Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Ta b l e 1
Coefficients of 9/7 Daubechies filters
Analysis Filters
Synthesis Filters
i
Low-Pass Filter
High-Pass Filter
i
Low-Pass Filter
High-Pass Filter
0
0.6029490182363
1.115087052
0
1.115087052
0.6029490182363
±
1
0.2668641184428
-0.591271763114
±
1
-0.591271763114
0.2668641184428
±
2 -0.07822326652898 -0.05754352622849
±
2 -0.05754352622849 -0.07822326652898
±
3 -0.01686411844287 0.09127176311424
±
3 0.09127176311424 -0.01686411844287
±
4 0.02674875741080
±
4
0.02674875741080
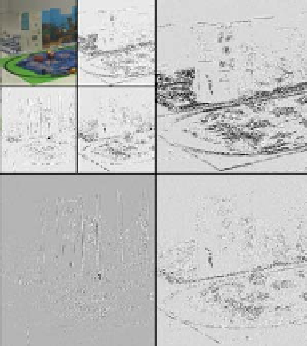
Fig. 3
An example of 2-
level wavelet decomposition
of and HD Video Frame.
LABRI corpus
The coefficients of Daubechies analysis /synthesis filters 9/7 used for lossy com-
pression are given in table 1. The decomposition process can be re-iterated on the LL
subband thus resulting in a wavelet pyramid with
K
decomposition levels. Figure 3
contains an example of 2-level decomposition of an HD 1080p video frame.
Hence, if the HD video is encoded in the JPEG2000, the wavelet pyramid
obtained after a partial decoding and de-quantizing of wavelet coefficients with-
out inverse transform contains low-frequency and high-frequency information at
several levels. In the following we will present its exploitation in the scalable index-
ing and retrieval of video content.
2.2
Scalable Extraction of Low and Mid-level Features from
Compressed Streams
In the overall set of problems to be resolved in the task of video indexing one can
distinguish:
-
temporal partitioning, linear or non-linear, into semantically homogeneous se-
quences such as video shots and video scenes. This partition can be used for
various tasks such as generation of video summaries [13], video retrieval with
query-by-clip scenarios or query by key-frame, navigation in video content.