Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
)=
w
f
(
h
,
τ
f
(
t
)
ψ
h
,
τ
(
t
)d
t
,
(3)
R
where
ψ
is the complex conjugate of
ψ
. The synthesis can be performed under
conditions of admissibility in Eq. (1) as
1
K
ψ
)
d
h
d
τ
f
(
t
)
L
=
f
(
t
)
ψ
f
(
h
,
τ
(4)
h
2
+
R
×
R
where
K
ψ
is the common value of the integrals in Eq. (1). Under certain conditions
it is possible to built an orthonormal wavelet basis. Nevertheless, the basis functions
are often difficult to construct. Hence bi-orthogonal wavelets are considered such
that two bases, the direct
B
=
and the dual
B
=
{
e
i
}
{
e
i
}
, satisfying condition of
duality (
e
i
,
e
j
)=
δ
ij
, serve for analysis and synthesis respectively.
In JPEG2000, bi-orthogonal wavelets are used. Image and video compression are
applied to the discrete signals, hence instead of continuous case, a discrete wavelet
transform (DWT) has to be performed. In this transform the wavelets are defined on
discretely sampled space, for instance a dyadic case can be considered with
h
= 2
k
,
=
l
2
k
,
(
k
,
l
)
2
τ
∈
Z
(5)
This transform allows re-covering good approximations converging to
f
k
∈
Z
l
∈
Z
w
f
(2
k
,
l
2
k
)
f
(
t
)=
ψ
2
k
,
l
2
k
(
t
)
(6)
Mallat [12] showed that the DWT could be computed with a bank of filters. This
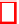
is the way the DWT is realised in JPEG2000 with Daubechies filters. Figure 2
depicts the analysis process applied to an image where the arrows correspond to
the sub-sampling by a factor of 2 and squares depict discrete convolution opera-
tion.The resulting subbands are denoted as LL for low-pass filtering results on lines
and columns, LH for consecutive low and high-pass filtering, HL for filtering in the
inverse order and HH for two consecutive high-pass filtering steps. The subbands
HL, LH and HH are called ”High Frequency” (HF) subbands while LL is called
”Low Frequecy” (LF)subband.
L
L
LL1
LH1
H
HL1
H
L
Fig. 2
One level wavelet
analysis on an image in
JPEG2000 standard
HH1
H