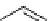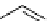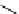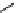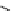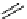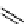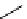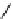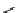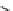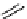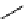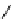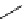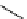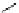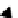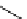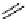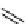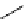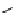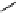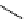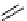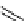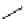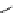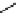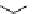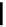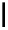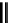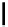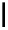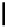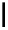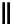Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
11
CN
N
NH
2
Rosenmund-von
Braun reaction
*
R
NH
H
3
CO
X
NH
2
SCF, NH
3
450 bar, 250°C
H
3
CO
R
[
11
C]CuCN
11
CNBr
X
11
CN
Pt/NH
3
1000 °C
R
11
CH
4
[
11
C]HCN
Pd Cat.
R
O
I
O
t
Bu
CN
NHBOC
1, KOH, DMF,
2. TFA
CN
N
11
C
O
O
H
2
N
*
OH
NH
2
scheme 4.18
synthesis of [
11
C]HCN and selected [
11
C]cyanation reactions.
4.2.4
[
11
c]cyanation reactions
[
11
C]HCN is a useful synthon for the introduction of nitrile groups into a range of tracer compounds. Nitrile labelling is
important because the CN group is found in many organic compounds and natural products. [
11
C]HCN is typically prepared
via the reaction of
11
CH
4
with NH
3
over a platinum catalyst [83] and can be directly reacted with precursor molecules, as in
the synthesis of labelled amino acids [84] or converted to
11
CNBr [85, 86] or [
11
C]CuCN [87] for further reaction. [
11
C]CuCN
can be reacted with aryl halides via the rosenmund von Braun reaction [87-89]. Palladium-mediated reactions of [
11
C]HCN
with aryl iodides have also been used to introduce the
11
CN group into target molecules [90, 91] (scheme 4.18).
The [
11
C]cyano functional group provides further opportunity for conversion to other products such as carboxylic acids,
amides [91], tetrazoles [87], amidines [89], and amino acids [84, 92]. C-11 cyanogen bromide has been applied to the synthesis
of
11
C-labelled guanidines [85]. The first step is the reaction of
11
CNBr with amines to rapidly form C-11 cyanamides, followed
by a high pressure, high temperature supercritical fluid (sCF) synthesis method to afford the corresponding C-11 guainidines
(scheme 4.18). recently, a convenient synthesis of [
11
C]glutamine, a potential marker for imaging tumour metabolism, has
been reported by reacting [
11
C]HCN with 4-iodo-2-amino-butanoic ester in the presence of KOH base followed by hydrolysis
with trifluoroacetic acid [92] (scheme 4.18).
4.2.5
[
11
c]carbonylation reactions
C-11 carbon monoxide is a highly versatile reagent that has been demonstrated to form a wide range of C-11 carbonyl labelled
compounds [93].
11
CO can be prepared quickly and with high radiochemical yield by either the high temperature reduction of
11
CO
2
over zinc [94] or molybdenum [95]. The molybdenum route is more popular because it is more reliable and requires
less maintenance. Palladium-mediated C-11 carbonylation reactions have been most widely exploited and have been used to
effectively label imides, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, amides, and acrylamides [96-99]. The palladium-catalysed carbon-
ylation of aryl and vinyl halides used for many of these labelling reactions, originally developed by Heck, proceeds via three
characteristic steps in the catalytic cycle: oxidative addition of an aryl halide species to the
in situ
palladium(0) catalyst,
insertion-migration of carbon monoxide to form a Pd-acyl, and nucleophilic attack followed by reductive elimination to form
the product. Carbon monoxide has low solubility in many organic solvents that can result in poor reactivity unless the pressure