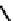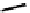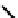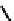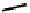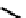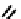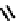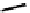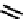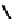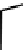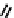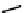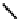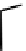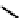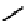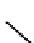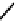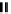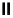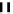Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
O
N
N
O
N
N
Tc
S
SH
11
S
S
Me
N
10
EtO
2
C
O
CO
2
Et
N
N
O
N
N
Tc
Tc
S
S
S
S
Cl
12
13
fIgure 6.4
Diamminedithiolate (DADT or BAT) ligands and complexes.
R
O
-
R
O
O
O
N
N
S
O
N
N
N
O
O
Tc
Tc
Tc
S
S
S
S
S
S
R=H, CH
2
COOH
R=Me, CH
2
COOH
14
15
16
N
N
HN
NH
MeHN
S
S
NHMe
17
fIgure 6.5
Diamidedithiolate (DADS) amidedithiolate and bis(thiosemicarbazone) ligands and complexes.
via attachment of a carboxylate at the methylated nitrogen and the use of the cyclic thiolester in
11
provides an elegant way
to achieve this, forming an amide link and thiolate group [52]. This has been used to
99m
Tc-label chemotactic peptides for the
imaging of inflammation [53] and bombesin for tumour imaging [54], both showing good targeting
in vivo.
A solid phase
approach to the synthesis of Tc complexes of these ligands by attachment of the thiolate sulphur to a bead via an iodoacetyl
group has the advantage that the large excess of ligand remains bound to the bead with only the complex in solution. This
minimises the number of steps required to obtain pure complex and thereby operator dose. This method was used to Tc label
chemotactic peptides in high yields [55].
The neutrality and lipophilicity of this type of complex means that they can traverse the BBB; this was exploited in com-
plex
12,
which is in clinical use under the name neurolite [56, 57]. This complex has chiral carbon centres. While the DD
form is rapidly washed out of the brain, the ll form is enzymatically hydrolysed to a monocarboxylate, which is then
retained. Interestingly, the ll form showed no brain retention in animal studies but did in man [58] - a caveat of the dangers
of extrapolating from pre-clinical studies to the clinic. An example of a second-generation Tc DADT complex for imaging
dopamine transporter sites in the brain is Trodat (
13
), which was shown in clinical trials to give good images despite the
location of the binding site within the G-protein cavity [59].
Variants of the n
2
S
2
coordination motif are provided by the introduction of amide groups in the DADS ligand systems.
The Co groups can be located in a variety of positions with symmetric versions being preferred to avoid geometric isomers.
Regardless of the substitution pattern, stable anionic Tc(V) and Re(V) complexes can be made in high yield directly from the
tetra-oxo metallates. Complex
14
(R = H) was among the first to be investigated with Tc [60, 61], and Tc and Re complexes
of the derivative with a carboxyl group on the ethylene backbone (R = CH
2
CooH) were also described (Figure 6.5) [62].
In order to avoid the negative charge in bioconjugates the series of ligands with only one amide (
15
), designated mAmA
were introduced [60]. This ligand type forms very stable complexes with Tco and Reo cores, and the derivative with
R = CH
2
CooH has been used extensively to label biomolecules [62]. These are covered together with many other examples
in two reviews that have appeared on the labelling of small biomolecules with
99m
Tc [17, 63, 64]. A further permutation of