HSA-Z (HER2:342) was radiolabelled with
111
In and evaluated
in vitro
and
in vivo
by SPECT. The results
compared to the corresponding
64
Cu PET imaging. Radiolabelled DOTA-HSA-Z (HER2:342) conjugates displayed a significant
and specific cell uptake into SKOV3 cell cultures. Both SPECT and PET
in vivo
imaging in mice models indicated a high
tumour and liver uptake [48].
Furthermore, a bivalent single-chain antibody dimer fragment (called a diabody, which is a noncovalent dimer of a single-
chain antibody fragment) that retained the avidity of intact IgG but has more favourable blood clearance than intact IgG, was