Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
cation, a carbonate such as calcium carbonate is formed. Carbonates are not very soluble
in water, and this reaction results in deposition or precipitation.
Because of its involvement in maintaining or controlling pH, carbonate is an important
oxyanion. Exposure of samples to carbon dioxide may affect the pH of the sample and
consequently the availability and solubility of many components in that sample. Exposure
to high levels of carbon dioxide during sampling or sample transport is thus expected to
have an effect on the analytical results.
9.2.6.2. Sulfur and Sulfate
Sulfur can occur as an element in nature. In soil and water, however, it does not remain in
the elemental form long. Under reducing conditions it is reduced to hydrogen sulfide
(H
2
S), and under oxidizing conditions it is oxidized to sulfuric acid (H
2
SO
4
). Soils and
soil samples exposed to elemental sulfur, most commonly labeled as flowers of sulfur,
will suffer a dramatic decrease in their pH. This in turn can lead to the release of
materials into the soil solutions that are not normally found there. Soil sulfur, however, in
the form of sulfate as the anion
is always present, is stable, and does not affect
pH.
Sulfur is an essential element in the nutrition of plants, animals, and microorganisms.
Plants can take in many different forms of sulfur—sulfate being one of them—and
incorporate it into various needed organic sulfur compounds. Calcium and magnesium
sulfates are commonly used to ameliorate various soil conditions caused by poor soil
structure and are also used as a source of calcium under conditions in which it is not
desirable to change a soil's pH [17].
9.2.6.3. Phosphate
The oxyanion phosphate is a common and essential component of life. It occurs
in different forms, depending on the pH of its surroundings and associated metals.
Commonly one or two of its negative charges are satisfied by protons, and thus it occurs
as or as These are the two most common forms occurring in the
normal pH range of water and soil. The 1
−
and 2
−
charges on these forms are typically
satisfied by sodium, potassium, calcium, or magnesium.
U
nder very acid conditions phosphate occurs as phosphoric acid (H
3
PO
4
), while under
very basic conditions it occurs as phosphate Because of the extreme pHs under
which these forms are found, their occurrence indicates unusual soil or environmental
conditions.
Looking at phosphate it would be assumed that this oxyanion would act as all anions
are expected to act. It does not. All species of phosphates react with metals to form
insoluble, plant-unavailable phosphates. Under acid conditions either monobasic
or dibasic phosphate reacts with iron and aluminum to form-
insoluble and unavailable iron and aluminum phosphates. Under basic conditions
insoluble and unavailable calcium phosphates form. Phosphate species can also react with




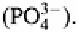

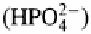
Search WWH ::

Custom Search