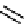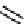Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
derivatives [41,42]), guanidines connected to cyclic peptides and macrolides through long
alkyl chains (fusaricidins [43,44] and azalomycins [45], respectively), and cyclic (capreo-
mycins [46] and tuberactinomycins [47]) and acyclic guanidine derivatives (miraziridine A
[48]) were also reported. Another series of natural products was found in higher plants,
marine sources such as dinoflagellates (saxitoxins) [7,49], pufferfish (tetrodotoxin) [6,7],
sea firefly (Vargula luciferin) [50], sponges and so on.
10.3.1 Natural Guanidines from Microorganisms
10.3.1.1 Argifin
Argifin (20) was isolated from the cultured broth of a fungal strain Gliocladium sp. FTD-
0668 by Omura et al. [51,52] and the structure determined to be a cyclic peptide with
arginine residue [53] (Figure 10.6). This compounds has inhibitory activity towards
chitinase. Total synthesis [54] and computational analysis of a chitinase-argifin complex
[55] have also been reported.
O
N
HO
2
C
NH
NH
O
O
CO
2
H
O
NH
O
O
N
Me
H
Me
H
H
H
Ph
argifin (
20
)
H
Me
OH
R
2
O
O
NH
N
N
H
N
H
NH
2
H
H
O
O
HN
R
1
O
O
O
HO
H
N
N
H
OH
O
N
H
H
O
O
2
H
HO
2
C
H
H
plusbacin
A
1
(
21
): R
1
= (CH
2
)
10
Me, R
2
= OH; B
1
: R
1
= (CH
2
)
10
Me, R
2
= H
A
2
: R
1
= (CH
2
)
9
CHMe
2
, R
2
= OH; B
2
: R
1
= (CH
2
)
9
CHMe
2
, R
2
= H
A
3
(
22
): R
1
= (CH
2
)
10
CHMe
2
, R
2
= OH; B
3
: R
1
= (CH
2
)
10
CHMe
2
, R
2
= H
A
4
: R
1
= (CH
2
)
12
Me, R
2
= OH; B
4
: R
1
= (CH
2
)
12
Me, R
2
= H
Figure 10.6
Structures of argifin (20) and plusbacins