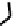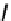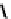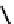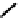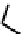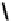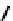Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
NCS
ROC
COR
N
HO
2
C
N
N
N
N
N
CO
2
H
HO
2
C
HO
2
C
CO
2
H
HO
2
C
HO
2
C
CO
2
H
R=OH, NHCH
2
C
6
H
5
10
11
fIGure 7.5
DTPA and CHX-A″-DTPA derivatives.
Stabilities of the Ga
3+
complexes are dependent on the basicity of the donor atoms: [Ga(NOTA)] (log
K
Gal
= 29.6) > [Ga(TRAP-OH)] (log
K
Gal
= 23.3) > [Ga(TRAP-H)] (log
K
Gal
= 21.9). The [Ga(TRAP-OH)] complex exhibits
unusual reversible rearrangement of the “in-cage” N
3
O
3
complex to the “out-of-cage” O
6
complex. These forms are pH-
dependent; the in-cage complex is present in acidic solutions, and at neutral pH, Ga
3+
ion binds hydroxide anion, which
induces deprotonation and coordination of the
P
-hydroxymethyl group(s), and the Ga moves out of the macrocyclic cavity.
Complex formation studies in acidic solutions indicate that Ga
3+
complexes of the phosphinate ligands are formed quickly
(minutes) and quantitatively even at pH < 2. Compared to common Ga
3+
chelators (e.g. 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-
1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA) derivatives), these novel ligands show fast complexation of Ga
3+
over a broad pH range.
The TRAP ligands have therefore been proposed as suitable alternatives for the development of new radiopharmaceuticals
but await radiochemistry and
in vitro/in vivo
investigations.
7.2.4 n
3
o
5
donor ligands
The DTPA-based ligands
10-11
have been widely used for coordinating and targeting radioisotopes (Figure 7.5). The struc-
ture of the Ga complex has not been determined but the structure of a bis(benzylamide) variant (R = H
2
NCH
2
Ph) with In has
been shown to have an eight-coordinate structure with an N
3
O
5
donor set with a water molecule also bound. This exists as at
least three isomers in solution [27].
111
In labelled DTPA complexes have been used to image EGFR for breast cancer [28] by coupling to a non-coordinated
carboxyl group, and the use of such compounds for Auger electron therapy is discussed below.
111
In labelled DTPA has also
been used to radiolabel peptidic nucleic acids that are antisense to m-RNA with the objective of imaging brain tumours [29].
Somastatin-expressing tumours have been imaged using
111
In-DTPA conjugated to octreotide, which was sold commercially
under the name Octreoscan
Tm
and was in regular clinical use for many years [30]. However, the binding to the somostatin
receptor types was relatively poor, and this agent has been superceded by other radiolabelled analogues of octreotide (see
under DOTA ligands below). The Fab satumomab targets a glycoprotein overexpressed in ovarian and colorectal cancer. It
has been conjugated to
111
In-DTPA and was one of the first antibody-based imaging agents to be FDA approved in the mid-
1990s, marketed under the name Oncoscint
Tm
. However, this was withdrawn from the market in 2002 due to the advent of
equivalent PET agents [31].
li et al. designed a dual modality probe for tumour imaging,
111
In-DTPA-lys(IRDye800)-cyclic(KRGDf), which was
found to bind efficiently to integrin α
v
β
3
present in cancerous melanoma cells [32]. The tumours were visualised using NIR,
optical, and SPECT imaging [32]. Several versatile probes for PET, SPECT, NIR fluorescence, or mRI imaging based on a
single folic acid-based precursor and using
67
Ga,
111
In, or
99m
Tc DTPA for SPECT, the fluorescent dye Cy 5.5 for optical
imaging, and
18
F for PET have been described [33]. The
111
In-DTPA folate complex has also been reported to have the
capacity to quantify macrophage activation [34].
The analogue of DTPA
10
(CHX-A″-DTPA) was designed both to improve the binding characteristics of the ligand
by using the stereochemically rigid cyclohexyl backbone and to provide an isothiocyanato group for conjugation to bio-
molecules. This ligand system, like DTPA, is perhaps ideally set up for tetravalent metal ions, but it has been used for
the
111
In labelling of trastumuzab (Herceptin), and the binding of the conjugate to tumour cells is comparable to that of
native Herceptin [35]. Furthermore, an interesting approach to
111
In SPECT imaging of apoptosis has been to conjugate
In-DTPA to a small phenylarsonous acid which binds to heat shock protein Hsp90, which is one of the most prevalent
in the cytosol of cells.
In vivo,
this conjugate provided good images of apoptosis and could prove useful to monitor the
impact of chemotherapy regimens [36].