Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
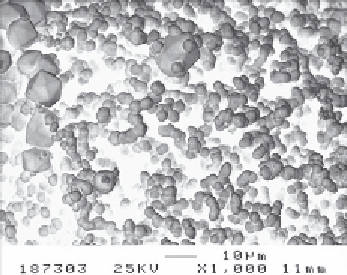
FIGURE 10.8
SEM images show different morphologies of Mo metals obtained from hydrogen reduc-
tion under (left) low and (right) high moisture content.
Source
: Reproduced with permission from Schul-
meyer [17].
As another example, molybdenum metal powder is produced industrially
by reducing high purity molybdenum compounds such as molybdenum tri-
oxide (MoO
3
, grey-green powder), ammonium hexamolybdate ((NH
4
)
2
Mo
6
O
19
,
yellow powder) and ammonium dimolybdate ((NH
4
)
2
Mo
2
O
7
, white powder),
with hydrogen gas [15]. The mechanism of reduction consists of two stages
[17]. The first stage involves a reaction from MoO
3
to MoO
2
via chemical
vapor transport process. In the second stage, MoO
2
is further reduced to
metal Mo:
MoO
+
2
H
→ +
Mo
2
H O
.
(10.9)
2
2
2
Different grain sizes and shapes of metal molybdenum can be obtained
by adjusting moisture content of H
2
at entry (Fig. 10.8).
10.5 HYDROGEN UTILIZATION IN MANUFACTURING PROCESSES
10.5.1 Welding Gas: Oxy-Hydrogen Welding
Hydrogen has been used for welding as early as the beginning of the last
century [18]. Hydrogen reacts with oxygen in a flame to form water, and
simultaneously produces enormous energy for the welding process:
−
1
2
H
+ →
O
2
H O H
;
∆
=−
572
kJ mol
⋅
.
(10.10)
2
2
2

Search WWH ::

Custom Search