Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
In the case of reducing the volume of ISI it is also required to instal
monitoring systems for leaks with high sensitivity.
At the same time, the requirements of the State Inspectorate for Nuclear
Security specify 100% inspection.
7.4 Quantitative approach to optimisation of ISI
7.4.1 Optimisation of ISI based on the characteristics of
probability of failure and a systemic approach
To achieve a more detailed presentation of the issue, the deterministic and
probabilistic aspects of optimisation of ISI are described below.
The methodology and optimisation methods set out belo are based on
economic criteria. The following optimised parameters are considered:
norms of defectiveness, the time interval between inspections (frequency
of inspection); inspection areas, inspection volumes over the entire length
of operation of an inspected object, combination of inspection methods.
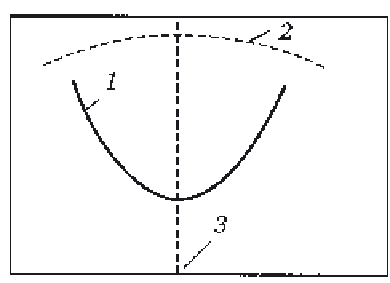
In general, the search for the optimum value of the investigated
inspection parameter can be depicted graphically as the search for the
extreme (minimum or maximum) value on the curve in the economic
characteristic - optimised parameter coordinate (Fig. 7.14).
In this section, the considered optimised parameters are different
inspection characteristics mentioned above. The optimisation criterion
is to achieve the minimum cost at maximum possible positive technical
result. The optimisation methods for ISI described below are based on
taking into account the probabilistic relationships of detection of defects
and failure.
With strict mathematical formulation of the problem of optimisation of
Optimised parameter
7.14
Graphical description of search for the optimum value of the
optimised parameter; 1) damage; 2) earnings; 3) optimum value.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search