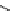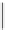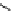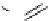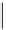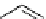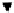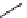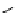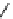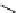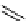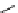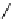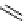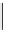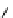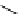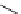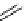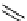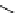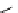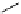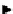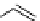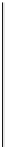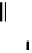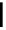Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
O
*
Rʹ
Rʹ
R
N
*
O
X
Pd Cat.
R
X
Rʹ - B(OH)
2
or
Rʹ - Sn(alkyl)
3
R
Rʹ
Pd Cat.
NH
2
Zn (400 °C) or
Mo (800 °C)
In situ activation
with LiN(TMS)
2
11
CO
2
R
11
CO
I
R
Cl
R''
HN
X
NH
2
Rʹ
H
2
N
Pd Cat.
O
Pd Cat.
NH
2
*
H
O
Cl
R
R″
*
N
Rʹ
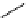
scheme 4.19
selected palladium-mediated [
11
C]carbonylation reactions using high pressure micro-autoclave system.
in the system is increased; the CO insertion step can therefore be rate limiting at low pressures. For labelling reactions using
11
CO, the high isotopic dilution of
11
CO results in very low partial pressures of
11
CO, thus inhibiting the
11
CO insertion step of
the catalytic cycle. several strategies in recent years have been developed to improve the reactivity of
11
CO by enhancing the
transfer of
11
CO into the solution phase to improve reactivity: (1) recirculation of the
11
CO gas through the reaction mixture;
[99] (2) increasing the pressure of
11
CO using a high-pressure HPLC micro-autoclave reactor systems; [96, 100] (3) Chemical
trapping agents to enhance solubility; [101-104] and (4) microfluidic reactors to enhance mass transport between gas and
liquid phases [105, 106].
The high pressure HPLC C-11 carbonylation system has been applied to a wide range of reactions, including suzuki and
stille C-11 carbonylation reactions using boronic acid [107, 108] and alkyl tin precursors [109] for the preparation of [
car-
bonyl
-
11
C]biaryl or aryl-benzyl ketones [97] (scheme 4.19). The synthesis of a wide range [
carbonyl
-
11
C]amides and esters
has been prepared using the high pressure autoclave system via
11
CO palladium-mediated carboxyaminations [98, 110-114].
Further investigations of these [
11
C]carboxyamination reactions showed that
in situ
activation using lithium bis(trimethylsilyl)
amide [112] and 1,2,2,6,6,-pentamethylpiperidine [113] enhanced rCys for less reactive amines such as aniline.
Two low pressure palladium-mediated C-11 carbonylation methods have been developed that rely on a pre-trapping and
solubilising step prior to Pd-mediated insertion. The first of these uses a BH
3
.THF solution to form BH
3
.
11
CO; the borane
acts as Lewis acid by accepting a lone pair of electrons from the
11
CO forming the adduct and solubilising the
11
CO [104].
in a typical procedure,
11
CO/He gas stream was bubbled through a solution of BH
3
.THF to give BH
3
.
11
CO, addition of the
cross-coupling regents, palladium catalyst, aryl halide, and suitable amine or alcohol nucleophiles gave reasonable yields of
[
carbonyl
-
11
C]amide or [
carbonyl
-
11
C]esters (scheme 4.20).
More recently, copper tris(pyrazolyl)borate complexes (scheme 4.21) have been used as highly efficient
11
CO trapping
agents and have proven to give higher trapping efficiencies and to be technically simpler to use than the borane trapping
methods for low pressure Pd-mediated carbonylation reactions [101, 103, 115, 116]. The tris(pyrazolyl)borate (Tp) ligands
(also referred to as scorpionates) enforce strict tridentate coordination geometry on the central copper ion while leaving a
vacant coordination site to permit
11
CO binding to the copper.
The choice of Tp ligand was found to be important for enhancing trapping efficiencies. The tris(3,5-dimethylpyrazolyl)-
borate (Tp*) was an excellent ligand because the methyl groups on the pyrazol rings enhance the back bonding between
the Cu and CO, stabilising this bond, and improve complex solubility in organic solvents compared to the non-methylated