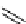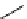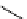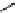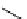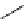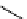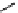Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
products could be separated, and isolation could be achieved via preparative HPLC in moderate rCys <20% [69].
11
CH
3
NO
2
has also been used to label the neurotransmitter phenethylamine; reaction of
11
CH
3
NO
2
with benzaldehyde to generate
[C-11]beta-nitrostyrene, followed by a reduction with LiAlH
4
, was reported to give [C-11]phenethylamine in moderate
rCys. More recently, Kato et al. have exploited
11
CH
3
NO
2
to prepare a range of labelled nitro and amine compounds. The
fluoride-assisted Michael addition of
11
CH
3
NO
2
to the α,β-unsaturated compound,
p
-chlorocinnamate, followed by a NiCl
2
/
NaBH
4
reduction step gave a reasonable 36% rCy of the amine within an acceptable timeframe. The nitroaldol reaction of
11
CH
3
NO
2
with formaldehyde and other aldehydes has also been used by Kato et al. to label a range of nitro compounds and
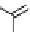
the resulting amines following a reduction step [68, 70]. Excellent rCys (68%) were obtained for the synthesis of the
labelled amino-triol compound [C-11]Tris (Figure 4.16). C-carboxylation of
11
CH
3
NO
2
has also proven to be a useful strategy
for the synthesis for nitroacetate compounds. [C-11]ethyl nitroacetate, an interesting C-11 intermediate, was prepared in
good rCy (75%) via the reaction of
11
CH
3
NO
2
with 1-ethoxycarbonylbenzotriazole and quantitatively converted to the
[C-11]glycine ethyl ester using Zn powder (scheme 4.16) [71].
4.2.3
[
11
c]phosgene reactions
C-11 phosgene (
11
COCl
2
) is a highly reactive gaseous small molecule labelling precursor that can be used to efficiently label
ureas, carbamates, and carbonates in the carbonyl position [72]. in some respects,
11
COCl
2
is an ideal C-11 labelling synthon
because of its reactivity and potential to form a wide range of compounds; however, its routine synthesis can be problematic,
which has resulted in only a handful of groups worldwide developing its chemistry. [C-11]phosgene is generally prepared
via the chlorination reaction of
11
CH
4
to form
11
CCl
4
followed by an oxidation reaction over iron or copper catalysts at high
temperature [73, 74]. recently, a new method of
11
COCl
2
has been reported for the room temperature conversion of
11
CCl
4
to
11
COCl
2
using a working-environmental gas detection tube (Kitagawa gas detector tube) [75]. This method involves
passing a stream
11
CCl
4
through a glass tube filled with i
2
O
5
and fuming H
2
sO
4
. Consistently high and reproducible rCys
of
11
COCl
2
were reported with the added benefits of room temperature conversion and a simpler experimental setup. Another
recent report describes the preparation of
11
COCl
2
using two quartz columns [76]. initially,
11
CH
4
is reacted with Cl
2
at
510 °C to form
11
CCl
4
, followed by removal of Cl
2
by reaction with antimony the
11
CCl
4
gas stream that is heated to 750 °C
in the second empty quartz tube, giving 30-35% rCy of
11
COCl
2
. With regard to radiolabelling target molecules C-11, phos-
gene has been used for the rapid preparation of C-11 labelled ureas [77-79], carbamates, carbamoyl chlorides [80], amides
[80], and uric acids [81, 82] (scheme 4.17).
NO
NHRR
′
*
NRR,
NaOEt
N
O
NO
*
*
Cl
OEt
N
Ph-MgX
Ni catalyst
N
O
*
Ph
OCH
3
O
NH
2
HN
11
COCl
2
H
2
N
O
H
NH
2
O
N
N
N
*
HN
O
*
O
H
O
H
scheme 4.17
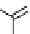
Various reactions [
11
C]phosgene to form C-11 labelled carbonyl compounds.