Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Risk category
Inspection intervals
Very high
1 year
High
2 years
Average
4 years
Low
4 years
Very low
4 years
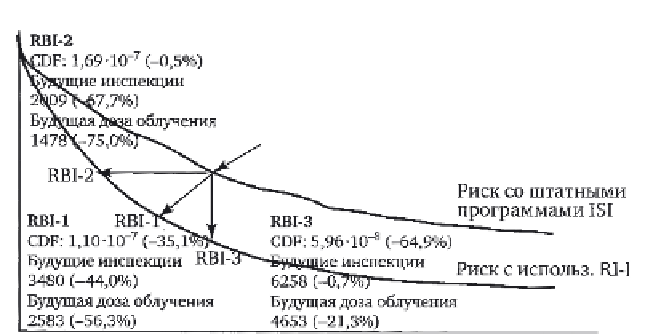
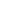
RBI-2
CDF: 1.69·10
-7
(-0.5%)
Future inspections
2009 (-67.7%)
Future radiation dose
1478 (-75.0%)
CDF: 1.70·10
-7
6214 future inspections
5914 future radiation dose
No RI-ISI
RBI-2
Risk using standard ISI
programmes
RBI-1
RBI-3
CDF: 5.96·10
-8
(-64.9%)
Future inspections
6258 (-0.7%)
Future radiation dose
4653 (-21.3%)
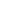
RBI-3
RBI-1
CDF: 1.10·10
-7
(-35.1%)
Future inspections
3480 (-44.0%)
Future radiation dose
2583 (-56.3%)
Risk using RI-ISI
7. 1 3
Dependence of risk on frequency and volume of inspection
during operation obtained on the basis of the risk matrix (Fig. 7.2).
RBI-2: Minimise inspection at the given risk levels;
RBI-3: Minimise risk at the given inspection cost.
The results of these studies can be summarised as follows:
• using quantitative risk analysis for 2 units of the Ignalinsk nuclear
power plant, the number of future inspections can be reduced by
44%, with the risk reduced by 35%;
• Radiation exposure of personnel can be reduced by 3300 mSv (by
56%) as compared to the tubes subjected to standard inspection.
After completion of the project RI-ISI, the Ignalinsk NPP has been using
the results of preliminary research and has been preparing a new inspection
programme, taking into account the welds with the highest level of risk.
The number of inspection has not been reduced but the risk was reduced
significantly.
The Lithuanian regulatory authorities (VATESI) have agreed to use the
RI-ISI programme for austenitic piping and are waiting for proposals of
the Ignalinsk nuclear power plant.

























































Search WWH ::

Custom Search